Mapping the Digital Underbelly: A Comprehensive Look at Hacker Networks
Related Articles: Mapping the Digital Underbelly: A Comprehensive Look at Hacker Networks
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Mapping the Digital Underbelly: A Comprehensive Look at Hacker Networks. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping the Digital Underbelly: A Comprehensive Look at Hacker Networks

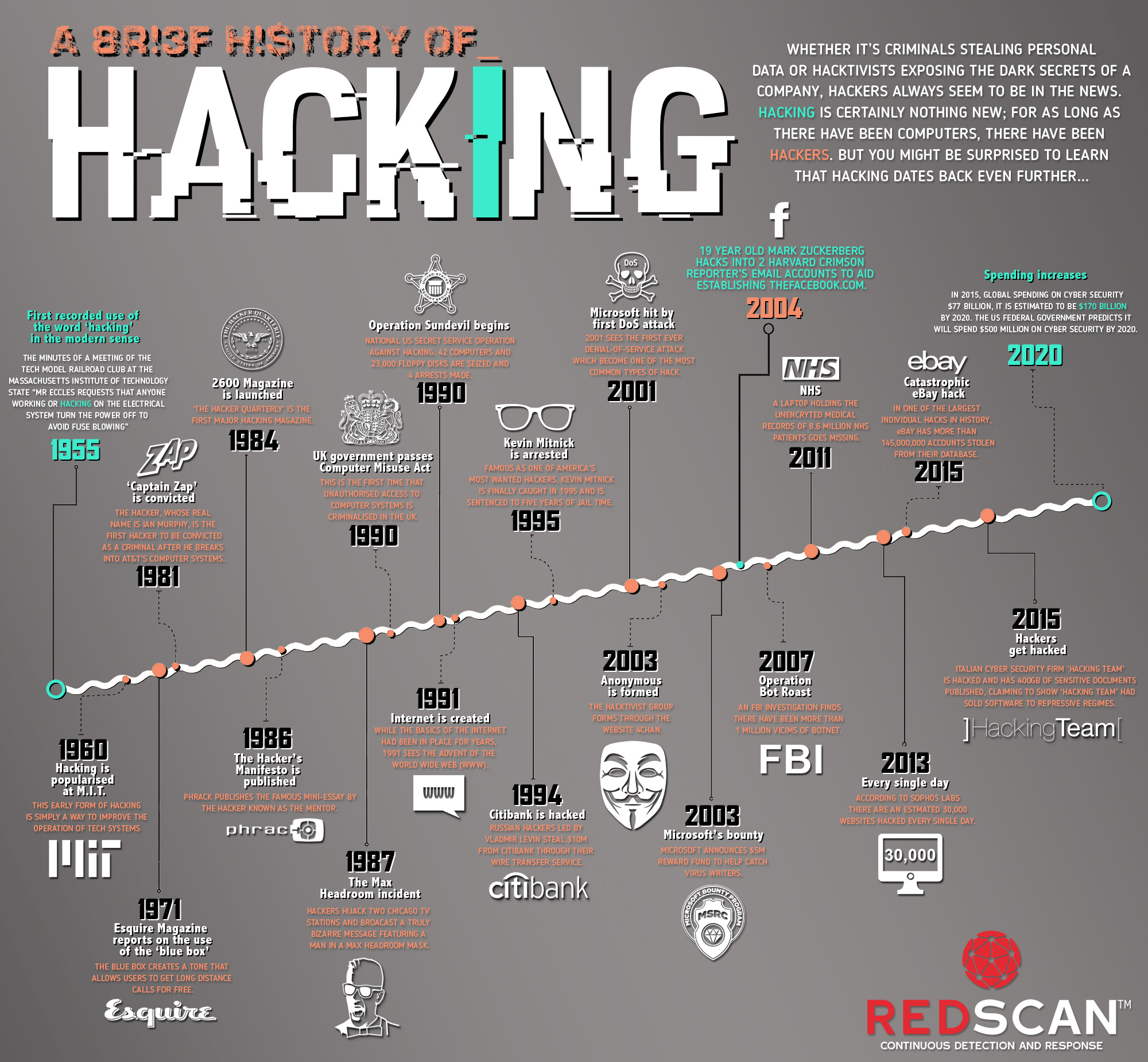
The internet, a vast and intricate network connecting billions of individuals, is a double-edged sword. While it fosters communication, collaboration, and knowledge sharing, it also provides a haven for nefarious activities. Cybercriminals, often operating in clandestine networks, exploit vulnerabilities in the digital landscape, posing significant threats to individuals, organizations, and national security. Understanding the structure and dynamics of these networks is crucial for mitigating cyber risks and safeguarding our interconnected world.
