Exploring the Power of the Map Function in Java: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Exploring the Power of the Map Function in Java: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Exploring the Power of the Map Function in Java: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Exploring the Power of the Map Function in Java: A Comprehensive Guide
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Exploring the Power of the Map Function in Java: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3.1 Understanding the Essence of the Map Function
- 3.2 Diving into the Mechanics of Map
- 3.3 Unleashing the Power of Map: Real-World Applications
- 3.4 Addressing Common Questions about Map
- 3.5 Tips for Effective Map Function Utilization
- 3.6 Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Map in Java
- 4 Closure
Exploring the Power of the Map Function in Java: A Comprehensive Guide
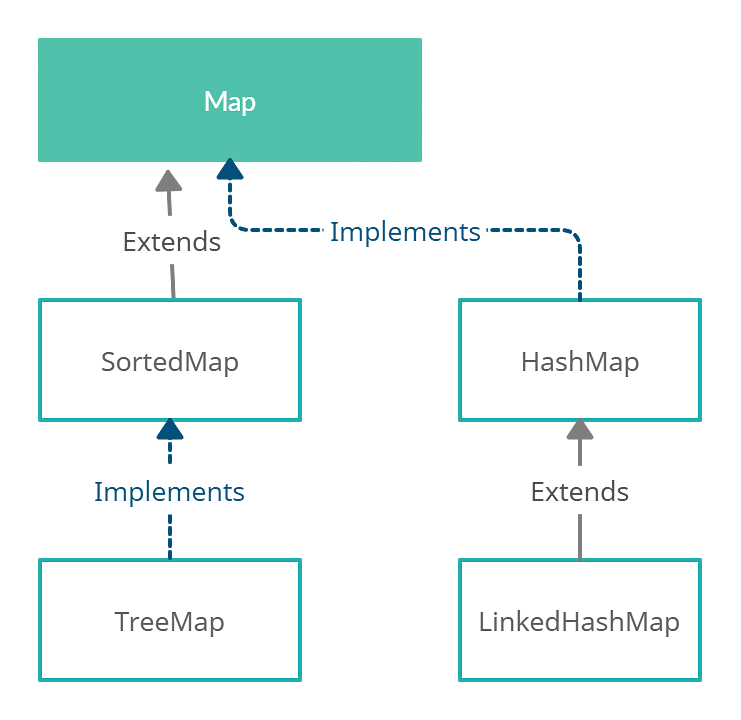
The Java map function, often found within the realm of streams, serves as a potent tool for transforming collections of data. It enables developers to apply a specific operation to each element within a collection, generating a new collection with modified elements. This ability to streamline data manipulation makes the map function an invaluable asset in a wide range of Java programming scenarios.
Understanding the Essence of the Map Function
At its core, the map function operates on the principle of applying a transformation to each element of a collection. This transformation can be anything from a simple arithmetic operation to a complex custom function, allowing for highly flexible data manipulation. The map function, in essence, iterates through each element of the collection, applies the specified transformation, and then collects the results into a new collection.
Diving into the Mechanics of Map
The map function finds its home within the Stream interface in Java. Streams provide a powerful way to process collections of data in a declarative and efficient manner. The map function is accessed through the map() method, which takes a function as an argument. This function, often referred to as a "mapping function," defines the transformation to be applied to each element.
Here’s a basic example to illustrate the concept:
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
public class MapExample
public static void main(String[] args)
List<Integer> numbers = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
// Doubling each number using the map function
List<Integer> doubledNumbers = numbers.stream()
.map(number -> number * 2)
.toList();
System.out.println("Original numbers: " + numbers);
System.out.println("Doubled numbers: " + doubledNumbers);
In this example, the map() method applies the lambda expression number -> number * 2 to each element in the numbers list. This expression effectively doubles each number, resulting in a new list doubledNumbers containing the transformed values.
Unleashing the Power of Map: Real-World Applications
The map function’s versatility extends far beyond simple arithmetic operations. Let’s explore some real-world scenarios where it shines:
1. Data Transformation:
-
Converting String to Integer: Imagine you have a list of strings representing numbers. The
mapfunction can efficiently transform these strings into integers using a mapping function likeInteger::parseInt. -
Capitalizing Strings: You can use the
mapfunction to capitalize all the strings in a list by applying a mapping function that utilizes thetoUpperCase()method. -
Extracting Data from Objects: If you have a list of objects, you can use the
mapfunction to extract specific data from each object, creating a new list with the extracted values.
2. Data Filtering and Processing:
-
Filtering based on Criteria: The
mapfunction can be combined with thefilterfunction to perform selective data manipulation. For example, you can usemapto transform only those elements that meet certain criteria, as defined by thefilterfunction. -
Complex Data Transformations: The
mapfunction can be chained together to perform multiple transformations on a collection. This allows you to perform complex data processing operations in a concise and elegant manner.
3. Enhancing Code Readability and Maintainability:
-
Streamlined Data Manipulation: The
mapfunction promotes a functional programming style, enabling you to express data manipulations in a declarative way. This often leads to more readable and concise code. -
Simplified Code Structure: By encapsulating the transformation logic within the mapping function, the
mapfunction promotes code modularity and reusability.
Addressing Common Questions about Map
Q1: Can the map function modify the original collection?
The map function itself does not modify the original collection. Instead, it generates a new collection containing the transformed elements. This behavior ensures that the original data remains intact.
Q2: What happens if the mapping function throws an exception?
If the mapping function throws an exception during the transformation process, the map function will propagate the exception. It’s crucial to handle exceptions appropriately to ensure the stability of your program.
Q3: What are some best practices for using the map function?
-
Keep mapping functions concise and focused: Aim for a clear and understandable transformation logic within the mapping function.
-
Consider exception handling: Be prepared to handle potential exceptions that might arise during the transformation process.
-
Chain
mapwith other stream operations: Utilize themapfunction in conjunction with other stream operations likefilter,reduce, andcollectto achieve complex data manipulation.
Tips for Effective Map Function Utilization
-
Prioritize clarity over brevity: While the
mapfunction promotes conciseness, strive for clarity in the mapping function definition. Ensure that the transformation logic is easily understandable. -
Leverage lambda expressions: Lambda expressions provide a concise and elegant way to define mapping functions, enhancing code readability.
-
Test thoroughly: Validate the behavior of the
mapfunction with thorough testing to ensure that it produces the desired results.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Map in Java
The map function in Java empowers developers to transform collections of data with ease and efficiency. Its ability to apply custom operations to each element, combined with its integration into the powerful stream API, makes it a vital tool for data processing and manipulation. By understanding the mechanics and applications of the map function, developers can unlock its potential to create elegant, concise, and maintainable code.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Exploring the Power of the Map Function in Java: A Comprehensive Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!