The Nile River Valley: A Lifeline Across Time
Related Articles: The Nile River Valley: A Lifeline Across Time
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Nile River Valley: A Lifeline Across Time. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Nile River Valley: A Lifeline Across Time

The Nile River, the longest river in the world, is a geographic and historical marvel. Its valley, cradled between the Sahara Desert and the Ethiopian Highlands, is a testament to the enduring power of water and the ingenuity of human adaptation. Understanding the Nile River Valley map is crucial for grasping the history, culture, and ecological significance of this vital region.
The Nile River’s Geography and Hydrology:
The Nile River flows for over 6,650 kilometers, traversing eleven countries in northeastern Africa. Its journey begins in the Ethiopian Highlands, where the Blue Nile and the Atbara rivers originate. These tributaries converge in Sudan, forming the main Nile, which then flows northward through Egypt before emptying into the Mediterranean Sea.
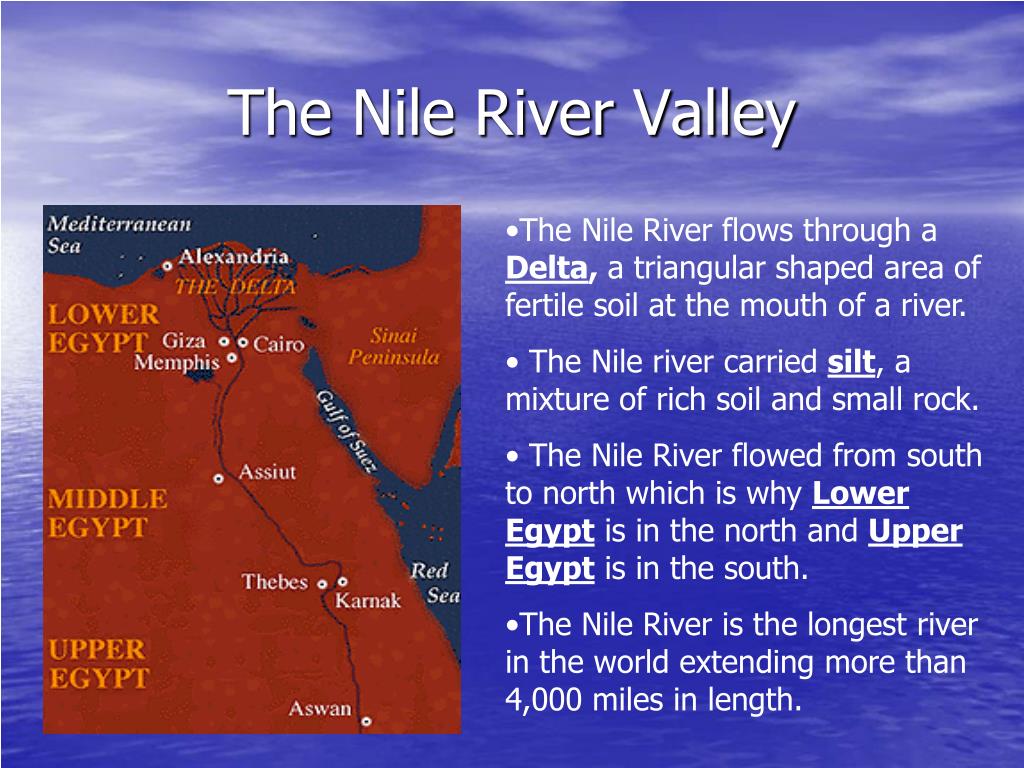
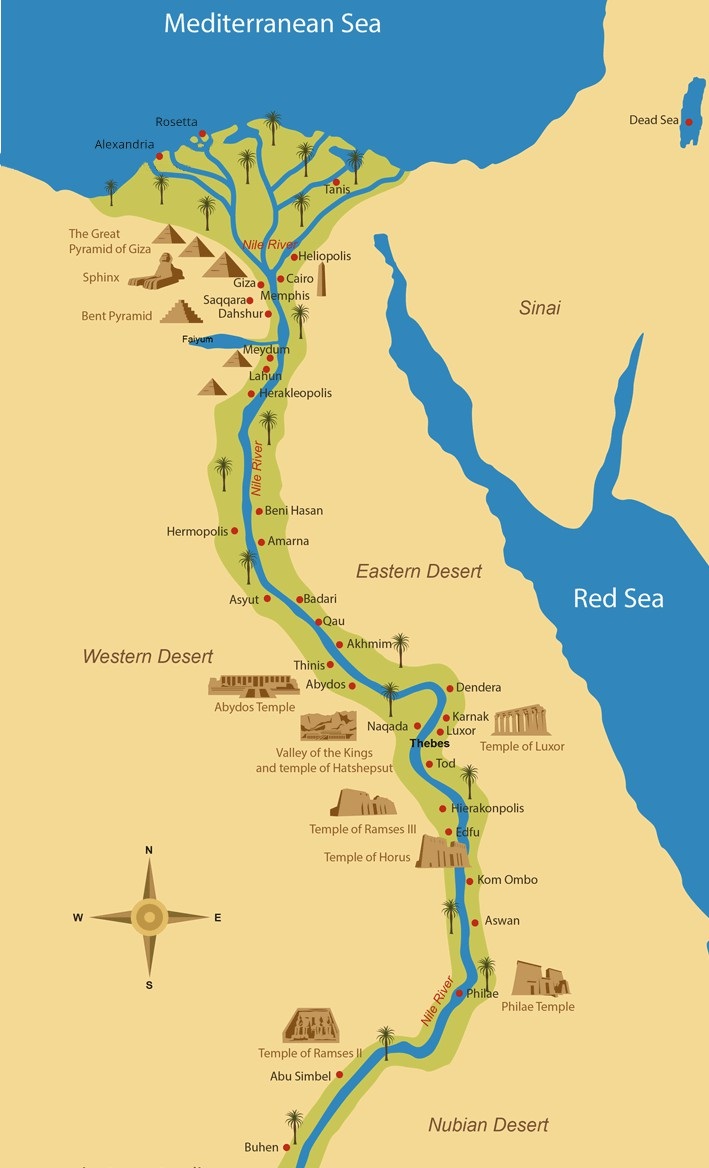
The Nile River Valley map reveals a distinct geographical pattern. The valley widens in Sudan, creating vast plains known as the "Sudanese Nile Valley." Further north, the valley narrows in Egypt, forming a fertile strip known as the "Nile Delta," where the river branches out into numerous distributaries. This delta region is a vital agricultural area, providing sustenance to millions.
