The Majestic Peaks of West Virginia: A Geographical Exploration
Related Articles: The Majestic Peaks of West Virginia: A Geographical Exploration
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Majestic Peaks of West Virginia: A Geographical Exploration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Majestic Peaks of West Virginia: A Geographical Exploration

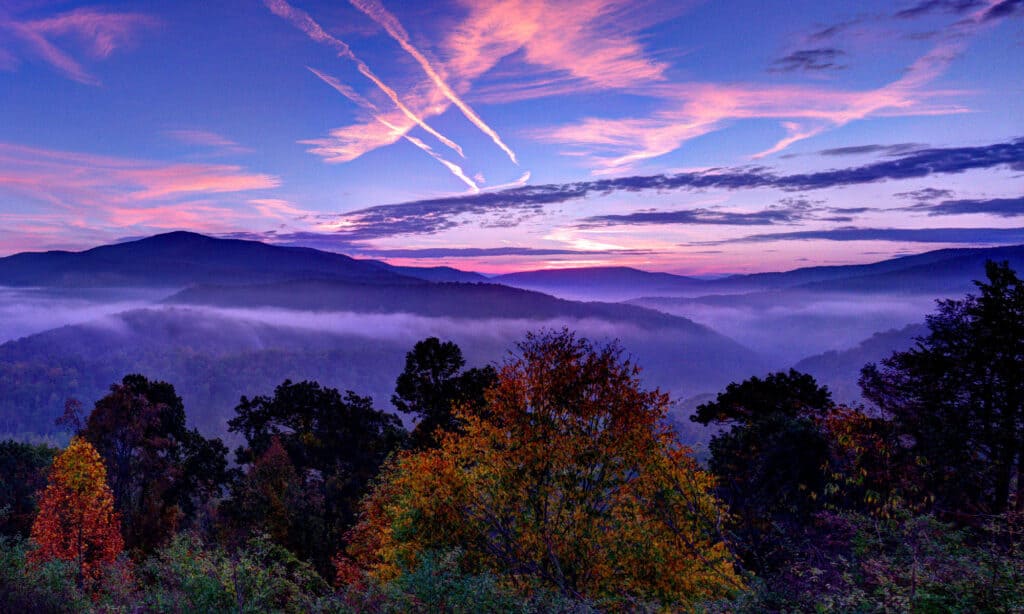
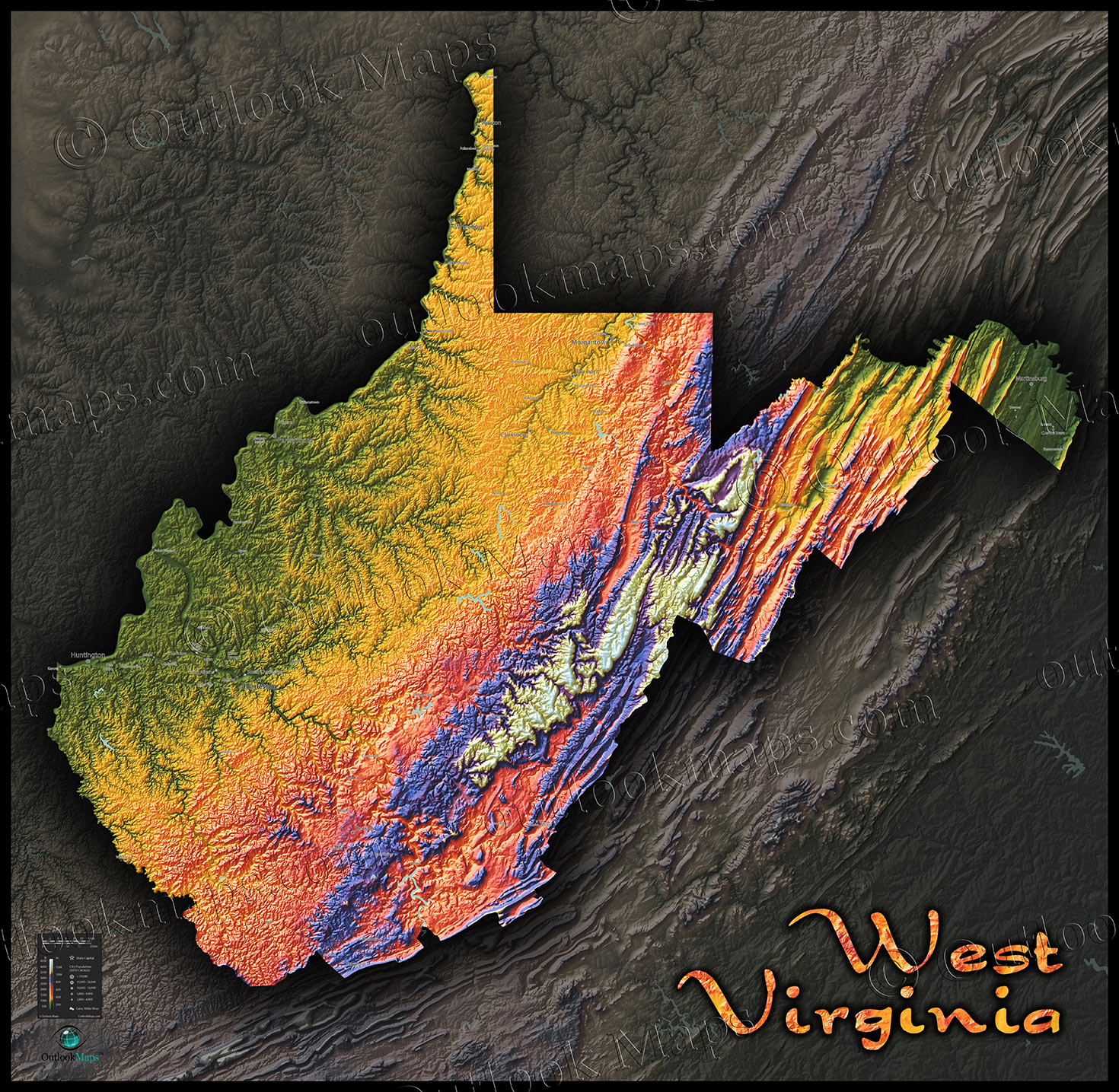
West Virginia, nestled in the heart of Appalachia, is a state defined by its rugged beauty. Its landscape is a tapestry of rolling hills, verdant forests, and, most prominently, towering mountains. These mountains, a testament to the region’s ancient geological history, are not just scenic landmarks; they are the very essence of West Virginia, shaping its climate, ecology, and culture.
A Mountainous Landscape: Understanding the Topography
The state’s mountainous terrain is a result of the Appalachian uplift, a geological process that began millions of years ago. The collision of tectonic plates pushed up the earth’s crust, forming the Appalachian Mountains. This uplift, combined with erosion by wind and water, sculpted the distinctive ridges and valleys that characterize West Virginia.
The state is divided into two major physiographic provinces: the Appalachian Plateau and the Valley and Ridge Province.
- The Appalachian Plateau: This region, covering the eastern and northern portions of West Virginia, is characterized by broad, flat-topped plateaus dissected by deep valleys. The plateau is a region of high elevation, with numerous peaks exceeding 4,000 feet.
- The Valley and Ridge Province: This region, located in the western and central parts of the state, is defined by parallel ridges and valleys. The ridges are composed of resistant sandstone and limestone, while the valleys are carved from softer shale and dolomite. The Valley and Ridge Province is renowned for its scenic beauty, with winding rivers, fertile valleys, and dramatic mountain views.
