Navigating the Digital Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at Cyber Threat Maps
Related Articles: Navigating the Digital Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at Cyber Threat Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Digital Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at Cyber Threat Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the Digital Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at Cyber Threat Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the Digital Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at Cyber Threat Maps
- 3.1 Understanding the Concept: Mapping the Digital Battlefield
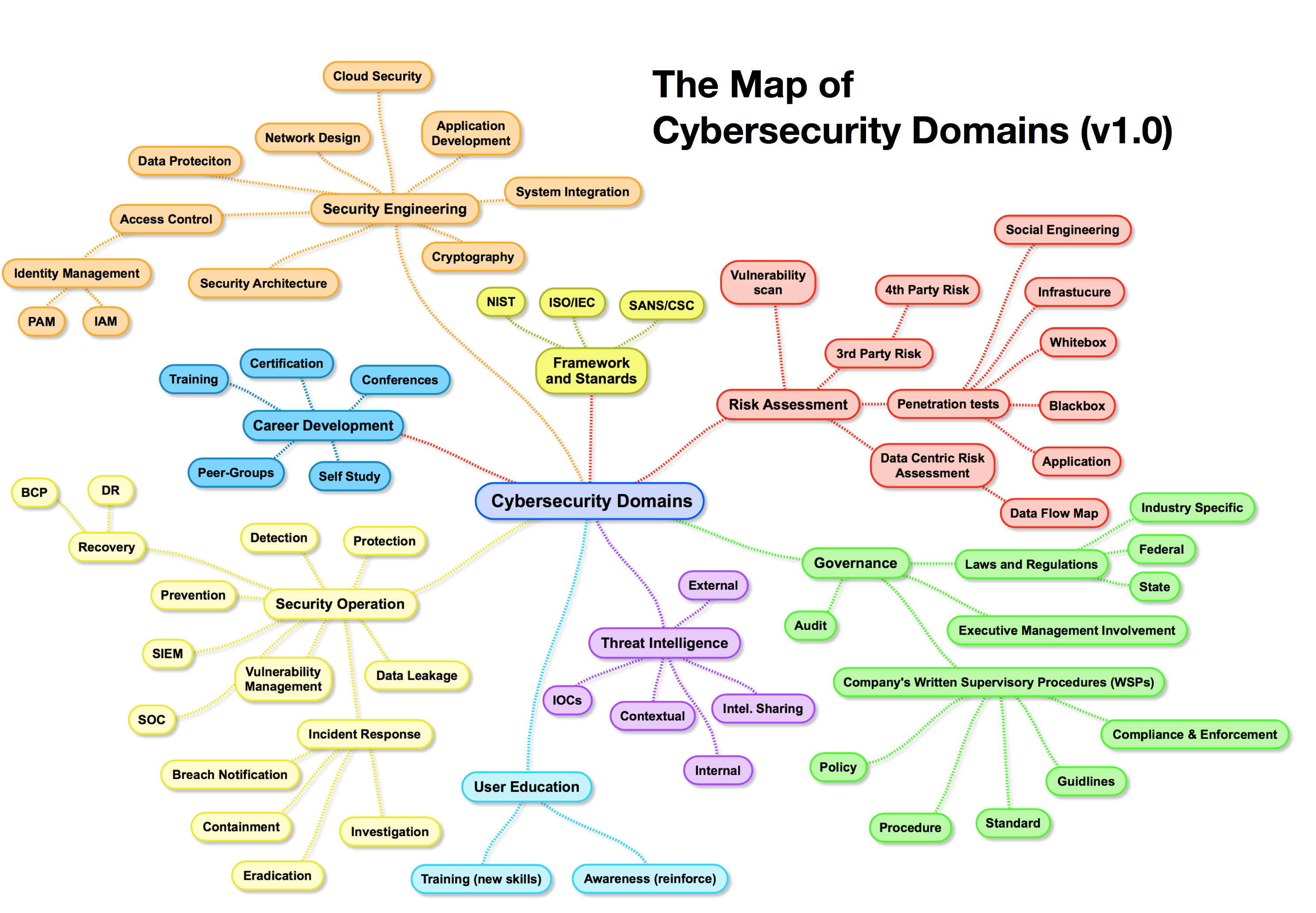
- 3.2 Key Components of a Cyber Threat Map
- 3.3 The Value of Cyber Threat Maps: A Strategic Advantage
- 3.4 FAQs about Cyber Threat Maps
- 3.5 Tips for Effective Use of Cyber Threat Maps
- 3.6 Conclusion: A Vital Tool for Navigating the Digital Landscape
- 4 Closure
Navigating the Digital Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at Cyber Threat Maps

The digital world is a vast and ever-evolving landscape, teeming with opportunities but also fraught with hidden dangers. As our reliance on technology grows, so too does the potential for cyberattacks. To navigate this complex terrain effectively, organizations and individuals alike need a clear understanding of the threats they face. This is where cyber threat maps come into play.
