Navigating the Landscape of Iteration: A Comprehensive Guide to foreach and map
Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape of Iteration: A Comprehensive Guide to foreach and map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Landscape of Iteration: A Comprehensive Guide to foreach and map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape of Iteration: A Comprehensive Guide to foreach and map
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the Landscape of Iteration: A Comprehensive Guide to foreach and map
- 3.1 The Foundation of Iteration: foreach
- 3.2 The Power of Transformation: map
- 3.3 Choosing the Right Tool for the Job
- 3.4 FAQs: Demystifying foreach and map
- 3.5 Tips for Effective Usage
- 3.6 Conclusion: Mastering the Art of Iteration
- 4 Closure
Navigating the Landscape of Iteration: A Comprehensive Guide to foreach and map
In the realm of programming, iterating through collections of data is a fundamental operation. Two popular methods, foreach and map, stand out as essential tools for developers. Understanding their nuances and choosing the right approach is crucial for efficient and elegant code. This comprehensive guide delves into the depths of foreach and map, exploring their distinct characteristics, use cases, and the advantages each offers.
The Foundation of Iteration: foreach
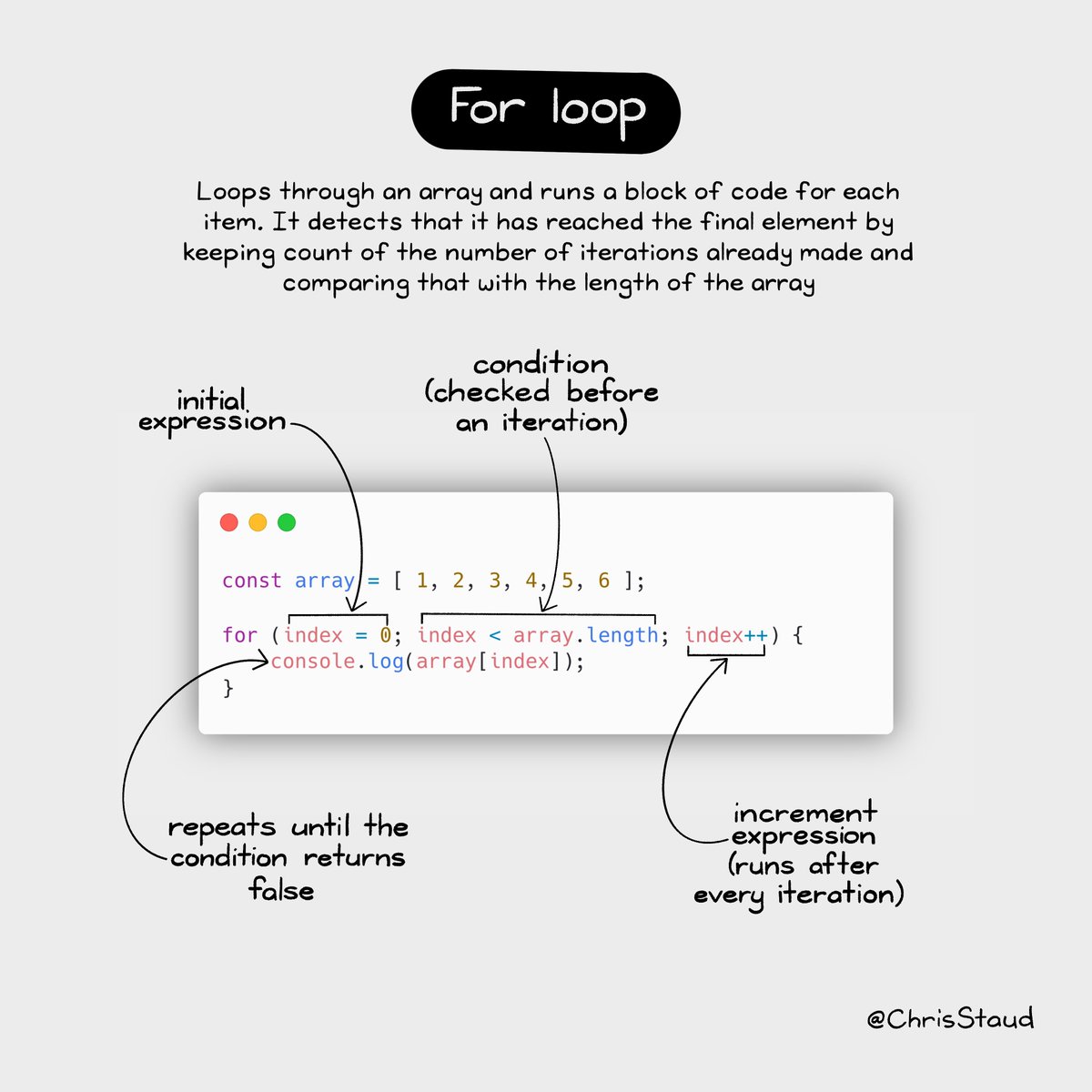
foreach, often known as a "for each" loop, provides a straightforward way to traverse elements within a collection. It iterates over each element in sequence, providing access to the individual item during each iteration. Its simplicity and readability make it a go-to choice for scenarios where the primary goal is to process each element in a collection.
