Unraveling the Mystery of Cicada Emergence: A Guide to Understanding Cicada Maps
Related Articles: Unraveling the Mystery of Cicada Emergence: A Guide to Understanding Cicada Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Mystery of Cicada Emergence: A Guide to Understanding Cicada Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unraveling the Mystery of Cicada Emergence: A Guide to Understanding Cicada Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unraveling the Mystery of Cicada Emergence: A Guide to Understanding Cicada Maps
- 3.1 Understanding Cicada Broods and Their Cycles
- 3.2 The Importance of Cicada Maps
- 3.3 Types of Cicada Maps
- 3.4 Frequently Asked Questions about Cicada Maps
- 3.5 Tips for Using Cicada Maps
- 3.6 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Unraveling the Mystery of Cicada Emergence: A Guide to Understanding Cicada Maps
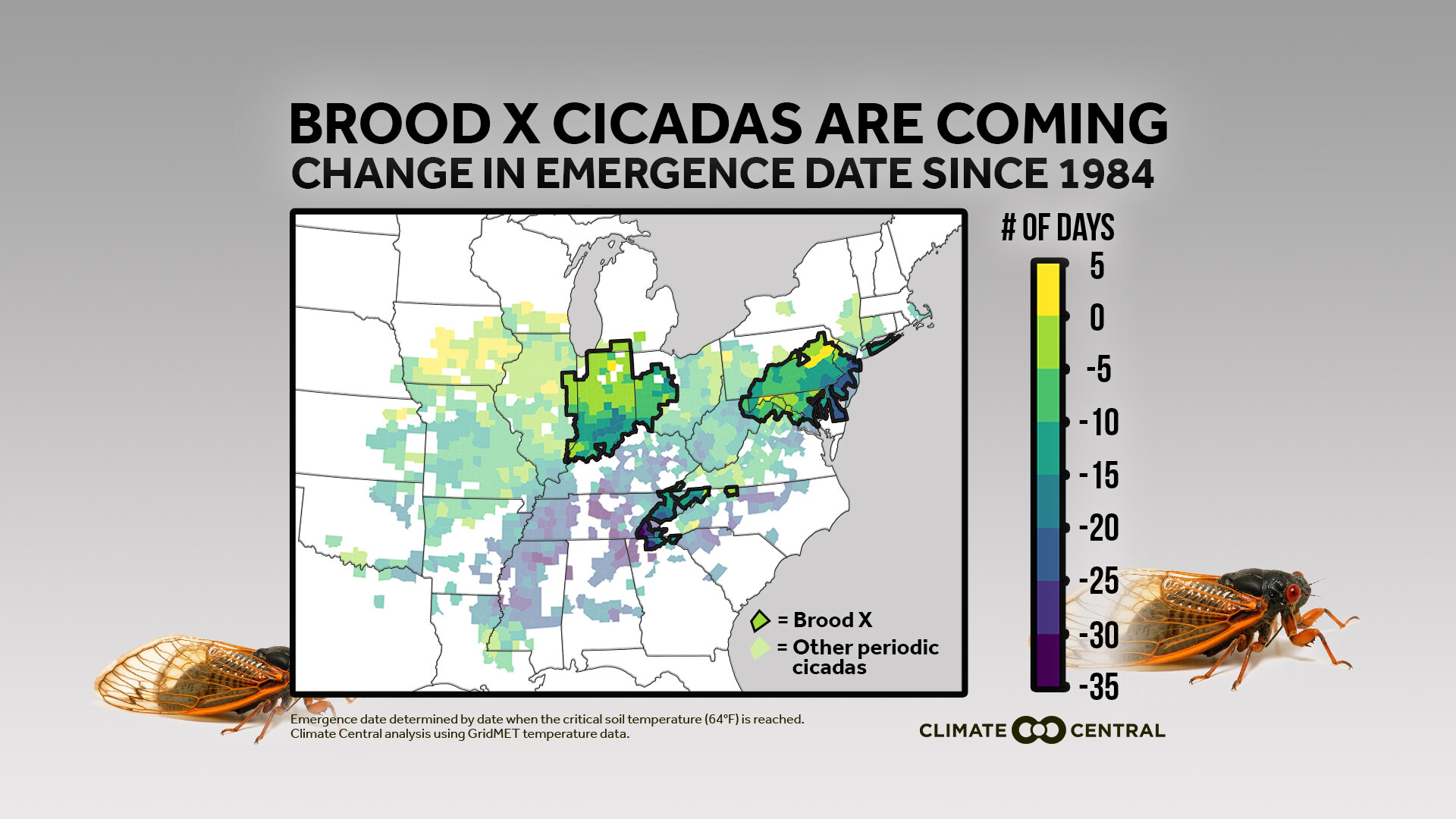
The periodic emergence of cicadas, particularly the brood-specific cycles of the "Magicicada" species, is a phenomenon that captivates both entomologists and the public alike. These insects, often referred to as "17-year cicadas" or "13-year cicadas," spend the vast majority of their lives underground, only to emerge in massive numbers after a precise period of time. Understanding the complex patterns of their emergence is crucial for research, conservation, and even public awareness. This is where cicada maps, visual representations of cicada brood distribution and emergence cycles, play a vital role.
