Navigating the North: A Comprehensive Look at the Map of Northern European Countries
Related Articles: Navigating the North: A Comprehensive Look at the Map of Northern European Countries
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the North: A Comprehensive Look at the Map of Northern European Countries. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the North: A Comprehensive Look at the Map of Northern European Countries

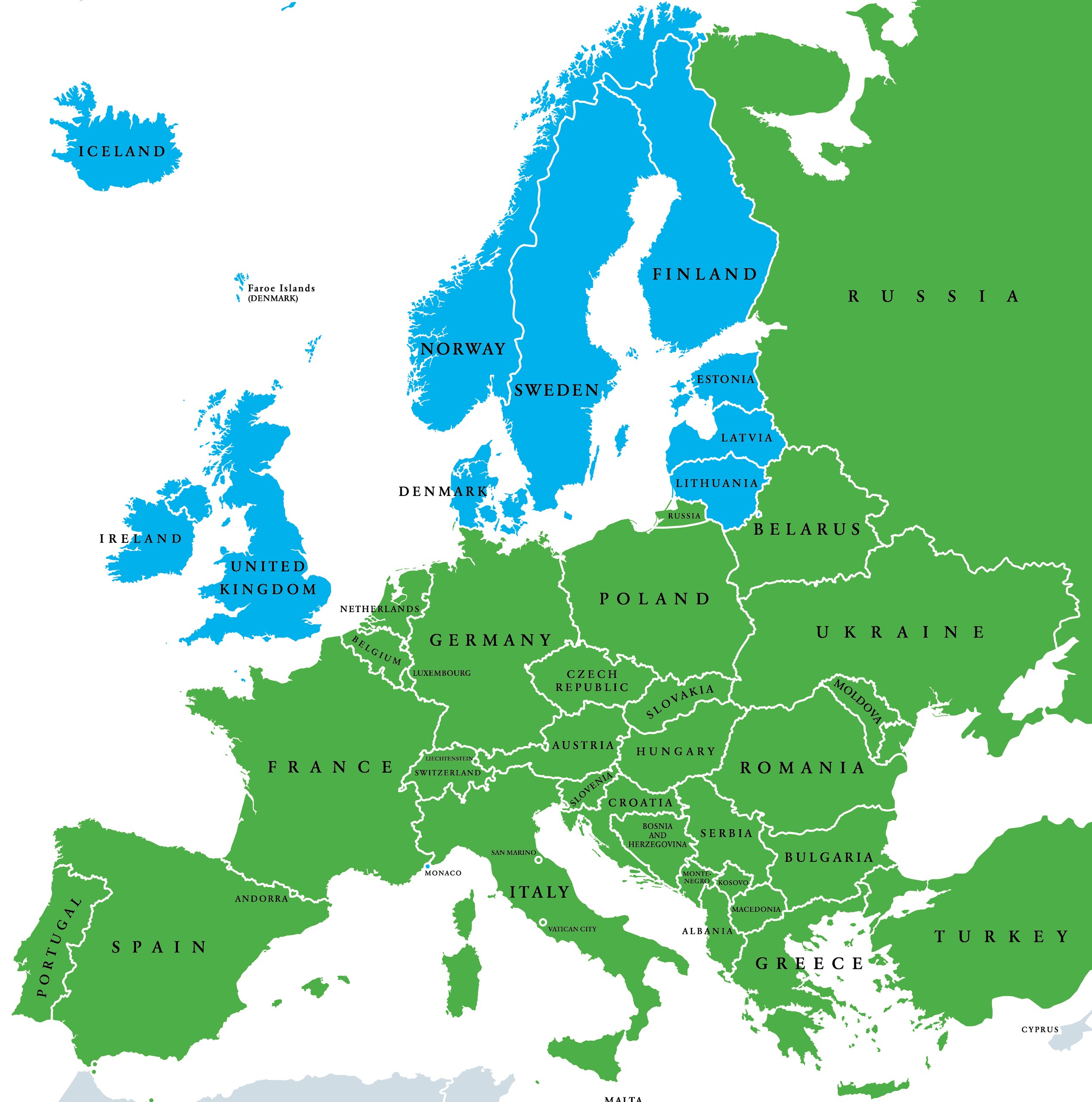
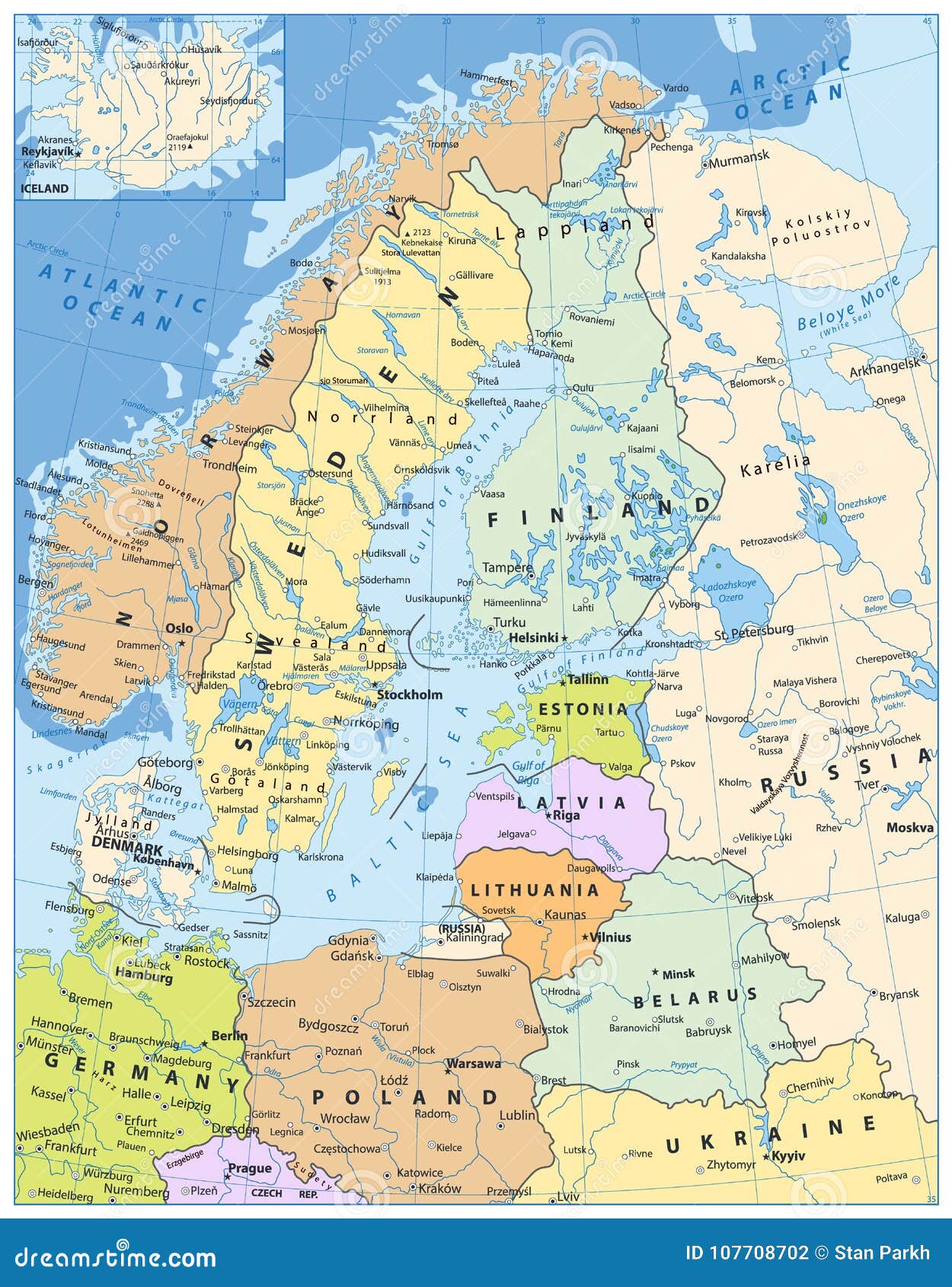
Northern Europe, a region often associated with breathtaking landscapes, vibrant culture, and a strong sense of identity, is comprised of a unique collection of countries. Understanding the geographical layout of these nations is essential for appreciating their historical development, cultural nuances, and economic interconnectedness. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the map of Northern Europe, highlighting its key features and the insights it offers into the region’s complex tapestry.