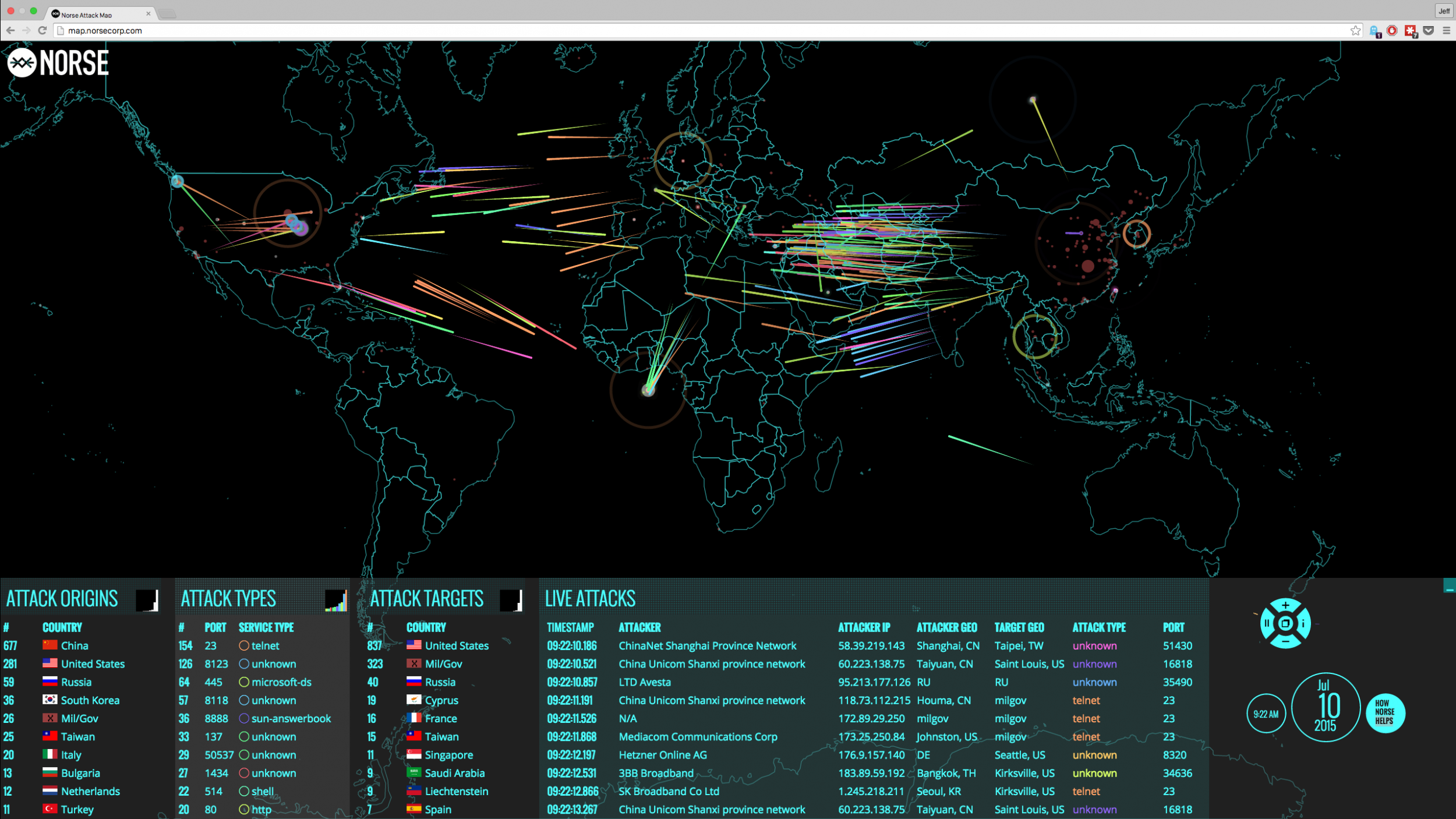
Visualizing the Invisible: The Concept of Hacker Maps
Hacker maps, also known as cybercrime maps, are visual representations of the global landscape of cybercrime. They utilize data and intelligence gathered from various sources, including law enforcement agencies, cybersecurity companies, and open-source intelligence, to depict the distribution, activities, and connections of hacker groups. These maps offer a powerful tool for:
- Understanding the Geography of Cybercrime: By identifying the locations of hacker groups, their targets, and their preferred attack vectors, security professionals can gain valuable insights into the global cybercrime landscape.
