Unveiling the Depths: A Comprehensive Guide to Lake Topography Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Depths: A Comprehensive Guide to Lake Topography Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Depths: A Comprehensive Guide to Lake Topography Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Depths: A Comprehensive Guide to Lake Topography Maps
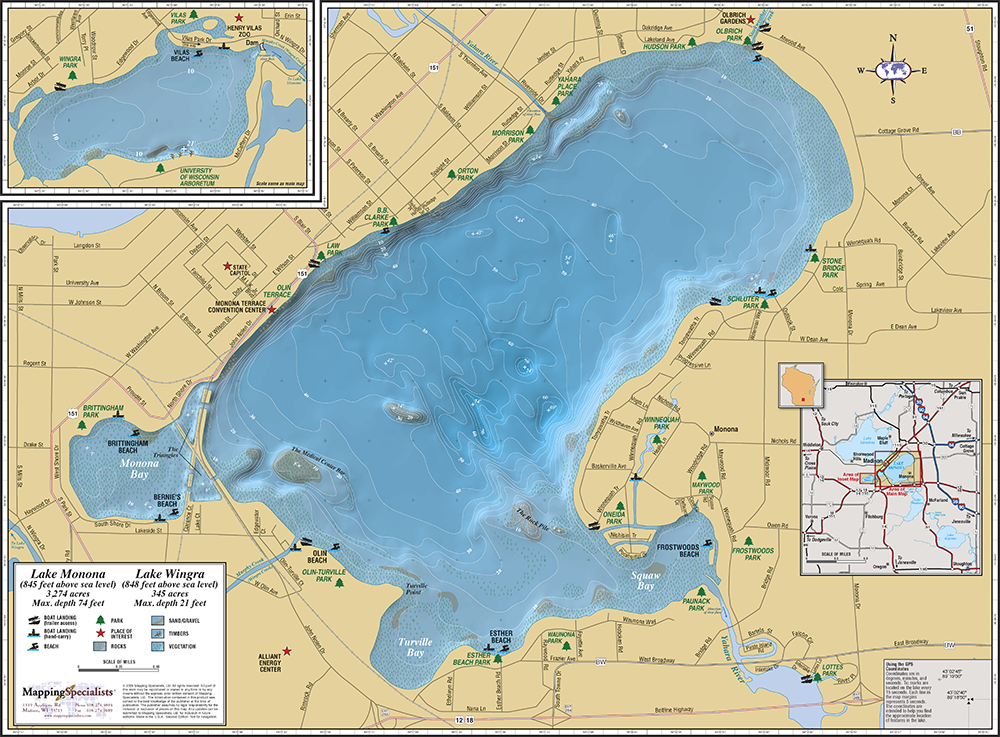
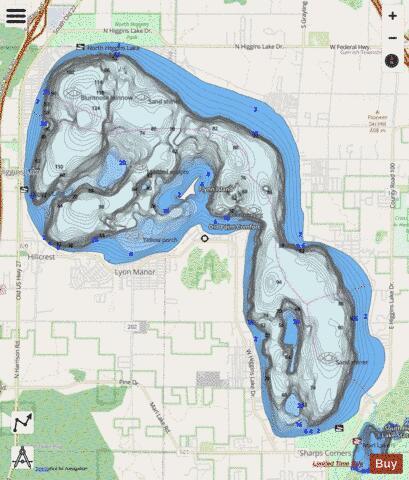
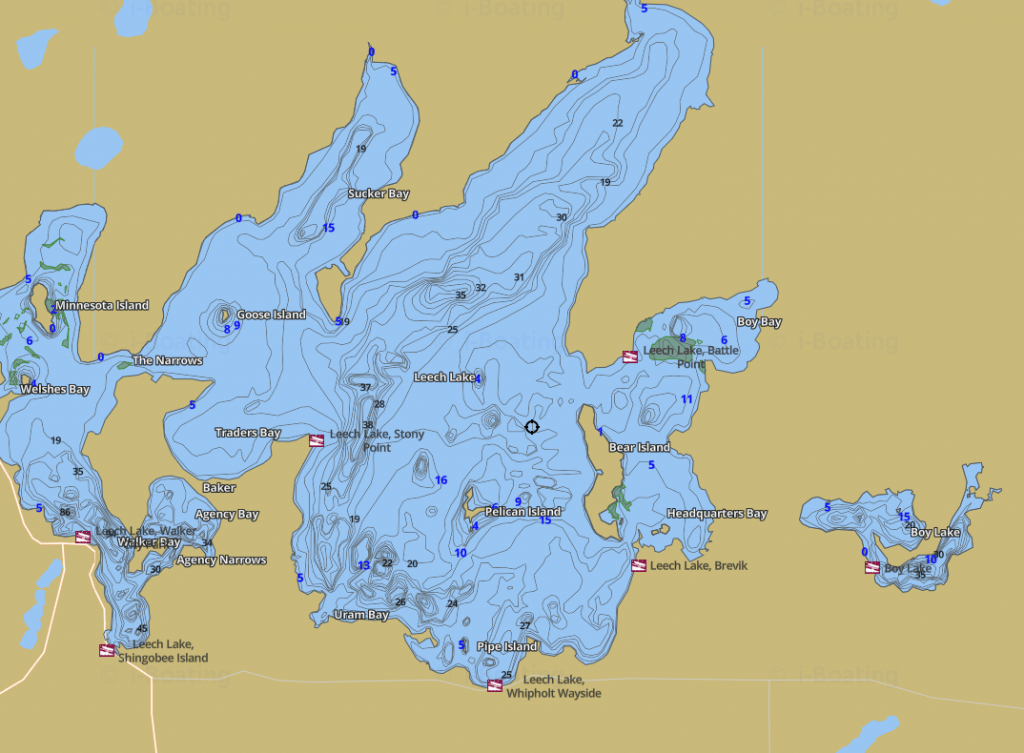
Lake topography maps, often referred to as bathymetric maps, are essential tools for understanding the underwater landscape of lakes. These maps depict the lake’s bottom contours, revealing the shape, depth, and features of the lakebed, providing valuable insights for a wide range of applications.
