Unveiling the Patterns of Shark Attacks: A Global Perspective
Related Articles: Unveiling the Patterns of Shark Attacks: A Global Perspective
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Patterns of Shark Attacks: A Global Perspective. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Patterns of Shark Attacks: A Global Perspective

The ocean, a vast and mysterious expanse, is home to an array of life, including the apex predator, the shark. While often portrayed as fearsome creatures, sharks play a vital role in maintaining healthy marine ecosystems. However, the occasional interaction between humans and these powerful animals can result in shark attacks, events that understandably spark fear and raise concerns about ocean safety.
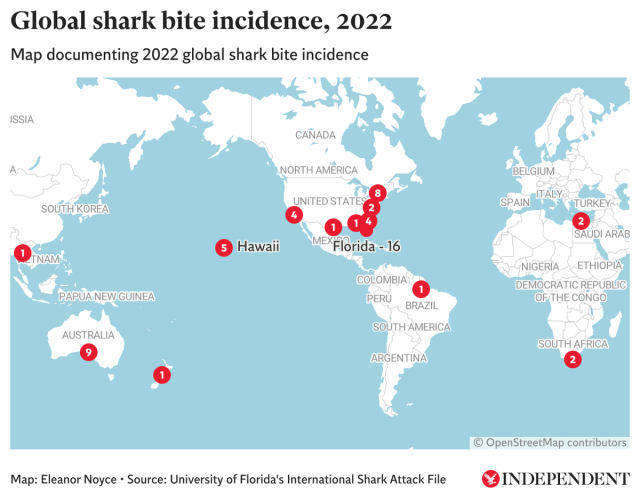
To better understand the global distribution and frequency of shark attacks, researchers and organizations have developed maps that visually represent these incidents. These maps offer valuable insights into the factors that influence shark attacks, helping to inform strategies for mitigating risk and promoting responsible ocean interactions.
Understanding the Data:
Shark attack maps are typically compiled using data collected from various sources, including:
- International Shark Attack File (ISAF): This database, maintained by the Florida Museum of Natural History, is a comprehensive record of shark attacks worldwide.
- Global Shark Attack File (GSAF): This international effort, spearheaded by the University of Florida, focuses on documenting and analyzing shark attacks, providing valuable data for research and public awareness.
- Local and regional databases: Many coastal areas maintain their own records of shark attacks, contributing to a more localized understanding of these events.
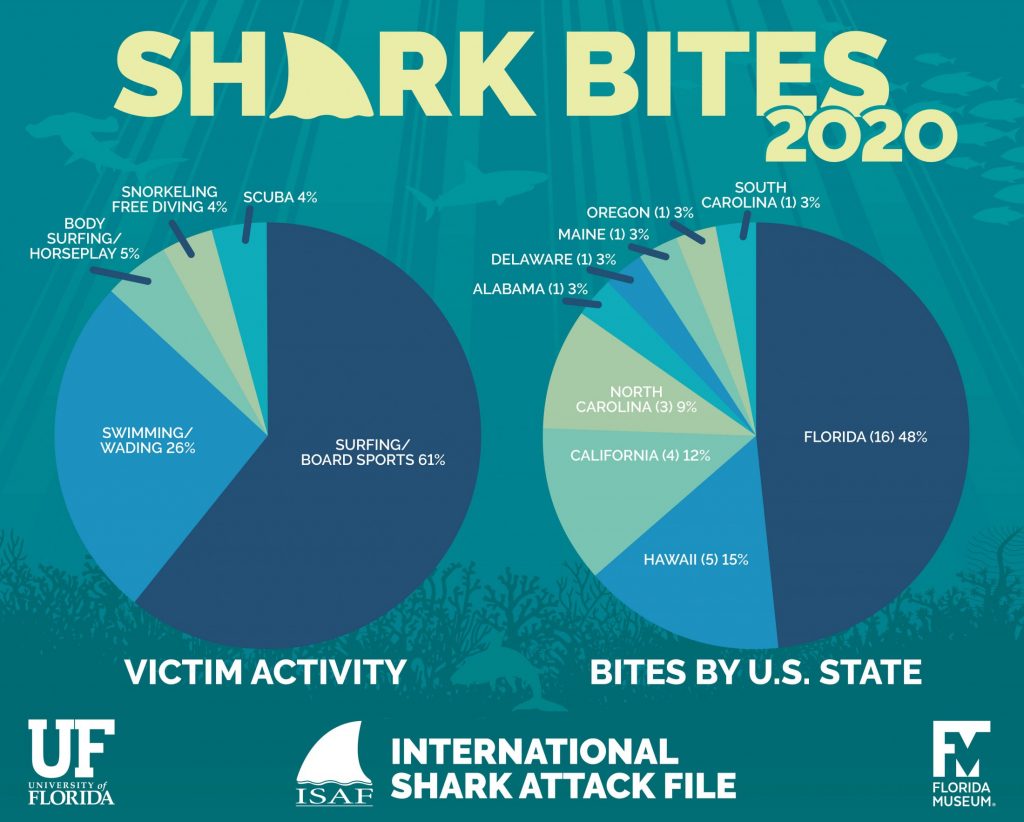
The data used in these maps typically includes information such as:
- Location: The precise coordinates of the attack, pinpointing the specific area where the incident occurred.