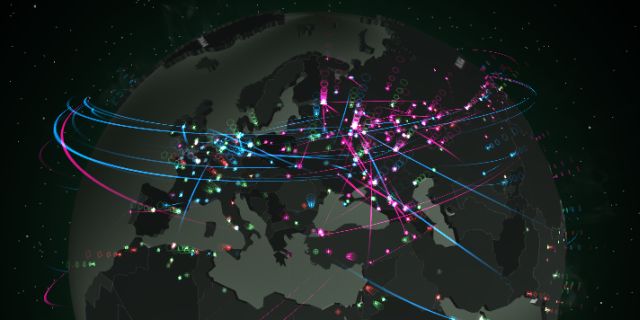
Understanding the Concept: Mapping the Digital Battlefield
A cyber threat map is a visual representation of the evolving landscape of cyber threats. It serves as a dynamic tool for understanding the current state of cybercrime, identifying emerging trends, and predicting potential future attacks. These maps are often interactive, allowing users to explore various threat categories, geographical locations, attack vectors, and associated actors.
Key Components of a Cyber Threat Map
1. Threat Actors: These are the individuals or groups responsible for carrying out cyberattacks. This category encompasses various entities, from nation-state-sponsored hackers to organized criminal groups, hacktivists, and lone wolves. Understanding the motivations, capabilities, and tactics of different threat actors is crucial for developing effective mitigation strategies.
2. Attack Vectors: This refers to the methods used by attackers to gain access to systems and data. Common attack vectors include phishing emails, malware, social engineering, exploiting vulnerabilities in software, and denial-of-service attacks. Identifying the most prevalent attack vectors allows organizations to prioritize their security measures.
3. Target Sectors: Cyberattacks are not indiscriminate. They often target specific industries or sectors, such as finance, healthcare, energy, and government. Understanding the vulnerabilities and critical assets within these sectors helps organizations develop tailored security strategies.
4. Geographical Distribution: Cyberattacks are not confined to specific geographical regions. They can originate from anywhere in the world, making it essential to understand the global landscape of cybercrime. Threat maps often include data on the origin of attacks, the geographical distribution of targeted organizations, and the prevalence of cybercrime in different regions.
5. Threat Intelligence: Cyber threat maps integrate real-time data and intelligence from various sources, including security researchers, government agencies, and private companies. This information is vital for staying ahead of emerging threats and adapting security measures accordingly.
The Value of Cyber Threat Maps: A Strategic Advantage
Cyber threat maps offer several significant benefits for organizations and individuals:
1. Enhanced Situational Awareness: By providing a comprehensive overview of the threat landscape, cyber threat maps empower organizations to make informed decisions regarding their security posture. They can identify the most pressing threats, prioritize resources, and allocate budgets strategically.
