Unlocking the Secrets Beneath Our Feet: A Deep Dive into the United States Soil Map
Related Articles: Unlocking the Secrets Beneath Our Feet: A Deep Dive into the United States Soil Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unlocking the Secrets Beneath Our Feet: A Deep Dive into the United States Soil Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unlocking the Secrets Beneath Our Feet: A Deep Dive into the United States Soil Map

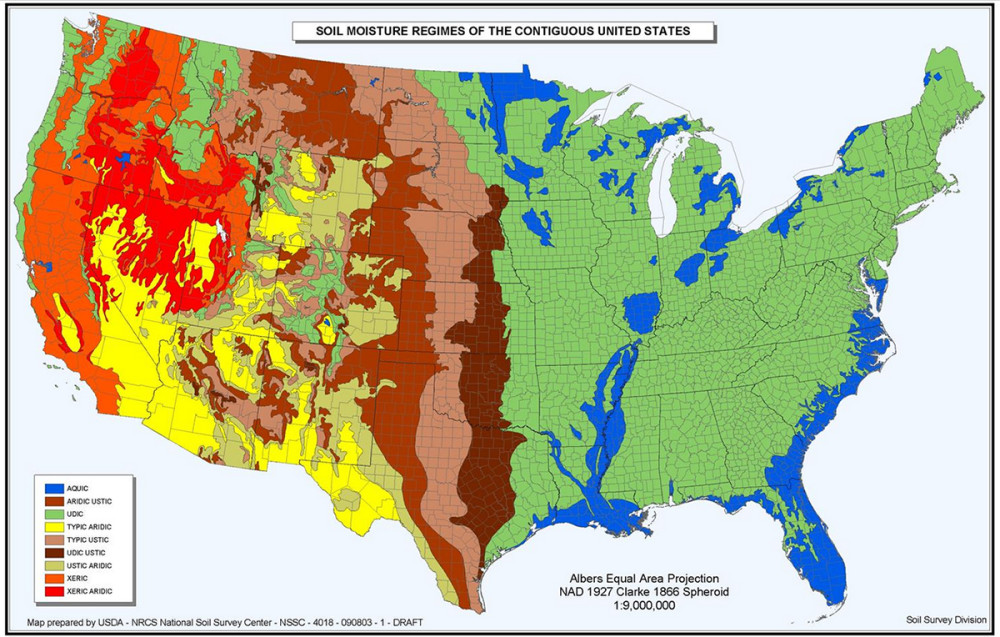
The United States, a land of diverse landscapes and ecosystems, rests upon a foundation of equally diverse soils. Understanding the composition, properties, and distribution of these soils is crucial for a multitude of endeavors, from agriculture and forestry to urban planning and environmental management. This is where the United States Soil Map, a comprehensive and dynamic resource, plays a pivotal role.
A Tapestry of Soil Diversity:
The United States Soil Map, developed and maintained by the Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS) of the United States Department of Agriculture, provides a detailed and nuanced picture of the nation’s soil landscape. It is a complex mosaic of distinct soil types, each with unique characteristics influenced by factors such as parent material, climate, topography, vegetation, and time.
The map is not a static representation but rather a dynamic tool that evolves as new data becomes available and our understanding of soil science advances. It is a collaborative effort involving scientists, researchers, and field experts who work tirelessly to refine and update the map, ensuring its accuracy and relevance.
Layers of Information:
The United States Soil Map encompasses a wealth of information beyond simply depicting soil types. It provides detailed insights into various soil properties, including:
- Soil Texture: This refers to the relative proportions of sand, silt, and clay in the soil, influencing its water-holding capacity, drainage, and suitability for different crops.
- Soil Structure: The arrangement of soil particles into aggregates, impacting aeration, water infiltration, and root growth.
- Soil Organic Matter: The amount of decomposed plant and animal matter in the soil, contributing to fertility, water retention, and soil structure.
- Soil pH: A measure of soil acidity or alkalinity, influencing nutrient availability and plant growth.
- Soil Depth: The vertical extent of the soil profile, impacting root development and water storage.
- Soil Drainage: The rate at which water moves through the soil, influencing plant growth and the risk of waterlogging.
- Soil Salinity: The concentration of salts in the soil, potentially affecting plant growth and irrigation requirements.
Unlocking the Potential:
The United States Soil Map serves as an invaluable tool for a wide range of applications, enabling informed decision-making across various sectors:
Agriculture: Farmers and ranchers rely on the map to understand the soil’s suitability for specific crops and livestock, optimizing production and minimizing environmental impact. It helps them identify areas with favorable soil properties for certain crops, guiding land management practices like irrigation, fertilization, and tillage.
Forestry: Forest managers use the map to assess the suitability of land for different tree species, ensuring sustainable forest management and maximizing timber production. It helps in identifying areas prone to erosion or susceptible to specific pests or diseases, enabling targeted interventions.
Urban Planning: Urban planners use the map to guide land development, considering soil properties and potential environmental impacts. It helps in identifying suitable locations for infrastructure, minimizing the risk of soil erosion, and promoting sustainable urban development.
Environmental Management: Environmental scientists and policymakers use the map to understand the distribution of sensitive soil types and assess potential risks from pollution or climate change. It helps in developing strategies for soil conservation, water quality protection, and mitigating the impacts of environmental stressors.
Beyond the Map: Connecting with the Land:
The United States Soil Map is not just a static document but a living resource that encourages engagement and exploration. It provides a framework for understanding the complex relationship between soil and the environment, fostering a deeper appreciation for the vital role soil plays in sustaining life.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Q: How can I access the United States Soil Map?
A: The map is freely available online through the NRCS Web Soil Survey (WSS) platform. Users can access detailed information on soil types, properties, and interpretations for any location in the United States.
Q: Is the United States Soil Map accurate and up-to-date?
A: The map is constantly being updated and refined as new data becomes available. The NRCS utilizes a rigorous process of data collection, analysis, and validation to ensure the map’s accuracy and relevance.
Q: How can I use the United States Soil Map to inform my land management practices?
A: The WSS platform provides various tools and interpretations that can be used to make informed decisions about land use, crop selection, irrigation, fertilization, and other management practices.
Q: What are the limitations of the United States Soil Map?
A: The map is a generalization of soil conditions across a large geographic area. While it provides valuable insights, it may not capture all the nuances of soil variability within a specific location.
Tips for Using the United States Soil Map:
- Start with a specific location: The WSS platform allows you to search for a particular address, farm, or geographic area.
- Explore different layers: The map offers various layers of information, including soil types, properties, and interpretations.
- Consult with experts: If you have specific questions or need further guidance, consider contacting local NRCS offices or soil scientists.
- Stay informed about updates: The NRCS regularly updates the map, so it is essential to check for the latest versions and data.
Conclusion:
The United States Soil Map is a testament to the power of scientific collaboration and the importance of understanding the fundamental resources that sustain us. It provides a valuable framework for informed decision-making, enabling us to manage our land resources responsibly, protect our environment, and ensure the long-term sustainability of our agricultural and ecological systems. By harnessing the information provided by the map, we can unlock the secrets beneath our feet and cultivate a future where soil health is paramount.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unlocking the Secrets Beneath Our Feet: A Deep Dive into the United States Soil Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!