- Date: The date and time of the attack, allowing for analysis of seasonal patterns and trends.
- Victim: Information about the victim, such as age, gender, and activity at the time of the attack.
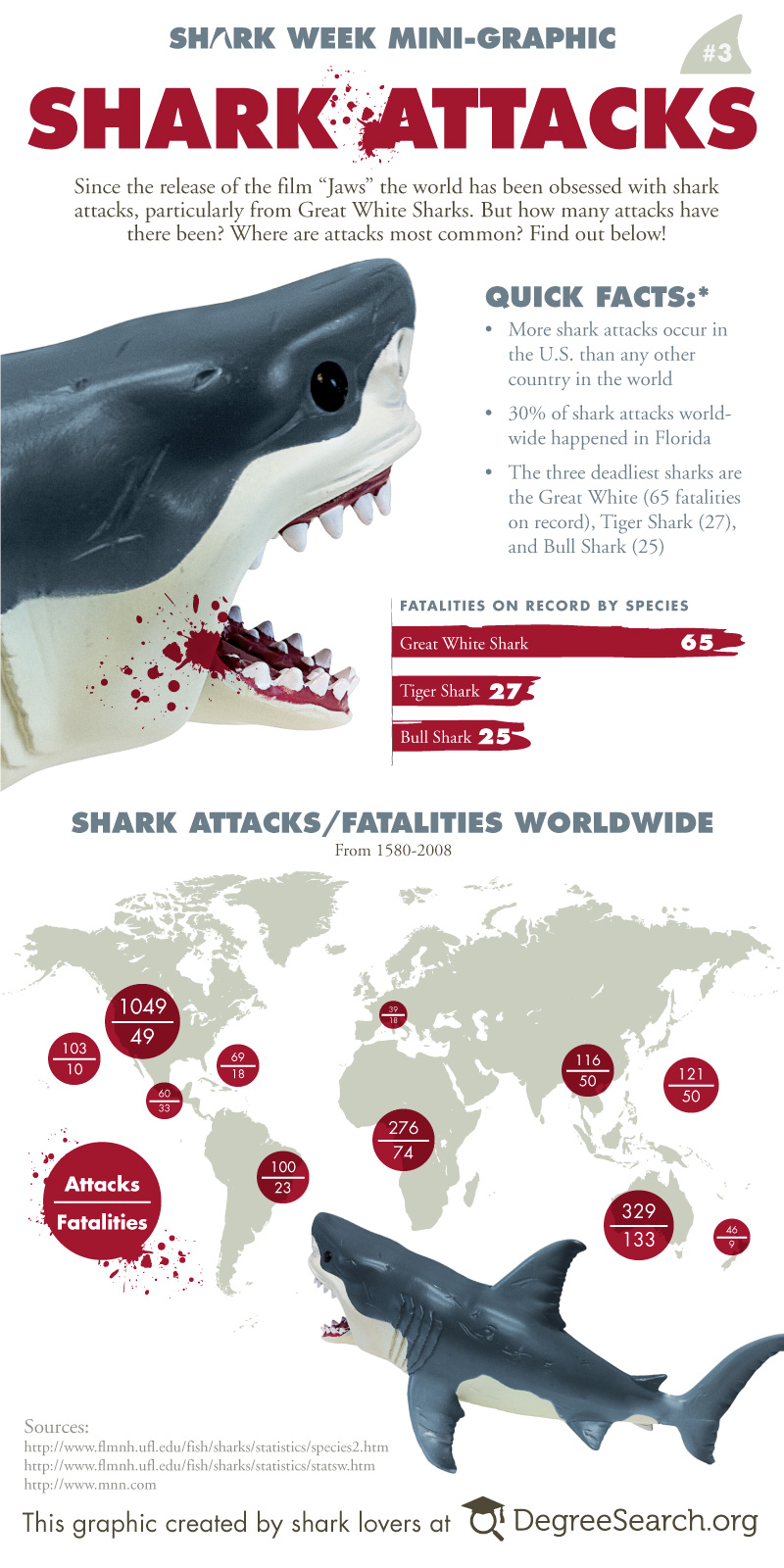
- Shark species: When possible, identification of the shark species involved in the attack, providing insights into the behavior and characteristics of different species.
- Severity: The severity of the attack, ranging from minor bites to fatal encounters.
Interpreting the Maps:
Shark attack maps are not simply visualizations of isolated events. They reveal patterns and trends that can be analyzed to gain a deeper understanding of the factors influencing these interactions.
Geographical distribution: The maps highlight the geographic areas with the highest concentration of shark attacks. These areas are often characterized by:
- High human activity: Coastal areas with popular beaches, surfing spots, and fishing grounds see increased human-shark interactions, potentially leading to more encounters.