- Predicting and Preventing Attacks: By analyzing historical data and trends, security teams can anticipate emerging threats and develop proactive measures to mitigate potential risks.
- Identifying Key Players and Networks: Hacker maps can shed light on the intricate relationships between different groups, revealing alliances, rivalries, and potential collaboration opportunities.
- Facilitating Law Enforcement Efforts: By providing valuable intelligence on the structure, activities, and communication patterns of hacker groups, these maps can assist law enforcement agencies in their investigations and prosecutions.
Types of Hacker Maps
Hacker maps can be broadly categorized based on their focus and methodology:
- Geographic Maps: These maps depict the distribution of cybercrime activity across different regions and countries, highlighting areas with high concentrations of hacker groups and their targets.
- Network Maps: These maps focus on the interconnectedness of hacker groups, illustrating alliances, collaborations, and information sharing between various entities.
- Attack Vector Maps: These maps analyze the methods and techniques used by hackers to compromise systems and steal data, providing insights into their preferred attack vectors and vulnerabilities.
- Threat Actor Maps: These maps focus on specific hacker groups, providing detailed information on their history, motivations, targets, and capabilities.
Data Sources for Hacker Maps
The accuracy and effectiveness of hacker maps depend heavily on the quality and completeness of the underlying data. Several sources contribute to the creation of these maps:
- Law Enforcement Agencies: Law enforcement agencies around the world actively collect and analyze data on cybercrime activities, sharing intelligence with cybersecurity professionals and researchers.
- Cybersecurity Companies: Cybersecurity firms, specializing in threat intelligence and incident response, gather data from their clients and their own research, providing valuable insights into the latest cyber threats.
- Open-Source Intelligence (OSINT): Openly available information, including news articles, social media posts, forums, and online communities, can provide valuable clues about hacker groups, their activities, and their targets.
- Academic Research: Researchers in cybersecurity and criminology contribute to the understanding of hacker groups by conducting in-depth studies and publishing their findings.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite their potential benefits, hacker maps face several challenges and limitations:
- Data Availability and Accuracy: The quality and completeness of data are crucial for accurate and reliable maps. Access to real-time data and accurate attribution of cybercrime activities remain significant challenges.
- Dynamic Nature of Cybercrime: Hacker groups are constantly evolving, adapting their tactics, and forming new alliances, making it difficult to maintain up-to-date and accurate maps.
- Privacy Concerns: The collection and analysis of data on hacker activities raise concerns about privacy and the potential for misuse of information.
- Interpretation and Bias: The interpretation of data and the construction of maps can be subjective, potentially introducing bias and influencing the understanding of the cybercrime landscape.
FAQs About Hacker Maps
Q: Are hacker maps always accurate?
A: The accuracy of hacker maps depends on the quality and completeness of the underlying data. While efforts are made to ensure accuracy, the dynamic nature of cybercrime and the challenges in data collection can limit their reliability.
Q: What are the ethical implications of creating and using hacker maps?
A: Ethical considerations are crucial when dealing with sensitive information related to cybercrime. Transparency, data privacy, and responsible use are essential to avoid misuse and potential harm.
Q: How can I access hacker maps?
A: Several organizations and companies provide access to publicly available hacker maps, often for educational and research purposes. However, access to highly sensitive data may be restricted to law enforcement and intelligence agencies.
Q: How can hacker maps help individuals and organizations protect themselves?
A: By understanding the distribution, activities, and tactics of hacker groups, individuals and organizations can better assess their risks and implement appropriate security measures.
Tips for Using Hacker Maps Effectively
- Consult multiple sources: Cross-reference information from different maps and sources to gain a more comprehensive understanding.
- Focus on trends and patterns: Look for emerging threats and shifts in hacker activities to anticipate future risks.
- Consider the limitations: Remember that hacker maps are snapshots of a dynamic landscape and may not reflect the latest developments.
- Use maps as a tool for proactive security: Utilize the insights gained from maps to strengthen security measures and mitigate vulnerabilities.
Conclusion
Hacker maps provide a valuable tool for understanding the global cybercrime landscape, assisting security professionals, law enforcement agencies, and researchers in their efforts to mitigate cyber threats. By visualizing the intricate networks of cybercriminals, these maps contribute to a more informed and proactive approach to cybersecurity. However, it is crucial to acknowledge the limitations of these maps and to approach their use with ethical considerations and responsible data management practices. As the digital landscape continues to evolve, the development and utilization of hacker maps will play a crucial role in safeguarding our interconnected world from the ever-present threat of cybercrime.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping the Digital Underbelly: A Comprehensive Look at Hacker Networks. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!