Unveiling the Tapestry of Loss: Exploring the Significance of Extinction Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Tapestry of Loss: Exploring the Significance of Extinction Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Tapestry of Loss: Exploring the Significance of Extinction Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Tapestry of Loss: Exploring the Significance of Extinction Maps
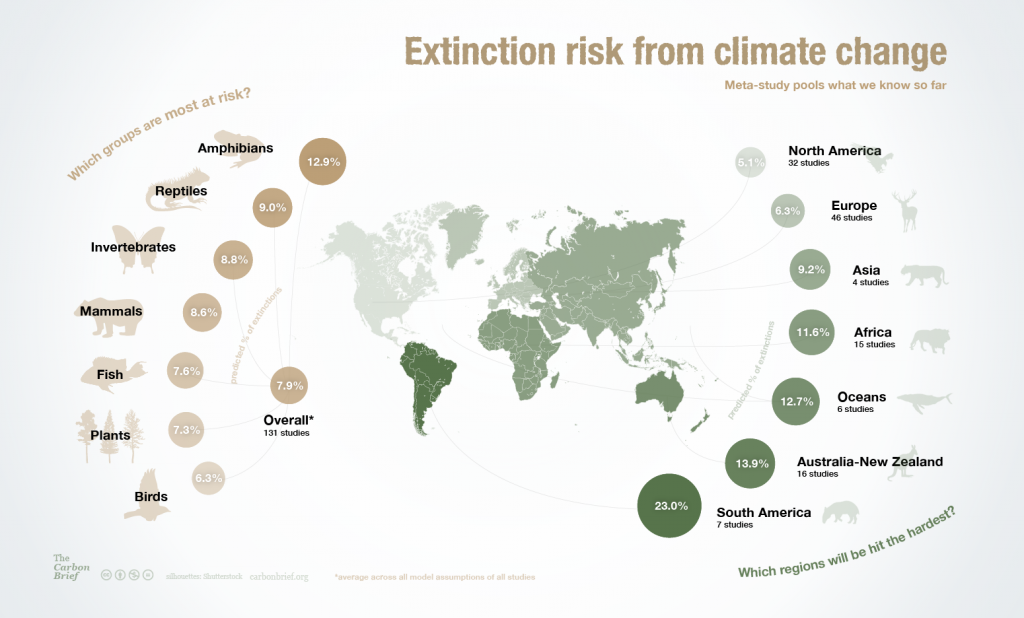
The Earth’s biodiversity is a delicate tapestry woven from countless threads, each representing a unique species. However, this intricate pattern is fraying at the edges, with species disappearing at an alarming rate. To understand the scale and impact of this ongoing extinction crisis, scientists and conservationists have developed powerful tools: extinction maps. These visual representations offer a stark and sobering glimpse into the past, present, and future of life on Earth, providing crucial insights into the dynamics of extinction and guiding conservation efforts.
Understanding the Concept: A Visual Chronicle of Loss
An extinction map is a geographical representation that visually depicts the distribution of extinct or critically endangered species across the globe. These maps serve as a visual chronicle of past extinctions, highlighting regions that have experienced significant biodiversity loss. They also pinpoint areas currently facing high extinction risk, allowing scientists to prioritize conservation efforts and identify hotspots of biological vulnerability.
The Anatomy of an Extinction Map: Layers of Data and Insight
Extinction maps are not simply static visualizations of extinct species. They are dynamic tools that integrate various layers of data, including:
- Species Distribution: Maps incorporate detailed information about the geographical range of extinct or critically endangered species, revealing areas where biodiversity has been most impacted.
- Extinction Timelines: By indicating the time of extinction for each species, maps provide a historical perspective on the rate and patterns of biodiversity loss.
- Threat Factors: Maps often incorporate data on the primary threats driving extinction, such as habitat loss, climate change, invasive species, and overexploitation. This information helps pinpoint the root causes of biodiversity decline and inform targeted conservation strategies.