Defining the Boundaries: Geographical and Cultural Considerations
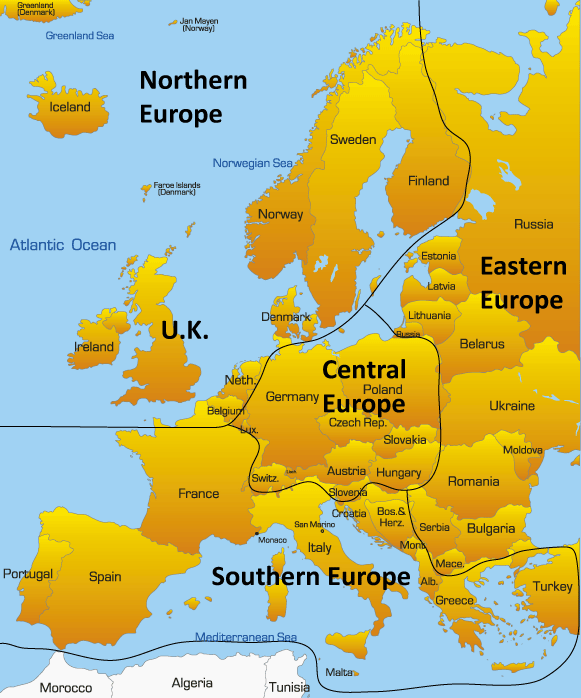
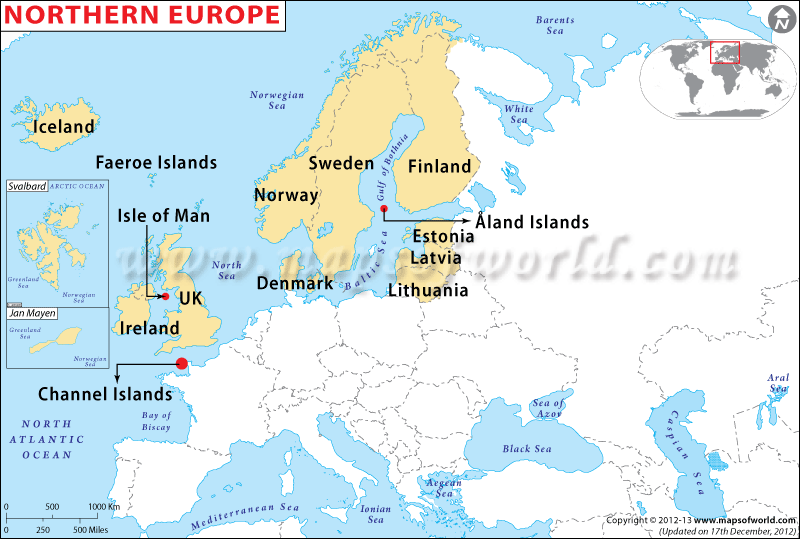
Defining the exact boundaries of Northern Europe can be a nuanced exercise, as there is no single, universally accepted definition. Geographically, the region is often considered to encompass the Scandinavian Peninsula (Norway, Sweden), Finland, Denmark, Iceland, and the three Baltic states (Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania). However, the inclusion of certain countries like Russia (specifically its northwestern region) or the United Kingdom (particularly Scotland) can be debated depending on the specific criteria being employed.