2. Proactive Security Measures: Threat maps facilitate proactive security measures by highlighting potential vulnerabilities and attack vectors. This allows organizations to implement preventive controls, patch software vulnerabilities, and train employees on cybersecurity best practices before an attack occurs.
3. Effective Incident Response: In the event of a cyberattack, cyber threat maps can assist in the incident response process. They provide valuable insights into the nature of the attack, the attackers involved, and potential mitigation strategies. This information allows security teams to respond quickly and effectively, minimizing damage and downtime.
4. Improved Collaboration: Cyber threat maps foster collaboration between different stakeholders, including security teams, IT departments, and business leaders. By sharing threat intelligence and insights, organizations can develop a more comprehensive and coordinated approach to cybersecurity.
5. Continuous Monitoring and Adaptation: The ever-evolving nature of cyber threats necessitates continuous monitoring and adaptation. Cyber threat maps provide a dynamic platform for tracking emerging trends, identifying new attack vectors, and adapting security measures accordingly.
FAQs about Cyber Threat Maps
1. What are the different types of cyber threat maps available?
There are various types of cyber threat maps available, catering to specific needs and audiences. These include:
- Global Threat Maps: These maps provide a broad overview of cyber threats worldwide, highlighting major trends, attack vectors, and geographical distribution.
- Sector-Specific Threat Maps: These maps focus on specific industries or sectors, such as finance, healthcare, or energy, providing insights into the unique threats and vulnerabilities within those sectors.
- Regional Threat Maps: These maps concentrate on specific geographical regions, providing localized threat intelligence and insights.
- Organization-Specific Threat Maps: These maps are tailored to individual organizations, providing customized threat intelligence based on the organization’s specific assets, vulnerabilities, and risk profile.
2. How can I access and utilize cyber threat maps?
Cyber threat maps are available from various sources, including:
- Government Agencies: Agencies like the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) in the United States and the National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC) in the United Kingdom provide publicly available threat maps.
- Private Companies: Security vendors and research firms often offer their own threat maps, often with more detailed information and insights.
- Open-Source Platforms: Several open-source platforms, such as the ThreatConnect platform, allow users to access and contribute to threat intelligence.
3. What are the limitations of cyber threat maps?
While cyber threat maps offer valuable insights, they have limitations:
- Data Accuracy and Completeness: The accuracy and completeness of threat data can vary depending on the source and methodology used.
- Dynamic Nature of Threats: The cyber threat landscape is constantly evolving, making it challenging to keep threat maps updated in real-time.
- Focus on Known Threats: Threat maps primarily focus on known threats and vulnerabilities, potentially overlooking emerging threats or zero-day exploits.
- Interpretation and Analysis: Interpreting and analyzing threat data from cyber maps requires expertise and understanding of cybersecurity concepts.
Tips for Effective Use of Cyber Threat Maps
- Identify your specific needs and requirements: Determine the type of information you need from a threat map, such as global trends, sector-specific threats, or organization-specific vulnerabilities.
- Choose reliable and reputable sources: Select threat maps from trusted sources, such as government agencies, reputable security vendors, or research firms.
- Integrate threat map data with other security tools: Combine threat map insights with other security tools and processes, such as vulnerability scanning, incident response, and employee training.
- Continuously monitor and adapt: Regularly review threat maps to stay updated on emerging trends and adapt security measures accordingly.
- Collaborate with other stakeholders: Share threat intelligence and insights with other departments and stakeholders within your organization.
Conclusion: A Vital Tool for Navigating the Digital Landscape
Cyber threat maps are a vital tool for navigating the complex and ever-evolving digital landscape. They provide a comprehensive understanding of the threat landscape, empower organizations to make informed security decisions, and facilitate proactive mitigation strategies. By leveraging the insights offered by cyber threat maps, organizations can enhance their cybersecurity posture, protect their critical assets, and navigate the digital world with greater confidence.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Digital Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at Cyber Threat Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!