- Conservation Status: Maps can include classifications of species according to their conservation status, such as critically endangered, endangered, or vulnerable. This allows for a nuanced understanding of the severity of the extinction threat and the urgency of conservation actions.
The Power of Visual Representation: A Tool for Awareness and Action
Extinction maps are powerful tools for raising awareness about the extinction crisis. Their visual nature effectively conveys the magnitude of biodiversity loss, making the issue more relatable and impactful. By showcasing the geographic distribution of extinctions and the specific threats driving them, maps highlight the global nature of the crisis and emphasize the need for international cooperation in conservation efforts.
Furthermore, extinction maps serve as a valuable resource for conservation practitioners. They provide a clear visual representation of the areas most vulnerable to biodiversity loss, allowing for the prioritization of conservation efforts and the development of targeted strategies. By identifying areas with high concentrations of threatened species, maps guide conservationists to focus resources on regions where they can have the greatest impact.
Beyond Static Data: Integrating Dynamic Factors for a Holistic View
Modern extinction maps are not static representations of the past. They are increasingly incorporating dynamic factors, such as:
- Climate Change Impacts: As climate change alters habitats and disrupts ecosystems, maps are incorporating projections of future species distributions and extinction risks based on climate models.
- Human Activity: Maps are incorporating data on human population density, land use changes, and infrastructure development to understand how human activities influence extinction risk.
- Conservation Success Stories: Maps can also highlight regions where conservation efforts have been successful in preventing extinctions or mitigating threats, providing inspiration and demonstrating the potential for positive change.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about Extinction Maps
1. How are extinction maps created?
Extinction maps are created through a collaborative process involving scientists, conservationists, and data analysts. They use a combination of field observations, museum records, scientific literature, and digital databases to compile information on species distribution, extinction dates, and threat factors.
2. What are the limitations of extinction maps?
Extinction maps are powerful tools, but they have limitations. They rely on available data, which may be incomplete or biased, especially for species with limited knowledge or in remote regions. Additionally, predicting future extinction risks is inherently uncertain due to the complexity of ecological interactions and the influence of human activities.
3. How can extinction maps be used to inform conservation?
Extinction maps provide valuable insights for conservation planning. They help identify areas of high biodiversity loss, prioritize conservation efforts, and guide the development of targeted strategies to mitigate threats. By understanding the geographic patterns of extinction risk, conservationists can focus resources on regions where they can have the greatest impact.
4. What are the ethical implications of extinction maps?
While extinction maps provide crucial insights into biodiversity loss, they also raise ethical concerns. The visualization of extinction risk can potentially lead to the prioritization of certain species over others, raising questions about the value of different life forms. It is crucial to use extinction maps responsibly, ensuring that all species are considered and that conservation efforts are based on scientific principles and ethical considerations.
Tips for Using Extinction Maps Effectively
- Consult Multiple Sources: When interpreting extinction maps, it is important to consult multiple sources and consider the limitations of each data set.
- Contextualize Data: Always consider the context of the data presented on extinction maps. Factors such as habitat fragmentation, climate change, and human activities can influence extinction risk beyond species distribution alone.
- Engage with Experts: Consult with conservation experts and scientists to gain a deeper understanding of the data presented on extinction maps and the implications for conservation.
- Promote Awareness: Use extinction maps as a tool to raise awareness about the extinction crisis and engage the public in conservation efforts.
Conclusion: A Call to Action for a Sustainable Future
Extinction maps serve as a powerful reminder of the fragility of life on Earth and the urgent need for conservation action. They provide a visual chronicle of past extinctions, highlight areas facing imminent threats, and guide efforts to protect biodiversity. By understanding the patterns and drivers of extinction, we can develop more effective conservation strategies and work towards a sustainable future for all species. The tapestry of life is woven with threads of resilience and hope, and it is our responsibility to ensure that this delicate pattern continues to flourish for generations to come.








Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Tapestry of Loss: Exploring the Significance of Extinction Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!