Understanding Cicada Broods and Their Cycles
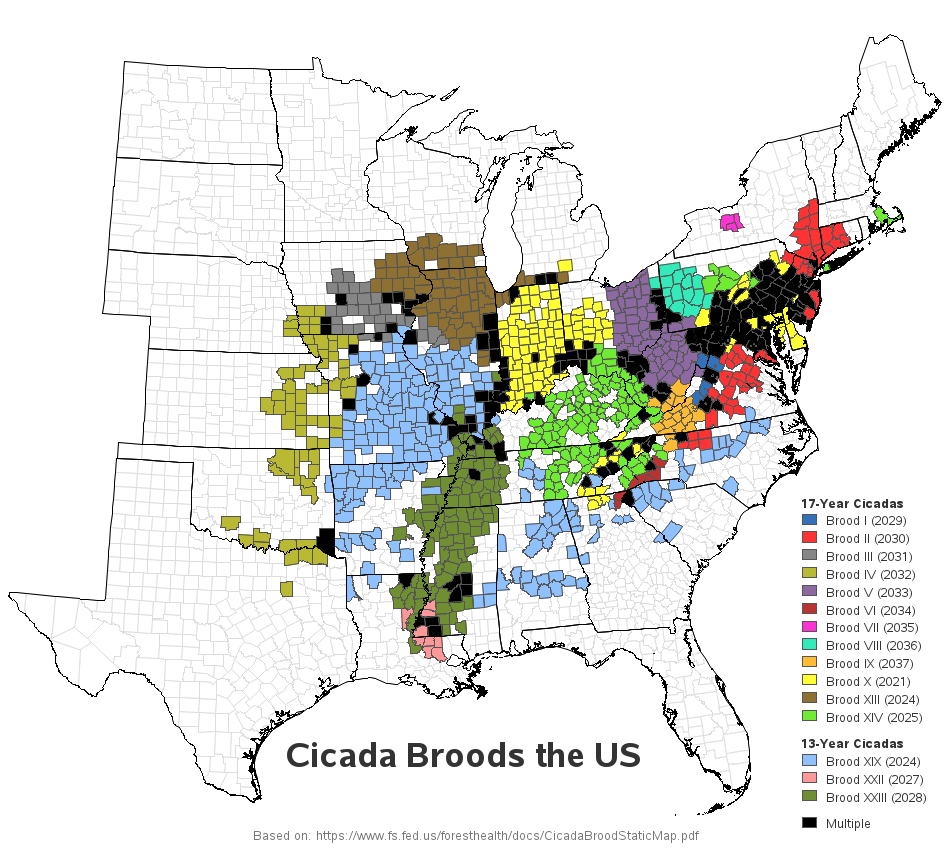
Cicada emergence patterns are not random; they are governed by a complex system of brood cycles. North America is home to numerous cicada broods, each characterized by a specific emergence year and geographic range. The most well-known broods are the "17-year cicadas" and "13-year cicadas," named for their distinct developmental periods.
The "17-year cicadas" belong to the genus Magicicada and are further divided into seven distinct broods, each designated by a Roman numeral (I-VII). These broods emerge in different years, ensuring that not all 17-year cicadas emerge simultaneously. Similarly, the "13-year cicadas" are divided into four broods (VIII-XI), also emerging on staggered schedules.