Cultural factors also play a significant role in shaping the perception of Northern Europe. Shared historical experiences, linguistic similarities, and a common cultural heritage have fostered a sense of collective identity amongst the Scandinavian countries, while the Baltic states, despite their proximity, have distinct cultural influences rooted in their history as part of the former Soviet Union.
Navigating the Map: Key Features and Insights
The map of Northern Europe reveals several key features that offer valuable insights into the region’s history, geography, and cultural dynamics:
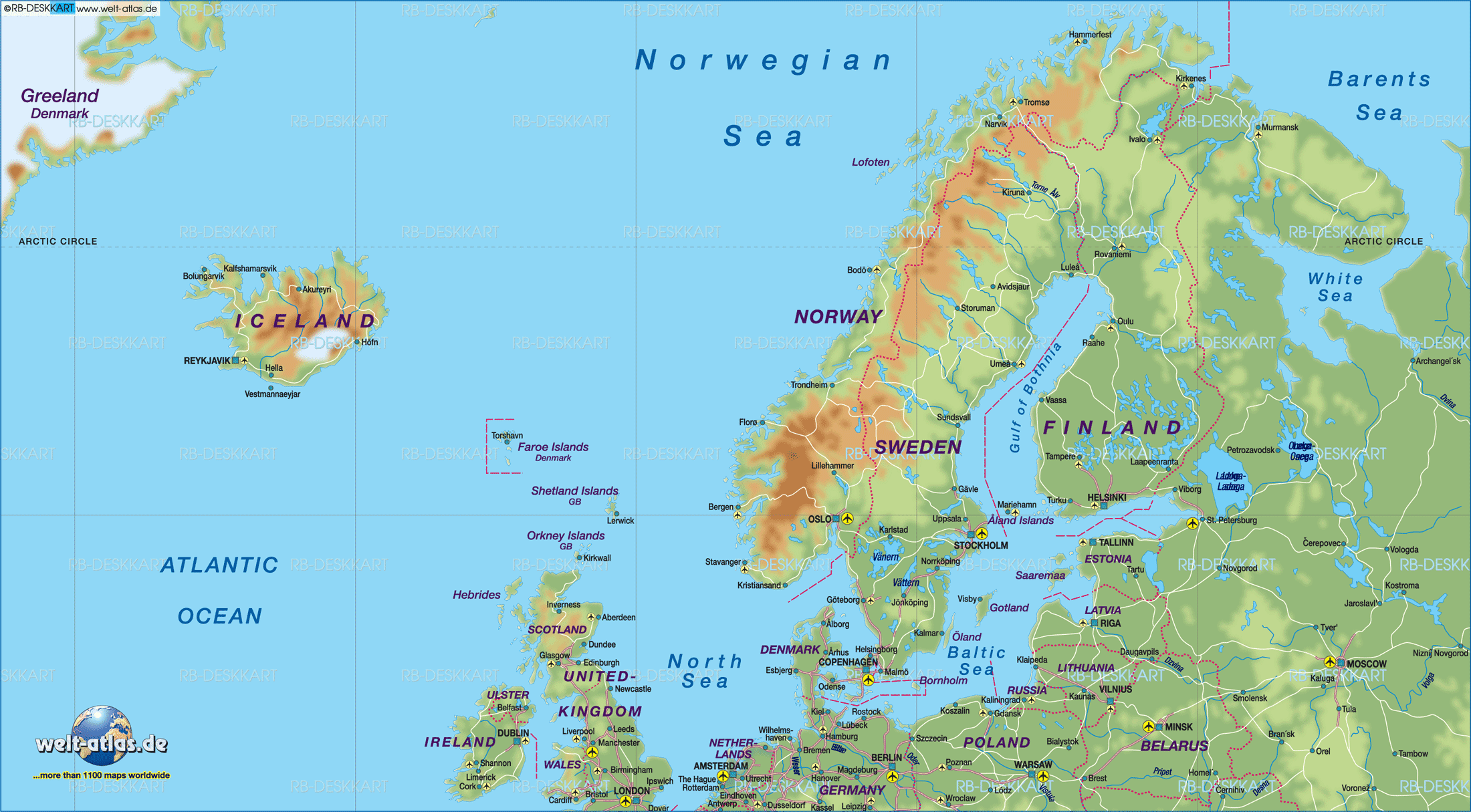
1. The Scandinavian Peninsula: A Land of Fjords and Mountains
Dominating the map is the Scandinavian Peninsula, home to Norway and Sweden. This vast landmass is characterized by its rugged terrain, featuring towering mountains, deep fjords, and vast forests. This geography has shaped the history and culture of these nations, influencing their economies, traditions, and lifestyles. Norway’s dramatic coastline and its rich fishing industry are testaments to its maritime heritage, while Sweden’s vast forests have historically played a significant role in its forestry and timber industries.
