The Indus River: A Lifeline Through History and Geography
Related Articles: The Indus River: A Lifeline Through History and Geography
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Indus River: A Lifeline Through History and Geography. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Indus River: A Lifeline Through History and Geography

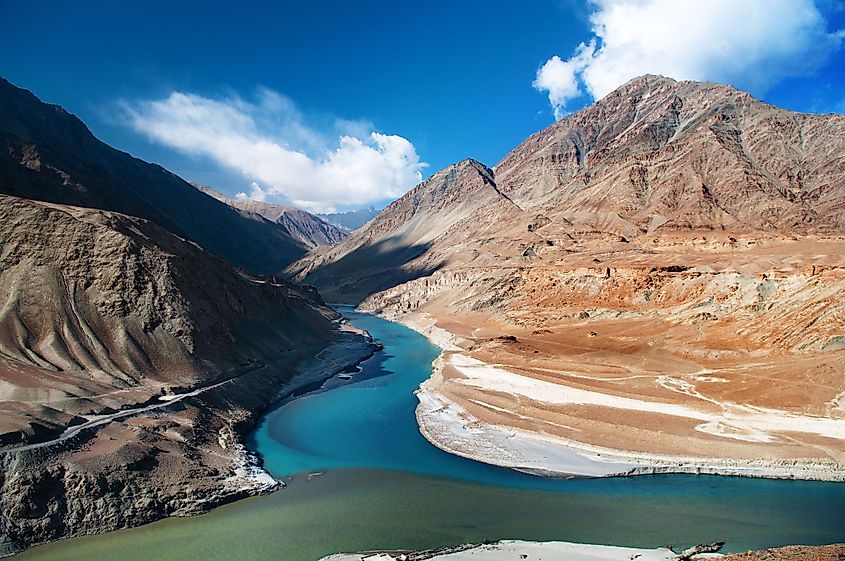
The Indus River, a vital artery of life and civilization, flows through the heart of South Asia, carving its path through the rugged terrains of the Himalayas and the vast plains of Pakistan. This ancient waterway, spanning over 3,000 kilometers, has played a pivotal role in shaping the cultural, economic, and social landscapes of the region for millennia.
A Journey Through Time and Terrain:
The Indus River’s journey begins in the icy heights of the Kailash Range in Tibet, where it is known as the Sengge Zangbo. As it descends from the Himalayas, it cuts through the rugged Karakoram Range, carving deep gorges and valleys. Entering Pakistan, the river transforms into a powerful force, nurturing the fertile plains of Punjab and Sindh. Its course then traverses the Thar Desert, eventually reaching the Arabian Sea near the city of Karachi.
A Cradle of Civilization:
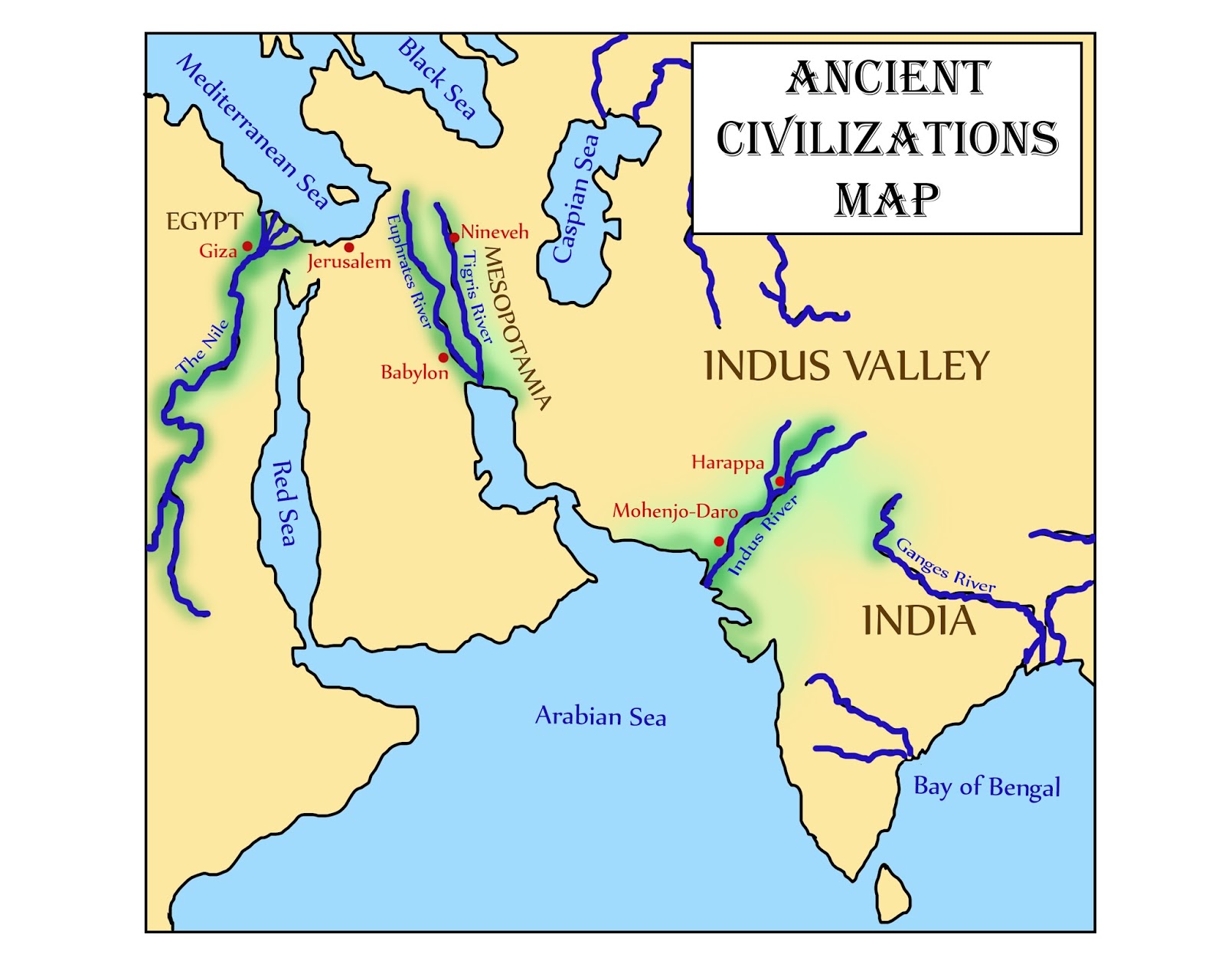
The Indus River basin is renowned for its ancient civilization, the Indus Valley Civilization, which flourished between 3300 and 1300 BCE. Archaeological evidence suggests a highly developed urban society with sophisticated city planning, advanced irrigation systems, and remarkable craftsmanship. The Indus civilization, with its unique script and artistic expressions, stands as a testament to the river’s enduring influence on human development.
A Lifeline for Modern Society:
Today, the Indus River remains a crucial resource for the region. Its waters sustain millions of people, providing irrigation for agriculture, drinking water for cities, and hydropower for industries. The river’s fertile floodplains support a vast agricultural economy, making Pakistan a significant producer of wheat, cotton, and rice.
Navigating Challenges:
Despite its immense importance, the Indus River faces several challenges. The river’s flow is highly variable, with seasonal fluctuations and occasional droughts posing significant threats to water security. Pollution from industrial waste and agricultural runoff has also degraded water quality in certain areas. Additionally, the construction of dams and barrages has altered the river’s natural flow, impacting downstream ecosystems and livelihoods.
Conservation and Management:
Recognizing the importance of the Indus River, governments and international organizations are working to address these challenges. Sustainable water management strategies are being implemented to ensure equitable access to water resources. Efforts are underway to reduce pollution and improve water quality through stricter regulations and technological advancements. Moreover, conservation initiatives are being undertaken to protect the river’s biodiversity and ecosystem integrity.
The Indus River on the World Map:
The Indus River’s geographical significance is evident on a world map. Its prominent course highlights its role as a major transboundary river, flowing through China, India, and Pakistan. Its position on the map underscores its influence on the geopolitical landscape of South Asia.
FAQs on the Indus River:
1. What is the source of the Indus River?
The Indus River originates in the Kailash Range in Tibet, China.
2. Where does the Indus River flow?
The Indus River flows through China, India, and Pakistan, ultimately emptying into the Arabian Sea.
3. What are the main tributaries of the Indus River?
The Indus River has numerous tributaries, including the Zanskar River, the Shyok River, the Hunza River, the Gilgit River, the Kabul River, the Jhelum River, the Chenab River, the Ravi River, and the Sutlej River.
4. What are the major cities located along the Indus River?
Major cities located along the Indus River include Leh, Skardu, Gilgit, Islamabad, Rawalpindi, Lahore, Multan, Sukkur, and Karachi.
5. What are the major challenges facing the Indus River?
The Indus River faces challenges such as water scarcity, pollution, and the impact of dam construction.
6. How is the Indus River being managed?
Governments and international organizations are working to manage the Indus River through sustainable water management strategies, pollution control measures, and conservation initiatives.
Tips for Understanding the Indus River:
- Study a map: Examining the Indus River’s course on a world map provides a visual understanding of its geographical significance.
- Explore historical resources: Researching the Indus Valley Civilization reveals the river’s profound historical and cultural significance.
- Engage with contemporary issues: Staying informed about current challenges facing the Indus River, such as water scarcity and pollution, helps understand the river’s contemporary relevance.
Conclusion:
The Indus River, a powerful symbol of life and civilization, continues to play a vital role in shaping the destiny of South Asia. Its journey through time and terrain, its influence on ancient civilizations, and its enduring importance to modern societies highlight its profound impact on human history and the natural world. As we navigate the challenges of the 21st century, understanding and managing the Indus River effectively will be crucial for ensuring a sustainable future for the region and its people.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Indus River: A Lifeline Through History and Geography. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!