Key Mountain Ranges and Peaks
Within these provinces lie several prominent mountain ranges and individual peaks that define West Virginia’s landscape:
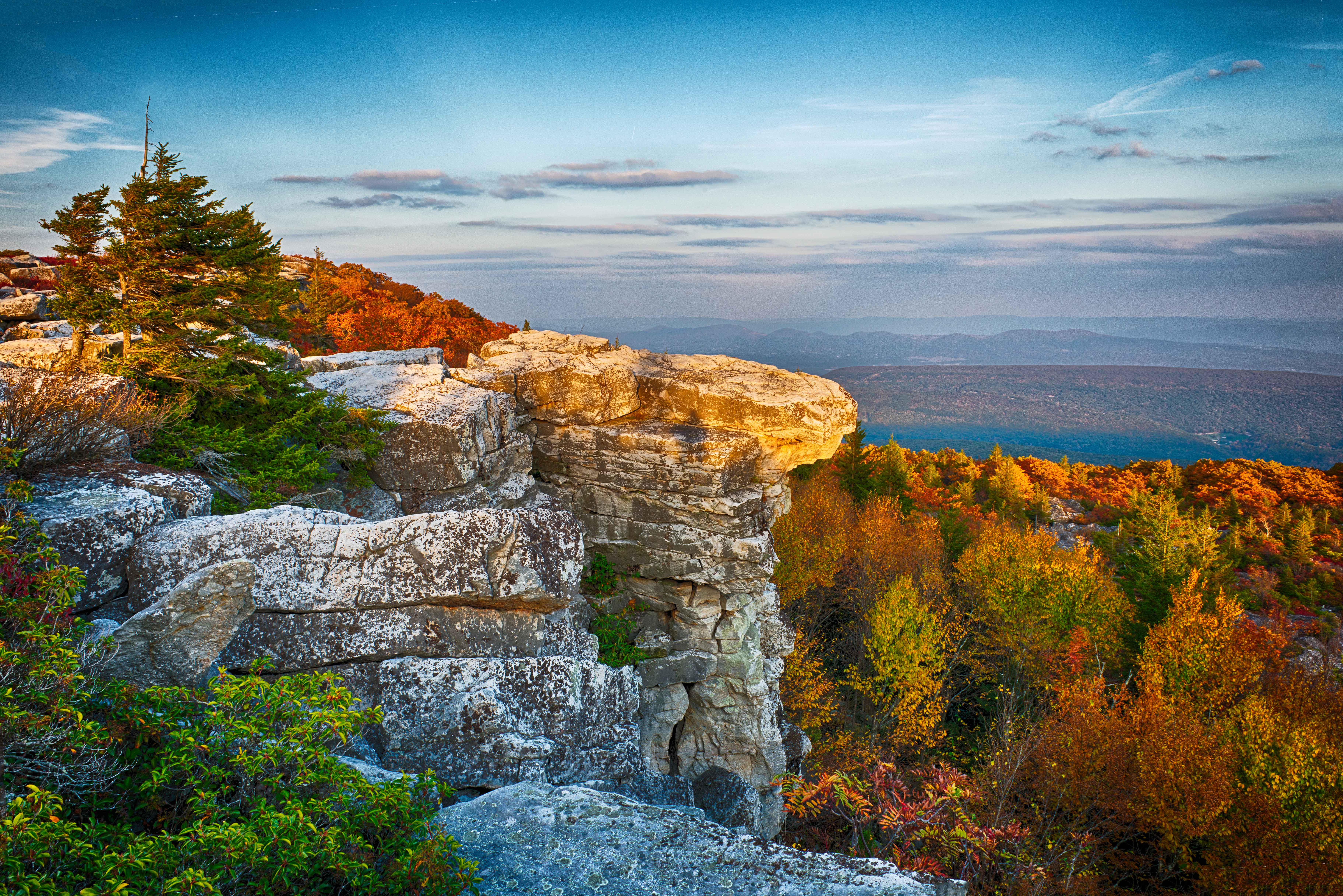
- The Allegheny Mountains: This range forms the eastern boundary of West Virginia and is a significant part of the Appalachian Plateau. It’s home to iconic peaks like Spruce Knob (the highest point in the state) and Seneca Rocks.
- The Blue Ridge Mountains: While the majority of the Blue Ridge Mountains are located in Virginia, the range’s southernmost extension reaches into West Virginia. This region is characterized by its rounded peaks and deep valleys, offering stunning vistas.
