Shaping California’s Political Landscape: A Deep Dive into the Congressional Map
Related Articles: Shaping California’s Political Landscape: A Deep Dive into the Congressional Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Shaping California’s Political Landscape: A Deep Dive into the Congressional Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Shaping California’s Political Landscape: A Deep Dive into the Congressional Map

California, a state renowned for its diverse population and dynamic political scene, is also home to a complex and ever-evolving system of congressional representation. The state’s congressional map, a critical tool for defining electoral districts, directly impacts the balance of power in the U.S. House of Representatives and, by extension, the nation’s political landscape. This intricate map, which undergoes redrawing every ten years following the decennial census, is a subject of intense scrutiny and debate.
Understanding the Basics: How the Map Works
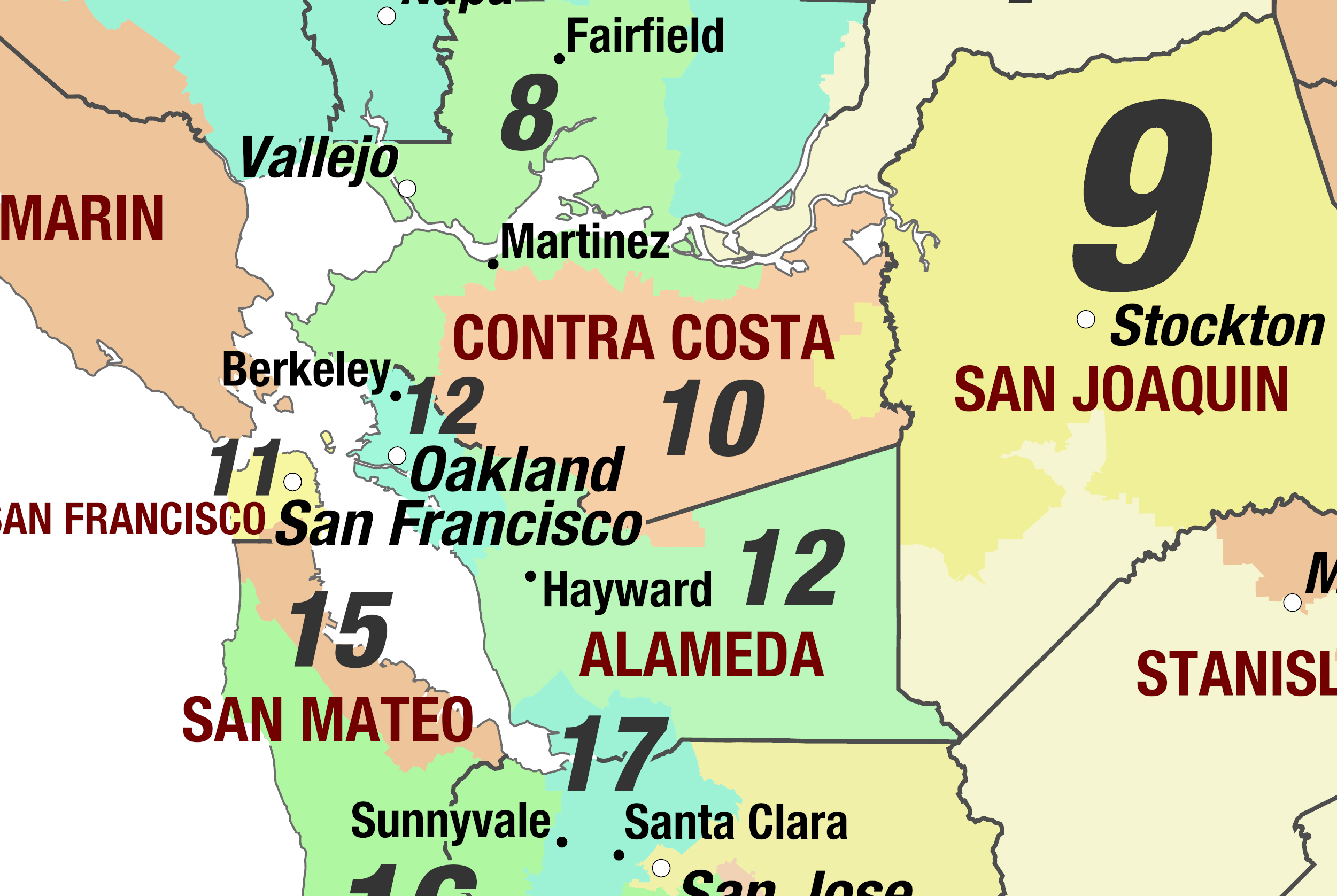
