Navigating the Frozen Frontier: A Guide to Canada’s Ice Roads
Related Articles: Navigating the Frozen Frontier: A Guide to Canada’s Ice Roads
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Frozen Frontier: A Guide to Canada’s Ice Roads. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Frozen Frontier: A Guide to Canada’s Ice Roads
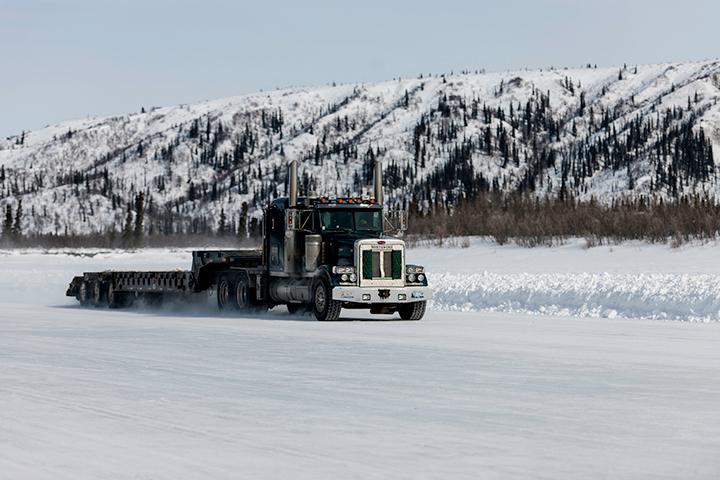

Canada’s vast and unforgiving landscape is punctuated by frozen waterways that, during the winter months, transform into temporary arteries of transportation. These ice roads, a testament to human ingenuity and adaptation, provide crucial access to remote communities and resource extraction sites, bridging the gap between isolation and connection. This article delves into the intricate world of Canada’s ice roads, examining their construction, operation, safety, and significance within the Canadian context.
A Frozen Canvas: The Construction and Maintenance of Ice Roads
The creation of an ice road is a complex process that relies on the interplay of nature and human intervention. The foundation for these temporary roadways is laid by winter’s grip, as temperatures plummet and lakes and rivers freeze over. The thickness of the ice, a crucial factor determining the road’s capacity, is monitored closely by engineers and experts.
Once a suitable ice thickness is achieved, typically ranging from 40 to 60 centimeters, construction begins. This involves clearing snow, grading the ice surface, and reinforcing weak spots. Specialized equipment, including heavy-duty graders and ice augers, are employed to sculpt the roadbed, ensuring a smooth and stable surface.
Maintaining these ice roads is an ongoing endeavor, requiring constant monitoring and adaptation. Regular inspections are conducted to assess the ice thickness and identify any potential weaknesses. Snow removal, ice patching, and the deployment of warning signs are essential to ensure the safety of travelers.
Navigating the Ice: The Operation and Regulation of Ice Roads
The operation of ice roads is governed by strict regulations and guidelines, ensuring safety and responsible use. Access is typically granted to authorized vehicles and individuals, with weight restrictions and speed limits enforced. Designated routes and designated areas for loading and unloading goods are established to minimize disruption and maintain the integrity of the ice.
The duration of an ice road’s operation is dictated by the unpredictable forces of nature. As temperatures rise and the ice begins to thaw, the road’s integrity is compromised. The closure of an ice road is typically announced with ample warning, allowing for the safe transport of remaining goods and personnel.
The Vital Lifeline: The Significance of Ice Roads in Canada
Ice roads play a vital role in connecting remote communities and resource extraction sites in Canada, particularly in the northern territories. They provide a cost-effective and efficient means of transporting essential goods, supplies, and equipment, facilitating economic activity and improving the quality of life for residents.
Benefits of Ice Roads:
- Economic Development: Ice roads enable the extraction and transportation of natural resources, such as diamonds, gold, and oil, contributing to the Canadian economy.
- Community Access: They provide essential access to remote communities, facilitating the delivery of goods, services, and medical supplies, enhancing the well-being of residents.
- Infrastructure Development: Ice roads serve as temporary infrastructure, allowing for the construction and maintenance of permanent infrastructure, such as pipelines and power lines.
- Environmental Considerations: Ice roads offer a less disruptive alternative to conventional road construction, minimizing environmental impact in sensitive ecosystems.
Safety and Sustainability: Challenges and Considerations
While offering significant advantages, ice roads present unique challenges and risks.
Safety Concerns:
- Ice Conditions: The unpredictable nature of ice can lead to unexpected changes in thickness and stability, posing risks to vehicles and travelers.
- Weather Conditions: Extreme weather events, such as blizzards and sudden thaws, can render ice roads impassable and dangerous.
- Wildlife Encounters: Wildlife, such as caribou and polar bears, can pose a threat to travelers, requiring caution and awareness.
Sustainability Considerations:
- Environmental Impact: Construction and operation of ice roads can disrupt sensitive ecosystems and contribute to greenhouse gas emissions.
- Alternative Transportation: The development of alternative transportation options, such as all-weather roads and air transport, can reduce reliance on ice roads and mitigate environmental impact.
FAQs about Canada’s Ice Roads:
1. What is the typical length of an ice road season?
The ice road season typically lasts from late December to early April, depending on the location and weather conditions.
2. Are ice roads safe for all types of vehicles?
No, ice roads are designed for specific types of vehicles with appropriate weight and tire configurations. Heavy-duty trucks and specialized vehicles are typically used for transportation.
3. What are the risks associated with traveling on ice roads?
Risks include unexpected changes in ice thickness, sudden thaws, weather events, wildlife encounters, and vehicle breakdowns.
4. How are ice roads maintained?
Maintenance includes regular inspections, snow removal, ice patching, and the deployment of warning signs.
5. Are ice roads regulated?
Yes, ice roads are subject to strict regulations and guidelines, including weight restrictions, speed limits, and designated routes.
6. How are ice roads monitored for safety?
Ice roads are monitored by engineers and experts who conduct regular inspections and assess ice thickness and stability.
7. What is the environmental impact of ice roads?
Ice roads can have a temporary impact on sensitive ecosystems, but they are generally considered a less disruptive alternative to conventional road construction.
Tips for Traveling on Ice Roads:
- Plan Your Trip: Research the route, check weather conditions, and obtain permits if required.
- Travel with a Companion: Always travel with another vehicle or individual for safety.
- Maintain Vehicle Condition: Ensure your vehicle is in good working order and equipped for winter conditions.
- Be Aware of Ice Conditions: Pay attention to ice thickness and stability, and avoid areas with cracks or open water.
- Follow Regulations: Adhere to weight restrictions, speed limits, and designated routes.
- Stay Informed: Monitor weather conditions and road closures.
- Be Prepared for Emergencies: Carry essential supplies, including food, water, warm clothing, and a first-aid kit.
Conclusion:
Canada’s ice roads are a testament to human ingenuity and adaptation, providing vital access to remote communities and resource extraction sites. While they present unique challenges and risks, their significance in connecting people and facilitating economic development cannot be overstated. As technology advances and environmental considerations evolve, the future of ice roads will likely see a shift towards more sustainable and efficient solutions, ensuring their continued role in shaping the Canadian landscape.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Frozen Frontier: A Guide to Canada’s Ice Roads. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!