The Importance of Cicada Maps
Cicada maps serve as invaluable tools for understanding and visualizing the intricate patterns of cicada emergence. They provide critical information for researchers, conservationists, and the general public, enabling them to:
- Predict Emergence Locations and Timing: Cicada maps act as predictive tools, indicating where and when specific cicada broods are expected to emerge. This knowledge is crucial for researchers studying cicada behavior, population dynamics, and the impact of environmental factors on their emergence.
- Monitor Brood Distribution and Abundance: By mapping the emergence locations and densities of various cicada broods, researchers can track changes in their distribution over time. This information is essential for assessing the health and resilience of cicada populations and identifying potential threats, such as habitat loss or climate change.
- Inform Public Awareness and Outreach: Cicada maps serve as valuable educational tools, allowing the public to learn about the fascinating life cycles of these insects and understand the significance of their periodic emergence. They can help dispel misconceptions and promote appreciation for these intriguing creatures.
- Facilitate Research and Conservation Efforts: By providing a clear picture of cicada brood distribution and emergence patterns, cicada maps facilitate research and conservation efforts aimed at protecting these unique insects. For example, they can help identify areas where cicada populations are vulnerable and require targeted conservation measures.
Types of Cicada Maps
Cicada maps are available in various formats and levels of detail, catering to different needs and purposes. Some common types of cicada maps include:
- Brood Distribution Maps: These maps depict the geographic range of each cicada brood, highlighting the areas where they are known to occur. They often use different colors or symbols to distinguish between different broods.
- Emergence Year Maps: These maps show the expected emergence years for different cicada broods across various regions. They are particularly useful for planning research projects or public outreach activities.
- Density Maps: These maps indicate the relative abundance of cicada broods in different locations. They can be used to assess the overall population size and identify areas with high cicada density.
- Interactive Maps: Online platforms offer interactive cicada maps that allow users to explore different layers of information, such as brood distribution, emergence year, and historical records.
Frequently Asked Questions about Cicada Maps
1. What are the benefits of using cicada maps?
Cicada maps provide valuable information about cicada emergence patterns, enabling researchers, conservationists, and the public to understand the distribution, abundance, and emergence timing of different cicada broods. This knowledge is crucial for research, conservation, and public awareness.
2. How are cicada maps created?
Cicada maps are created using data collected from various sources, including historical records, citizen science observations, and scientific studies. Researchers compile this information and use geographic information systems (GIS) software to create visual representations of cicada distribution and emergence patterns.
3. Where can I find cicada maps?
Cicada maps are readily available online through various resources, including university websites, government agencies, and citizen science platforms. Some popular sources include the website of the University of Connecticut’s "Magicicada" project, the Cicada Mania website, and the iNaturalist platform.
4. Are cicada maps updated regularly?
Yes, cicada maps are updated regularly as new data becomes available. Researchers and citizen scientists continuously monitor cicada emergence patterns and contribute their observations to update the maps and ensure their accuracy.
5. Can I contribute to cicada map creation?
Absolutely! Citizen science platforms like iNaturalist allow individuals to contribute their cicada observations, helping to improve the accuracy and completeness of cicada maps. By documenting your sightings, you can contribute to the understanding of cicada distribution and emergence patterns.
Tips for Using Cicada Maps
- Consult Multiple Sources: Utilize multiple sources of cicada maps to get a comprehensive understanding of cicada distribution and emergence patterns. Different sources may have different levels of detail and focus on specific regions or broods.
- Consider the Map’s Date: Pay attention to the date of the map, as cicada emergence patterns can change over time. Ensure that you are using the most up-to-date maps for accurate information.
- Verify Information: It is always advisable to verify information from cicada maps with other sources, such as scientific publications or expert websites.
- Use Maps for Educational Purposes: Cicada maps can be valuable tools for educating the public about the fascinating life cycles of these insects and the importance of their periodic emergence.
Conclusion
Cicada maps are invaluable tools for understanding and visualizing the intricate patterns of cicada emergence. They provide a wealth of information about cicada distribution, abundance, and emergence timing, enabling researchers, conservationists, and the public to make informed decisions about cicada research, conservation, and public outreach. By leveraging the power of these maps, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the fascinating life cycles of these insects and contribute to their long-term survival.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Mystery of Cicada Emergence: A Guide to Understanding Cicada Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!