Navigating the Tapestry of Latin America and the Caribbean: A Geographical Exploration
Related Articles: Navigating the Tapestry of Latin America and the Caribbean: A Geographical Exploration
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Tapestry of Latin America and the Caribbean: A Geographical Exploration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Tapestry of Latin America and the Caribbean: A Geographical Exploration

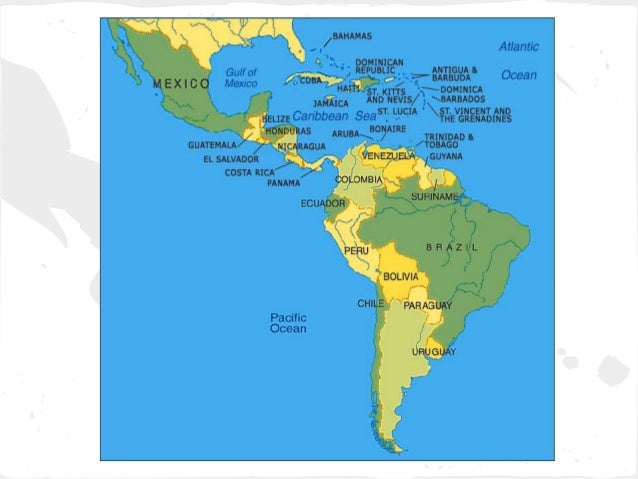
The Latin American and Caribbean region, often referred to as Latin America for brevity, is a vast and diverse tapestry of cultures, landscapes, and histories woven together by geographical proximity and shared experiences. Understanding the complexities of this region requires a nuanced approach, and a map serves as a crucial tool for navigating its intricacies.
A Region Defined by Diversity:
The Latin American and Caribbean map encompasses a sprawling expanse, stretching from the northernmost tip of Mexico to the southernmost point of Tierra del Fuego, encompassing over 20 independent nations. This geographical diversity translates into a kaleidoscope of landscapes, from the towering Andes Mountains to the Amazon rainforest, from the arid deserts of Chile to the lush Caribbean islands.
The Importance of Geographical Context:
The map reveals the region’s strategic location, bridging the North and South American continents, and acting as a crossroads between the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. This strategic position has historically shaped the region’s economic, political, and cultural development. It has facilitated trade and migration, influencing the region’s diverse cultural tapestry and the legacies of colonialism and globalization.
Key Geographical Features:
- The Andes Mountains: This formidable mountain range, running along the western edge of the continent, is a defining feature of Latin America. Its towering peaks, glaciers, and diverse ecosystems influence the region’s climate, biodiversity, and human settlement patterns.
- The Amazon Rainforest: This vast expanse of rainforest, covering much of Brazil and parts of several other countries, is a vital source of biodiversity and a crucial carbon sink. Its ecological importance extends beyond the region, impacting global climate and weather patterns.
- The Caribbean Sea: This warm, turquoise body of water, teeming with marine life, is home to numerous islands, each with its own unique history and culture. Its strategic location has made it a hub of trade and tourism, shaping the economies and identities of the islands.
- The Mesoamerican Region: This region, encompassing parts of Mexico, Central America, and the Caribbean, is home to ancient civilizations, vibrant cultures, and a rich history. Its diverse ecosystems, including rainforests, coastal plains, and volcanic mountains, support a wide range of biodiversity.
Understanding the Regional Landscape:
The Latin American and Caribbean map provides a visual framework for understanding the region’s diverse landscapes, ecosystems, and human settlements. It allows us to appreciate the geographical factors that have shaped the region’s history, culture, and development.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Q: What are the major geographic regions within Latin America and the Caribbean?
A: The region can be broadly divided into:
- Central America: Includes countries like Guatemala, Honduras, Nicaragua, Costa Rica, and Panama.
- The Caribbean: Comprises numerous islands, including Cuba, Puerto Rico, Jamaica, and the Dominican Republic, among others.
- South America: Includes countries like Brazil, Argentina, Colombia, Peru, Chile, and Venezuela, among others.
Q: What are the major rivers in Latin America and the Caribbean?
A: The region is home to several major rivers, including:
- The Amazon River: The largest river in the world by volume, flowing through Brazil and several other South American countries.
- The Orinoco River: A major river in Venezuela and Colombia.
- The Paraná River: A major river in Argentina, Brazil, and Paraguay.
- The Río de la Plata: An estuary formed by the confluence of the Paraná and Uruguay rivers.
Q: What are the major mountain ranges in Latin America and the Caribbean?
A: The region is home to several major mountain ranges, including:
- The Andes Mountains: The longest mountain range in the world, running along the western edge of South America.
- The Sierra Madre Occidental: A mountain range in western Mexico.
- The Sierra Madre Oriental: A mountain range in eastern Mexico.
- The Cordillera de la Costa: A mountain range in Venezuela.
Tips for Navigating the Latin American and Caribbean Map:
- Focus on the geographical features: Pay attention to the major rivers, mountain ranges, and bodies of water.
- Consider the political boundaries: Understand the location of different countries and their relationship to each other.
- Explore the regional diversity: Recognize the vast cultural and linguistic differences within the region.
- Use the map as a tool for learning: Use the map to research specific countries, cities, and landscapes.
Conclusion:
The Latin American and Caribbean map is not merely a collection of lines and borders, but a visual representation of a dynamic and complex region. It serves as a gateway to understanding the region’s rich history, diverse cultures, and unique landscapes. By studying the map, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the geographical factors that have shaped the region’s development and the challenges and opportunities it faces today. It allows us to navigate the tapestry of Latin America and the Caribbean, appreciating its intricate patterns and recognizing its enduring significance in the global context.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Tapestry of Latin America and the Caribbean: A Geographical Exploration. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!