Understanding the Basics:
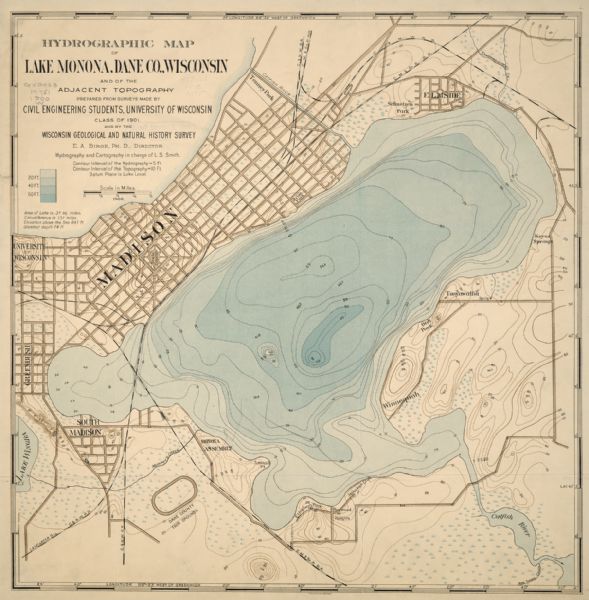
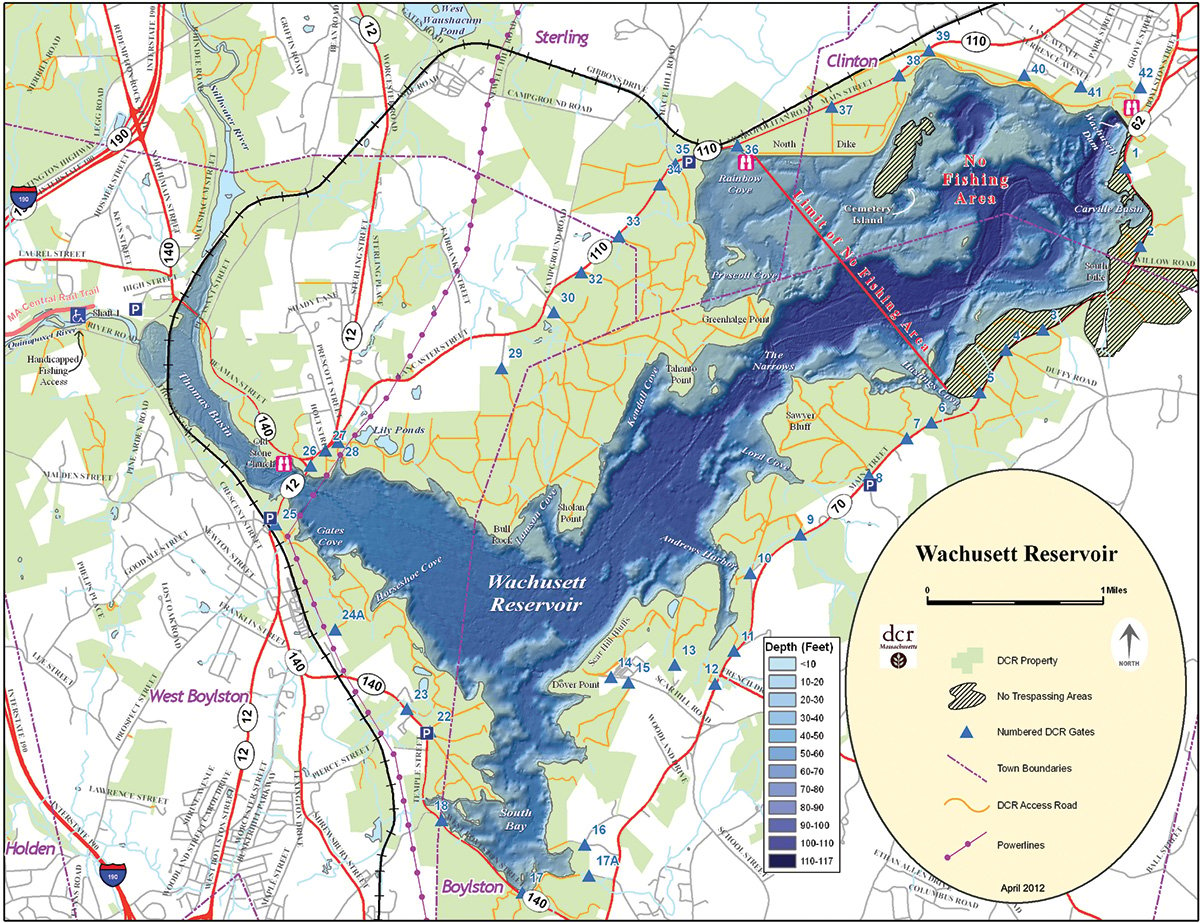
Lake topography maps are essentially underwater contour maps. They illustrate the lake’s depth at various points, using lines called "isobaths" to connect points of equal depth. These lines resemble the contour lines found on traditional topographic maps, which show elevation changes on land. Each isobath represents a specific depth increment, typically ranging from a few meters to tens of meters depending on the lake’s size and depth.
The Importance of Lake Topography Maps:
The significance of lake topography maps extends far beyond mere scientific curiosity. They serve as vital tools for:
- Environmental Management and Research: Lake topography maps are crucial for understanding lake ecology, water circulation patterns, and sediment distribution. They help researchers study the impact of human activities, such as pollution or dam construction, on lake ecosystems.
- Water Resource Management: By revealing the lake’s volume and depth, topography maps aid in water management strategies. They provide insights into water storage capacity, potential flood risks, and optimal locations for water intake and discharge points.
- Navigation and Safety: For boaters, anglers, and divers, lake topography maps are essential for safe navigation. They provide information about underwater hazards like submerged rocks, reefs, and steep drop-offs, allowing users to avoid potential accidents.