2. The Baltic Sea: A Vital Crossroads
The Baltic Sea, a shallow inland sea, acts as a vital link between the Northern European countries, facilitating trade and communication. It has historically been a significant waterway for maritime trade, connecting the region to other parts of Europe and beyond. The presence of numerous islands and archipelagos within the Baltic Sea adds further complexity to its geographical layout.
3. The Islands of Isolation and Innovation
Iceland, located in the North Atlantic Ocean, stands apart as a unique island nation. Its volcanic landscape and geothermal activity have shaped its distinctive ecosystem and culture. Denmark, while geographically distinct from the Scandinavian Peninsula, holds a unique position as the gateway to the Baltic Sea, connecting the region to the rest of Europe through its strategic location.
4. The Baltic States: A Bridge Between East and West
Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania, situated on the eastern edge of the Baltic Sea, represent a bridge between Eastern and Western Europe. Their history as part of the Soviet Union has left a lasting imprint on their culture and economy. However, they are also actively embracing their European identity, seeking closer integration with the European Union.
5. The Importance of Water: Rivers, Lakes, and Waterways
Northern Europe is characterized by a vast network of rivers, lakes, and waterways, playing a crucial role in its transportation, trade, and cultural development. The mighty Volga River, for instance, acts as a vital artery connecting Russia to the Baltic Sea. The numerous lakes scattered across Finland and Sweden offer stunning natural beauty and recreational opportunities.
Exploring the Benefits: Understanding the Map’s Significance
Beyond its geographical significance, the map of Northern Europe holds immense value in understanding the region’s cultural, economic, and political dynamics. It provides a visual framework for:
1. Understanding Historical Connections and Conflicts
The map reveals the historical relationships between the countries of Northern Europe, highlighting their shared past, their periods of conflict, and their evolving alliances. The Vikings, originating from Scandinavia, left a lasting mark on the history of the region, influencing its culture, language, and trade networks. The map also reveals the impact of the Cold War, with the Baltic states caught between the Soviet Union and the West.
2. Appreciating Cultural Diversity and Shared Heritage
The map helps to appreciate the cultural diversity within Northern Europe. While the region shares a common Nordic heritage, each country possesses its own distinct traditions, languages, and cultural expressions. Understanding the geographical distribution of these cultural elements provides insights into their historical development and their contemporary influence.
3. Recognizing Economic Interdependence and Cooperation
The map highlights the economic interconnectedness of the Northern European countries. Their shared access to the Baltic Sea, their reliance on trade, and their membership in the European Union have fostered strong economic ties. The map also reveals the importance of natural resources, such as timber, fish, and energy, in shaping their economic development.
4. Navigating Political Landscapes and International Relations
The map provides a visual representation of the political landscape of Northern Europe, showcasing the diverse political systems, the role of international organizations, and the complex web of alliances and partnerships that characterize the region. Understanding the geographical distribution of power and influence is crucial for navigating the intricacies of international relations in the region.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What are the most important cities in Northern Europe?