Syntax and Structure:
The syntax of foreach varies slightly depending on the programming language, but the core concept remains consistent. It typically involves declaring an iteration variable, specifying the collection to iterate over, and defining the code block to be executed for each element.
Example (PHP):
$fruits = ["apple", "banana", "orange"];
foreach ($fruits as $fruit)
echo $fruit . "<br>";
This code snippet iterates over the $fruits array, printing each fruit name on a separate line.
Benefits of foreach:
-
Simplicity: The syntax of
foreachis straightforward and easy to understand, making it ideal for beginners. -
Readability: The structure of
foreachclearly reflects the intent of iterating over a collection, enhancing code readability. - Direct Access: It provides direct access to each element during iteration, allowing for individual manipulation or processing.
Limitations of foreach:
-
Limited Transformation:
foreachprimarily focuses on iterating through elements, not on transforming them into new data structures. -
Mutable Data:
foreachoperates on the original collection, potentially modifying it during iteration. This can lead to unintended consequences in scenarios where immutability is desired.
The Power of Transformation: map
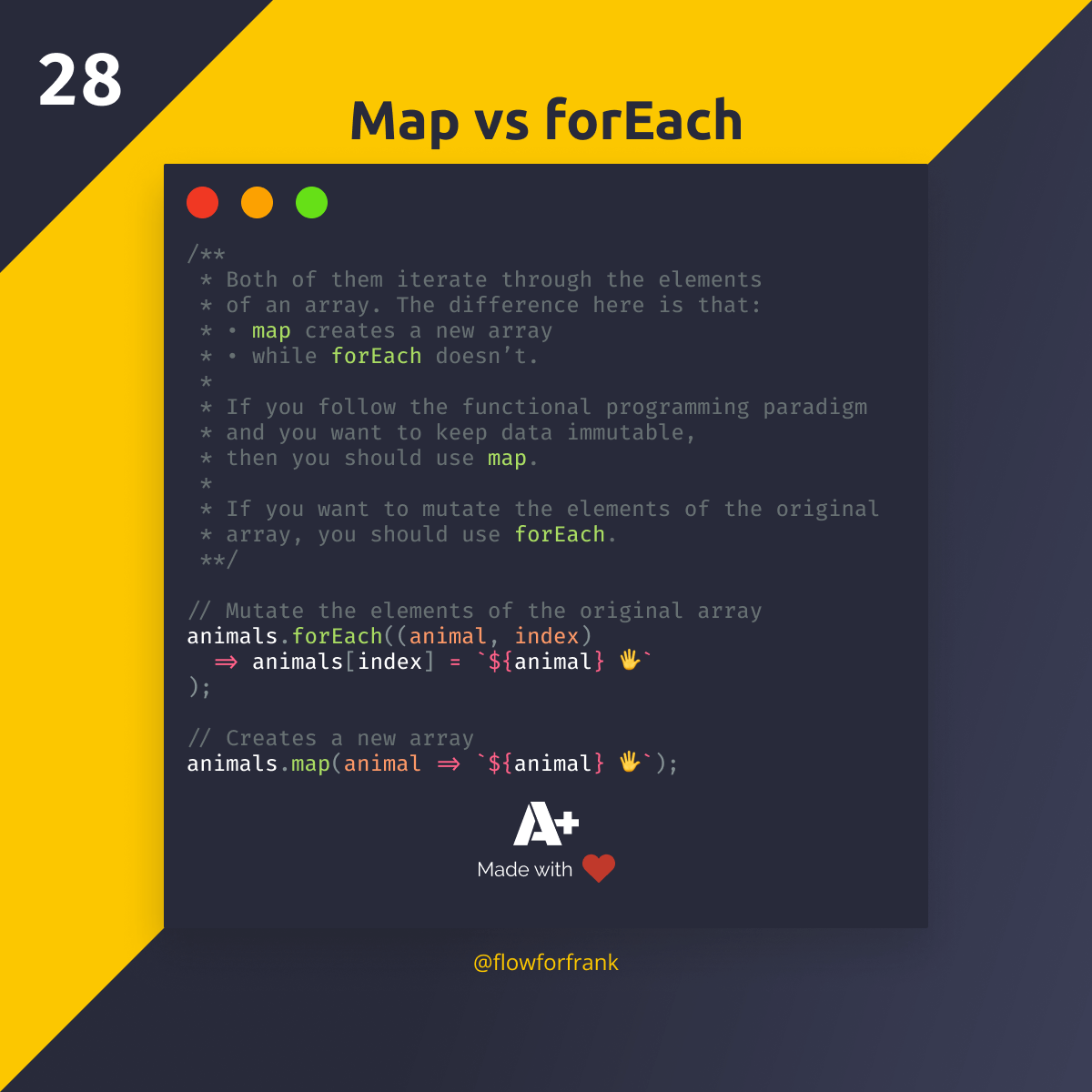
map, a higher-order function, takes a collection and a transformation function as input, applying the function to each element and generating a new collection with the transformed results. Its primary focus lies in creating a new collection based on the original, offering a powerful tool for data manipulation and processing.