- Hydropower Development: Topography maps are instrumental in planning and designing hydroelectric power plants. They reveal the lake’s potential for water storage and the feasibility of dam construction.
- Construction and Engineering Projects: When planning infrastructure projects near or on lakes, topography maps are essential for determining the best locations for bridges, piers, and pipelines, ensuring stability and minimizing environmental impact.
Creating Lake Topography Maps:
Generating accurate lake topography maps requires specialized techniques and equipment. The most common methods include:
- Echo Sounding: This traditional method uses sound waves to measure the depth of the lake. A transducer emits sound pulses that travel through the water, reflect off the lakebed, and return to the transducer. The time it takes for the sound to travel to the bottom and back determines the depth.
- Multibeam Sonar: This advanced technology uses multiple sound beams to map a wider area of the lakebed simultaneously. It provides a more detailed and accurate representation of the lake’s topography.
- LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging): This technology employs lasers to measure the distance between a sensor and the lakebed. It offers high-resolution data, particularly useful for mapping shallow water areas and identifying submerged features.
Interpreting Lake Topography Maps:
Understanding the information presented on lake topography maps requires some basic knowledge of map reading and interpretation. Key elements to consider include:
- Contour Lines: The isobaths represent depth contours, with closer spacing indicating steeper slopes and wider spacing indicating gentler slopes.
- Depth Values: Each isobath is labeled with its corresponding depth value, allowing users to determine the depth at any point on the map.
- Symbols and Legend: The map legend explains the meaning of various symbols and abbreviations used to represent specific features, such as submerged vegetation, rock outcrops, and artificial structures.
- Scale and Orientation: The map scale indicates the relationship between distances on the map and actual distances on the lake. The orientation, usually indicated by a north arrow, helps determine directions within the lake.
FAQs about Lake Topography Maps:
Q: What is the difference between a lake topography map and a bathymetric map?
A: The terms "lake topography map" and "bathymetric map" are often used interchangeably. Both refer to maps depicting the underwater landscape of a lake, showing depth contours and features of the lakebed.
Q: How accurate are lake topography maps?
A: The accuracy of lake topography maps depends on the mapping method used. Traditional echo sounding provides relatively accurate data, while multibeam sonar and LiDAR offer significantly higher accuracy and detail.
Q: Where can I find lake topography maps?
A: Lake topography maps can be obtained from various sources, including:
- Government Agencies: National and local government agencies responsible for water resources often publish lake topography maps.
- Research Institutions: Universities and research institutions engaged in lake studies may have access to detailed lake topography maps.
- Mapping Companies: Specialized mapping companies offer lake topography mapping services and may provide access to their data.
- Online Databases: Online databases, such as the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) website, may provide access to lake topography maps.
Q: What are the limitations of lake topography maps?
A: Lake topography maps, like any map, have limitations:
- Static Representation: Maps represent a snapshot of the lake at a specific time, and changes in water levels or sediment deposition can alter the topography.
- Accuracy Limitations: Mapping methods have inherent limitations, and errors can occur due to factors like water conditions, sensor accuracy, and data processing.
- Limited Detail: While maps provide a general overview of the lakebed, they may not capture all the fine details of the underwater landscape.
Tips for Using Lake Topography Maps:
- Consider the Map’s Source: Verify the map’s accuracy and date of creation to ensure it reflects the current lake conditions.
- Use the Legend: Familiarize yourself with the symbols and abbreviations used on the map to understand its features and information.
- Pay Attention to Scale: Understand the map’s scale to accurately interpret distances and depths.
- Combine with Other Data: Integrate lake topography maps with other relevant data, such as satellite imagery, water quality reports, and weather information, for a more comprehensive understanding of the lake.
Conclusion:
Lake topography maps are indispensable tools for understanding and managing these vital aquatic ecosystems. They provide invaluable insights into the underwater landscape, supporting environmental research, water resource management, navigation safety, and infrastructure development. By understanding the basics of lake topography maps and utilizing them effectively, we can better manage and conserve our lakes, ensuring their ecological integrity and sustainable use for future generations.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Depths: A Comprehensive Guide to Lake Topography Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!