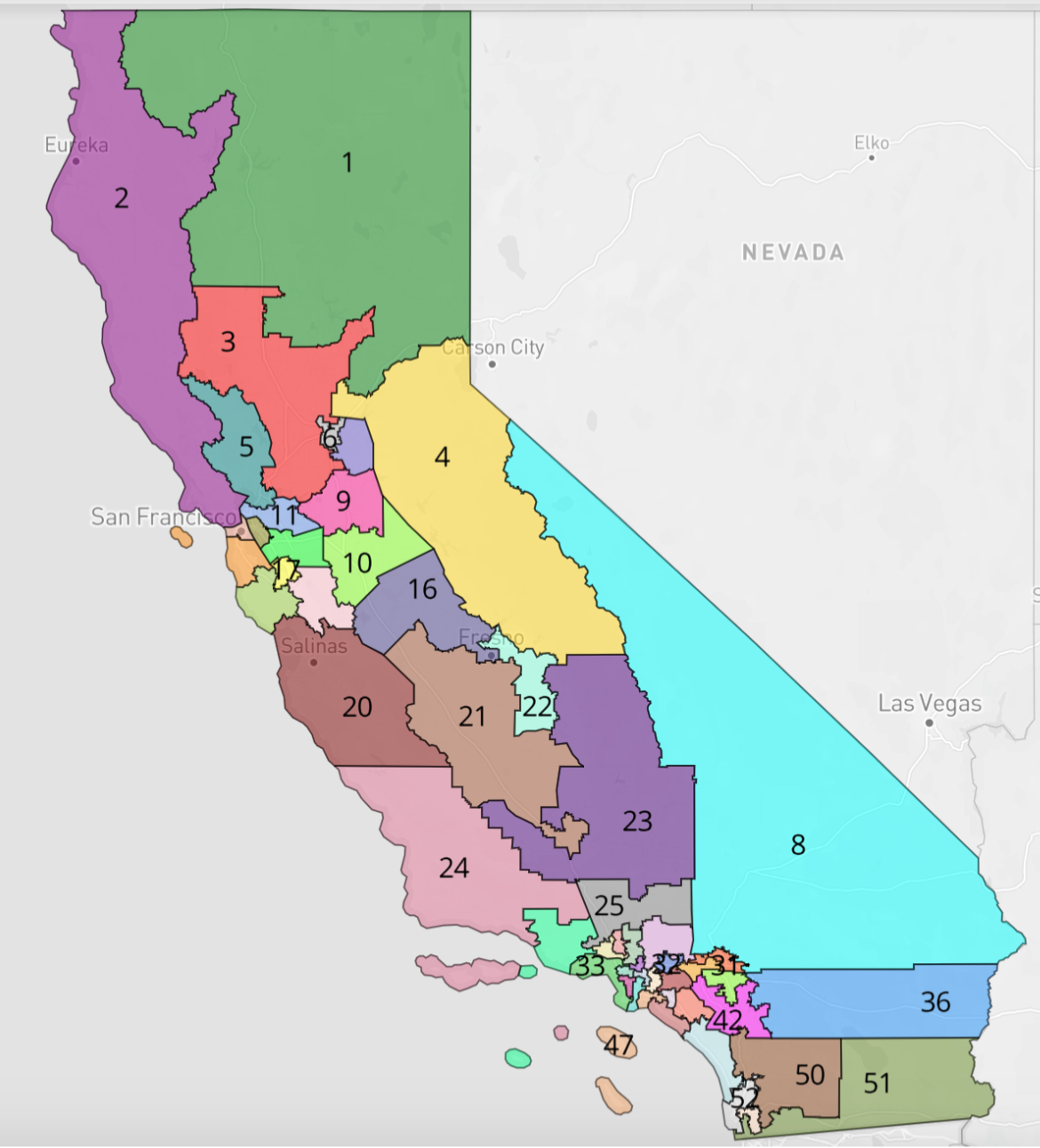
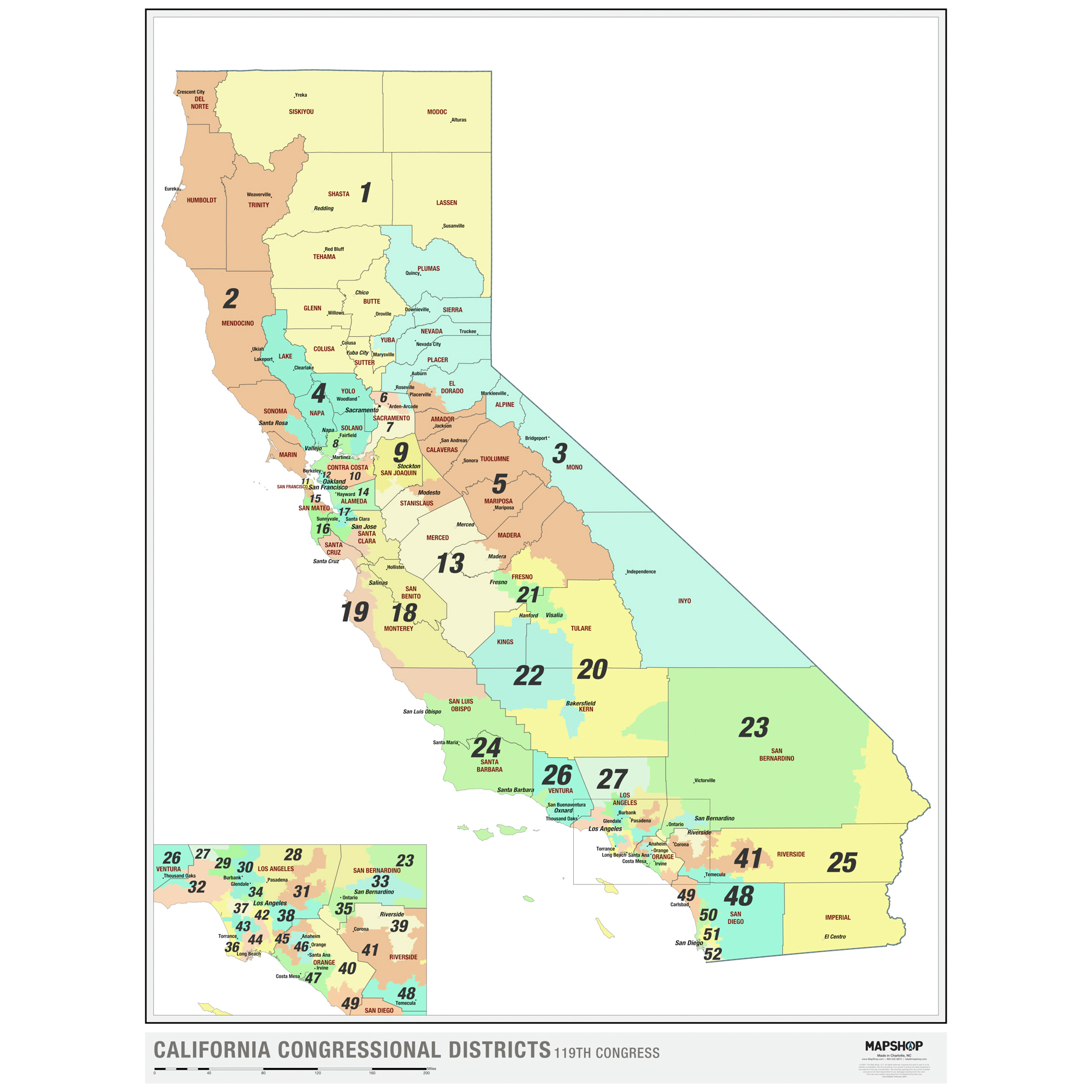
California’s congressional map divides the state into 53 districts, each electing one representative to the U.S. House of Representatives. The process of drawing these districts is known as redistricting, and it is governed by a set of principles aimed at ensuring fairness and equal representation. These principles include:
- Equal Population: Each district must have roughly the same number of people, reflecting the principle of "one person, one vote."