A: Some of the most significant cities in Northern Europe include:
- Stockholm (Sweden): The capital of Sweden, known for its stunning archipelago, rich history, and vibrant cultural scene.
- Oslo (Norway): The capital of Norway, renowned for its beautiful fjords, its thriving arts scene, and its role as a global hub for shipping and maritime industries.
- Copenhagen (Denmark): The capital of Denmark, famous for its charming canals, its innovative design, and its world-class museums.
- Helsinki (Finland): The capital of Finland, known for its unique blend of Nordic architecture, its vibrant design scene, and its proximity to the Baltic Sea.
- Riga (Latvia): The capital of Latvia, a historic city with stunning Art Nouveau architecture, a rich cultural heritage, and a growing reputation as a technological hub.
- Tallinn (Estonia): The capital of Estonia, a medieval city with well-preserved fortifications, a thriving startup ecosystem, and a growing international presence.
Q2: What are the main languages spoken in Northern Europe?
A: The dominant languages spoken in Northern Europe include:
- Swedish: The official language of Sweden, also spoken in parts of Finland and Norway.
- Norwegian: The official language of Norway, with two main dialects: Bokmål and Nynorsk.
- Danish: The official language of Denmark, also spoken in parts of southern Sweden.
- Finnish: The official language of Finland, a unique language belonging to the Finno-Ugric language family.
- Estonian: The official language of Estonia, closely related to Finnish.
- Latvian: The official language of Latvia, a Baltic language with its own unique grammatical features.
- Lithuanian: The official language of Lithuania, the only surviving Baltic language, closely related to Latvian.
- Icelandic: The official language of Iceland, a North Germanic language with a strong emphasis on preserving its ancient roots.
Q3: What are some of the most popular tourist destinations in Northern Europe?
A: Northern Europe is a popular tourist destination, offering a wide range of attractions, including:
- The Northern Lights (Aurora Borealis): A breathtaking natural phenomenon visible in the night sky of Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland.
- The Fjords of Norway: Dramatic and awe-inspiring waterways carved by glaciers, offering stunning scenery and opportunities for hiking, kayaking, and cruising.
- The Stockholm Archipelago (Sweden): A vast network of islands offering breathtaking coastal views, charming villages, and opportunities for boating, swimming, and exploring nature.
- The Baltic Sea Coast (Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania): A beautiful stretch of coastline with sandy beaches, charming seaside towns, and opportunities for exploring the region’s rich history and culture.
- The Icelandic Highlands (Iceland): A rugged and dramatic landscape with glaciers, volcanoes, geothermal hot springs, and stunning waterfalls.
- The Danish Islands (Denmark): A chain of islands offering picturesque landscapes, quaint villages, and opportunities for exploring the region’s rich maritime history.
Tips for Navigating the Map of Northern Europe
- Consider the Scale: Be mindful of the scale of the map to understand the relative distances between countries and cities.
- Use a Map with Key Features: Look for maps that highlight important geographical features, such as mountains, rivers, lakes, and coastlines.
- Explore Online Resources: Utilize interactive online maps that provide detailed information about specific locations, historical sites, and cultural attractions.
- Research Specific Interests: Tailor your exploration to your individual interests, whether it’s history, nature, culture, or food.
- Plan Your Itinerary: Consider the time of year, transportation options, and potential visa requirements when planning your trip.
Conclusion: A Region of Rich History and Enduring Identity
The map of Northern Europe serves as a powerful visual tool for understanding the region’s complex tapestry of history, culture, and geography. It reveals the interconnectedness of these nations, their shared experiences, and their distinct identities. By understanding the geographical layout of Northern Europe, we gain a deeper appreciation for its unique character, its enduring contributions to world history, and its vibrant cultural landscape.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the North: A Comprehensive Look at the Map of Northern European Countries. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!