The Nile’s Historical Significance:
The Nile River Valley has been a cradle of civilization for millennia. The ancient Egyptians, who flourished along the river’s banks, built monumental structures like the pyramids and temples, developed a sophisticated writing system, and advanced in mathematics, astronomy, and medicine. The river provided them with fertile land for agriculture, water for irrigation, and a vital transportation route.
The Nile Valley’s historical significance extends beyond ancient Egypt. The Nubian civilization, known for its rich culture and impressive architecture, thrived along the Nile in present-day Sudan. Later, the region became a crossroads of trade and cultural exchange, connecting the Mediterranean world with the African interior.
The Nile River Valley Map: A Key to Understanding the Region:
Examining the Nile River Valley map reveals several key features that shaped the region’s history and development:
- The Nile’s Course: The river’s journey from its source to its mouth dictates the flow of water, sediment, and nutrients, influencing the distribution of fertile land and the development of human settlements.
- The Nile’s Tributaries: The Blue Nile and the Atbara contribute significantly to the Nile’s flow, providing a vital source of water and sediment for agriculture.
- The Nile Delta: This fertile region, formed by the river’s deposition of silt, has been the heart of Egyptian civilization for centuries, providing agricultural abundance and supporting a dense population.
- The Cataracts: The Nile’s course is punctuated by several rapids, known as cataracts, which historically hindered navigation but also served as natural barriers, influencing the development of distinct cultural zones.
- The Nile Valley’s Topography: The valley’s gradual slope from south to north, coupled with the river’s flow, facilitated the development of irrigation systems and facilitated trade along the river’s course.
The Nile River Valley’s Importance Today:
The Nile River Valley remains a vital region in the 21st century. It supports a large population, sustains agriculture, and provides crucial water resources for drinking, irrigation, and industry. The Nile’s water resources are shared by eleven countries, necessitating complex water management agreements and cooperation for sustainable development.
The Nile River Valley is also facing challenges, including:
- Climate Change: Rising temperatures and changing rainfall patterns threaten the Nile’s water supply, potentially impacting agriculture and livelihoods.
- Population Growth: Rapid population growth in the Nile Valley puts increasing strain on water resources and agricultural land, demanding sustainable solutions for resource management.
- Pollution: Industrial and agricultural activities can pollute the Nile’s water, impacting human health and aquatic ecosystems.
FAQs about the Nile River Valley Map:
-
Q: Why is the Nile River Valley so important?
- A: The Nile River Valley has been a cradle of civilization for millennia, providing fertile land for agriculture, water for irrigation, and a vital transportation route. It continues to support a large population and is crucial for the economic and social development of the region.
-
Q: What are the major features of the Nile River Valley map?
- A: The Nile River Valley map showcases the river’s course, its tributaries, the Nile Delta, the cataracts, and the valley’s topography, all of which have played crucial roles in shaping the region’s history and development.
-
Q: What are the challenges facing the Nile River Valley today?
- A: The Nile River Valley faces challenges related to climate change, population growth, and pollution, all of which threaten the region’s water resources and agricultural productivity.
-
Q: How can the Nile River Valley be sustainably managed?
- A: Sustainable management of the Nile River Valley requires cooperation among the riparian countries, investment in water-efficient technologies, and efforts to mitigate the impacts of climate change and pollution.
Tips for Understanding the Nile River Valley Map:
- Study the River’s Course: Trace the Nile’s journey from its source to its mouth, noting its tributaries, the Nile Delta, and the cataracts.
- Focus on Key Geographic Features: Identify the Nile Delta, the cataracts, and the valley’s topography, understanding their influence on the region’s history and development.
- Consider the River’s Role in History: Explore the ancient civilizations that thrived along the Nile, their cultural achievements, and the impact of the river on their societies.
- Examine Current Challenges: Understand the contemporary issues facing the Nile River Valley, including climate change, population growth, and pollution, and explore potential solutions.
- Appreciate the Nile’s Significance: Recognize the Nile River Valley’s enduring importance as a source of life, a cradle of civilization, and a vital resource for the present and future generations.
Conclusion:
The Nile River Valley map is more than a geographical representation; it is a window into a rich and complex history, a testament to human ingenuity, and a reminder of the enduring power of water. Understanding the Nile River Valley map is crucial for appreciating the region’s past, present, and future, and for promoting sustainable development and cooperation among the nations that share this vital resource.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Nile River Valley: A Lifeline Across Time. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!