- Contiguity: Districts must be geographically connected, meaning no part of a district can be separated from the rest.
- Compactness: Districts should be drawn in a way that minimizes their overall area and avoids sprawling, oddly shaped boundaries.
- Respect for Communities of Interest: Districts should avoid dividing communities with shared interests, such as ethnic groups, economic interests, or cultural ties.
The History of California Redistricting: A Tale of Controversy and Change
The history of California’s congressional map is marked by a long and contentious process, often riddled with accusations of partisan gerrymandering, where districts are drawn to favor one party over another.
For decades, the state’s redistricting process was controlled by the legislature, leading to accusations of partisan bias. In 2008, California voters approved Proposition 11, which created the California Citizens Redistricting Commission (CRC), an independent body tasked with drawing congressional and state legislative districts. This shift aimed to remove the process from the control of politicians and ensure a more impartial and transparent redistricting process.
The CRC has faced its own challenges, including lawsuits alleging bias and accusations of failing to adequately represent minority communities. However, it has also been lauded for its efforts to create districts that are more competitive and reflect the state’s diverse population.
The 2020 Redistricting Cycle: A New Map, New Challenges
Following the 2020 census, the CRC embarked on the process of redrawing California’s congressional map. The new map, finalized in December 2021, reflects significant changes in the state’s population distribution, with significant growth in certain regions and declines in others.
The 2020 redistricting process was particularly challenging due to the unprecedented population shifts triggered by the COVID-19 pandemic. The CRC had to navigate these challenges while adhering to the principles of equal population, contiguity, compactness, and respect for communities of interest.
The Impact of the Congressional Map: Implications for Politics and Representation
The congressional map has a profound impact on California’s political landscape. It shapes the composition of the state’s delegation to the U.S. House of Representatives, influencing the balance of power in Congress and the ability of California’s representatives to advocate for their constituents’ interests.
Here are some key implications:
- Partisan Advantage: The map can create districts that favor one party over another, giving that party a greater chance of winning elections. This can lead to a situation where one party dominates the state’s congressional delegation, even if the overall population is closely divided.
- Representation of Minority Communities: The map plays a crucial role in ensuring adequate representation for minority communities. By drawing districts that reflect the demographics of these communities, the map can help ensure that their voices are heard in Congress.
- Competitive Districts: A map with more competitive districts can lead to more diverse representation and a more responsive political system. It can also encourage candidates to focus on issues that appeal to a broader range of voters.
FAQs on California’s Congressional Map
Q: How often is the congressional map redrawn?
A: The congressional map is redrawn every ten years, following the decennial census.
Q: Who is responsible for redrawing the congressional map in California?
A: The California Citizens Redistricting Commission (CRC) is responsible for redrawing the congressional map.
Q: What are the criteria used to draw the congressional map?
A: The CRC uses criteria such as equal population, contiguity, compactness, and respect for communities of interest to draw the congressional map.
Q: Can the congressional map be challenged in court?
A: Yes, the congressional map can be challenged in court. Lawsuits alleging bias or violations of the law have been filed in the past.
Q: How does the congressional map affect the political landscape in California?
A: The map shapes the composition of California’s delegation to the U.S. House of Representatives, influencing the balance of power in Congress and the ability of California’s representatives to advocate for their constituents’ interests.
Tips for Understanding and Engaging with the Congressional Map
- Stay Informed: Follow the work of the CRC and stay updated on the redistricting process.
- Participate in Public Hearings: Attend public hearings held by the CRC to provide input on the map.
- Contact Your Representatives: Contact your congressional representatives to express your views on the map.
- Educate Yourself: Learn more about the principles of redistricting and the history of the process in California.
Conclusion: A Vital Tool for Democracy
The California congressional map is a powerful tool that shapes the state’s political landscape and the representation of its diverse population in the U.S. House of Representatives. While the redistricting process is often complex and contentious, it is a vital part of ensuring fair and equitable representation in a democratic society. By understanding the principles and processes involved, citizens can engage in the redistricting process and contribute to shaping a map that reflects the needs and interests of all Californians.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Shaping California’s Political Landscape: A Deep Dive into the Congressional Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!