Syntax and Structure:
The syntax of map can vary slightly depending on the programming language, but it generally involves passing the collection and the transformation function as arguments.
Example (JavaScript):
const numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
const squaredNumbers = numbers.map(number => number * number);
console.log(squaredNumbers); // Output: [1, 4, 9, 16, 25]This code snippet squares each element in the numbers array using the map function, creating a new array squaredNumbers containing the transformed results.
Benefits of map:
-
Transformation:
mapexcels at transforming elements within a collection, creating a new collection with the desired modifications. -
Immutability:
mapoperates on the original collection without modifying it, preserving the integrity of the original data. - Functional Programming: It aligns with functional programming principles, promoting code that is more declarative, reusable, and easier to test.
Limitations of map:
-
Complexity: The syntax of
mapcan be more complex thanforeach, potentially requiring a deeper understanding of higher-order functions. -
Limited Control:
mapoffers less control over the iteration process compared toforeach, as it relies on the transformation function for specific actions.
Choosing the Right Tool for the Job
The choice between foreach and map hinges on the specific task at hand. Here’s a breakdown of scenarios where each method shines:
When to Use foreach:
-
Simple Iteration: When the primary goal is to process each element in a collection without transforming it,
foreachis the ideal choice. -
Modifying Existing Data: If the task involves modifying the original collection during iteration,
foreachprovides direct access to elements for manipulation. -
Readability and Clarity: When prioritizing code readability and simplicity,
foreachoffers a straightforward approach.
When to Use map:
-
Data Transformation: When the goal is to create a new collection based on a transformation of the original data,
mapis the preferred method. -
Immutability: If maintaining the integrity of the original collection is crucial,
mapensures that no modifications are made to the source data. -
Functional Programming: When adhering to functional programming principles,
mappromotes a declarative and reusable coding style.
FAQs: Demystifying foreach and map
1. Can foreach be used to transform data?
While foreach does not directly provide transformation capabilities, it can be used to achieve transformations by modifying the original collection within the loop. However, this approach can be less efficient and less readable than using map for data transformation.
2. Can map be used to iterate over a collection without transforming it?
While map can be used to iterate over a collection, it’s not its primary purpose. It’s more efficient and readable to use foreach when the goal is simply to iterate over elements without applying transformations.
3. What are the performance implications of using foreach vs. map?
In most cases, the performance difference between foreach and map is negligible. However, map can be slightly less efficient in scenarios where the transformation function is complex or involves extensive computations.
4. Can foreach and map be used together?
Yes, foreach and map can be used together in scenarios where both iteration and transformation are required. For example, you can use map to transform elements and then use foreach to process the transformed elements individually.
Tips for Effective Usage
- Prioritize Readability: Choose the method that best reflects the intent of the code and enhances its readability.
-
Consider Immutability: If preserving the original collection is important,
mapis the preferred choice. -
Use
mapfor Complex Transformations: For intricate data transformations,mapprovides a more structured and efficient approach. -
Optimize for Performance: In scenarios where performance is critical, consider the computational overhead of the transformation function when choosing between
foreachandmap.
Conclusion: Mastering the Art of Iteration
foreach and map are powerful tools for navigating the complexities of data iteration and transformation. Understanding their strengths and limitations empowers developers to choose the most appropriate method for each task, leading to efficient, readable, and maintainable code. By mastering these techniques, developers can unlock the full potential of data manipulation and processing, paving the way for elegant and effective solutions in the world of software development.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Landscape of Iteration: A Comprehensive Guide to foreach and map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!