- The Cumberland Mountains: Located in the southwestern corner of West Virginia, the Cumberland Mountains are known for their rugged terrain and dense forests. This range is home to numerous waterfalls and scenic hiking trails.
- The Blackwater Mountains: Situated in the eastern part of the state, the Blackwater Mountains are a sub-range of the Allegheny Mountains. They are named for the Blackwater River, which flows through the area and is known for its dark, tannin-stained water.
- The Cheat Mountains: These mountains, part of the Allegheny Plateau, are known for their deep forests, steep slopes, and numerous streams. The Cheat River, flowing through the range, is a popular destination for whitewater rafting.
The Significance of West Virginia’s Mountains
West Virginia’s mountains are not just scenic landmarks; they play a vital role in the state’s ecology, economy, and culture:
- Water Resources: The mountains act as a vast watershed, providing a source of fresh water for the state and beyond. The numerous rivers and streams that originate in the mountains are essential for drinking water, irrigation, and hydroelectric power generation.
- Biodiversity: The diverse habitats created by the mountains support a rich array of plant and animal life. From the majestic bald eagles soaring above the peaks to the delicate wildflowers blooming in the valleys, West Virginia’s mountains are a haven for biodiversity.
- Natural Resources: The mountains are rich in natural resources, including coal, natural gas, timber, and limestone. These resources have played a significant role in the state’s economy, though their extraction has also raised environmental concerns.
- Tourism and Recreation: The mountains attract millions of visitors annually, drawn to their natural beauty and outdoor recreation opportunities. Hiking, camping, fishing, skiing, and whitewater rafting are just a few of the popular activities enjoyed in West Virginia’s mountains.
- Cultural Heritage: The mountains have shaped the culture of West Virginia, influencing its music, folklore, and way of life. The region’s rich history of coal mining and timber harvesting has left a lasting impact on its people and their traditions.
FAQs
-
What is the highest point in West Virginia?
- Spruce Knob, located in the Allegheny Mountains, is the highest point in West Virginia, reaching an elevation of 4,863 feet.
-
What are some popular hiking trails in West Virginia’s mountains?
- Some popular hiking trails include the Appalachian Trail, the Blackwater Falls Trail, and the Seneca Rocks Trail.
-
What are the most common trees found in West Virginia’s mountains?
- The most common trees found in West Virginia’s mountains include oak, maple, hickory, and hemlock.
-
What are some of the wildlife species found in West Virginia’s mountains?
- West Virginia’s mountains are home to a variety of wildlife, including black bears, deer, bobcats, wild turkeys, and various bird species.
-
What are some of the challenges facing West Virginia’s mountains?
- West Virginia’s mountains face challenges related to environmental degradation, including deforestation, mining pollution, and climate change.
Tips for Exploring West Virginia’s Mountains
- Plan your trip: Research the specific areas you wish to visit and choose trails and activities appropriate for your skill level and physical condition.
- Pack for all weather: West Virginia’s weather can be unpredictable, so be prepared for rain, sun, and cooler temperatures even during the summer months.
- Respect the environment: Stay on designated trails, pack out all trash, and avoid disturbing wildlife.
- Be aware of potential hazards: Mountain trails can be steep and rocky, and there is always a risk of encountering wildlife.
- Consider using a guide: Hiring a guide can enhance your experience and ensure safety, especially if you are new to hiking or exploring unfamiliar areas.
Conclusion
West Virginia’s mountains are a defining feature of the state, shaping its landscape, ecology, and culture. From the majestic peaks to the winding valleys, the region offers a breathtaking tapestry of natural beauty and recreational opportunities. Understanding the importance of these mountains and the challenges they face is crucial for ensuring their continued preservation and enjoyment for generations to come. By appreciating their beauty and embracing responsible stewardship, we can help protect this vital part of West Virginia’s heritage.
/seneca-rocks-592612409-580d547f3df78c2c736db12b.jpg)






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Majestic Peaks of West Virginia: A Geographical Exploration. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!