- Shark habitat: Areas known to be shark habitats, such as coral reefs, seagrass meadows, and deep-water canyons, naturally have a higher likelihood of shark presence.
- Water temperature and salinity: Some shark species prefer specific water temperatures and salinity levels, influencing their distribution and potential for encountering humans.
Seasonal variation: Maps can reveal seasonal patterns in shark attacks, often linked to:
- Shark migration: Many shark species undertake seasonal migrations, moving between feeding grounds or breeding areas, potentially increasing encounters with humans during these periods.
- Water temperature: As water temperatures fluctuate, shark activity levels can change, potentially influencing the frequency of attacks.
- Tourist season: Coastal areas experience peak tourist seasons, resulting in increased human activity in the water and a greater chance of encounters with sharks.
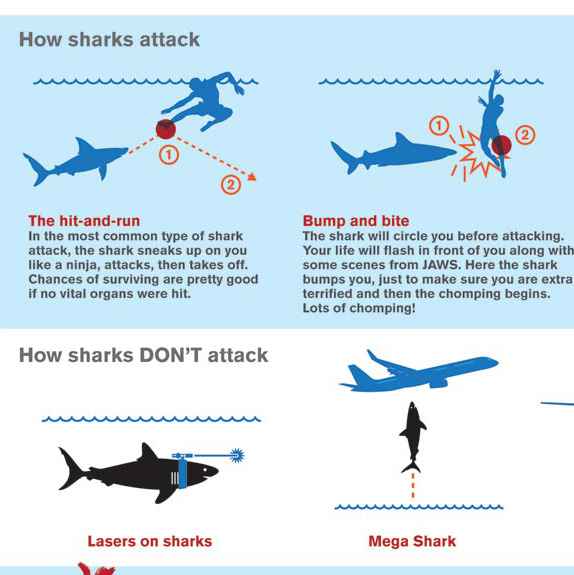
Species involvement: Maps can identify the shark species most commonly involved in attacks. This information helps researchers understand:
- Species-specific behavior: Certain shark species are known to be more aggressive than others, contributing to their higher involvement in attacks.
- Habitat overlap: Some shark species have a greater overlap with human activity zones, increasing the likelihood of interactions.
- Feeding patterns: Sharks’ feeding habits can influence their proximity to humans, particularly in areas where they actively seek prey.
Benefits of Shark Attack Maps:
The use of shark attack maps offers numerous benefits, including:
- Raising awareness: Visualizing the data helps to raise public awareness about the risks associated with shark encounters and promotes responsible ocean behavior.
- Improving safety: By identifying areas with high attack rates, authorities can implement measures to mitigate risk, such as installing warning signs, restricting certain activities, and implementing shark mitigation strategies.
- Research and conservation: Maps provide valuable data for scientists studying shark behavior, ecology, and conservation, helping to inform research efforts and contribute to the preservation of these important marine animals.
- Education: Maps can be used as educational tools to teach individuals about shark biology, behavior, and the importance of coexisting with these creatures.
FAQs about Shark Attack Maps:
Q: Are shark attack maps accurate?
A: The accuracy of shark attack maps depends on the quality and completeness of the data used. While efforts are made to ensure comprehensive data collection, it is important to note that some attacks may go unreported or misclassified.
Q: Do shark attack maps exaggerate the risk?
A: Shark attacks are relatively rare events. While maps highlight areas with higher attack rates, it is essential to remember that these areas still represent a small fraction of the vast ocean.
Q: Are shark attack maps a reliable predictor of future attacks?
A: While maps can provide insights into patterns and trends, they cannot predict future attacks with certainty. Many factors influence shark behavior, making it difficult to predict individual encounters.
Q: What can I do to stay safe in the water?
A: While shark attacks are infrequent, it is essential to practice responsible ocean behavior to minimize risk. This includes:
- Swimming in designated areas: Avoid swimming in areas known to have high shark activity or where there are warnings in place.
- Staying in groups: Swimming with others reduces the risk of individual encounters.
- Avoiding dusk and dawn: Sharks are more active at these times, so it is best to avoid swimming during these periods.
- Avoiding areas with potential prey: Sharks are attracted to areas where their prey is present, such as schools of fish or seals.
- Staying aware of your surroundings: Pay attention to your surroundings and be cautious of any unusual activity in the water.
Tips for Using Shark Attack Maps:
- Consider the source: Ensure the map you are using is based on reliable and verified data.
- Look for patterns: Analyze the distribution of attacks and identify areas with higher concentrations.
- Understand the context: Consider factors such as water temperature, salinity, and human activity levels when interpreting the map.
- Use the information responsibly: Use the map to inform your decisions about ocean safety and responsible behavior.
Conclusion:
Shark attack maps are valuable tools for understanding the global distribution and frequency of these events. By visualizing data and revealing patterns, these maps contribute to raising awareness, promoting safety, and informing research efforts. While shark attacks remain a rare occurrence, responsible ocean behavior and awareness of these maps can help minimize the risk and promote harmonious coexistence with these fascinating creatures.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Patterns of Shark Attacks: A Global Perspective. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!