Europe in 1944: A Continent at War
Related Articles: Europe in 1944: A Continent at War
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Europe in 1944: A Continent at War. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Europe in 1944: A Continent at War
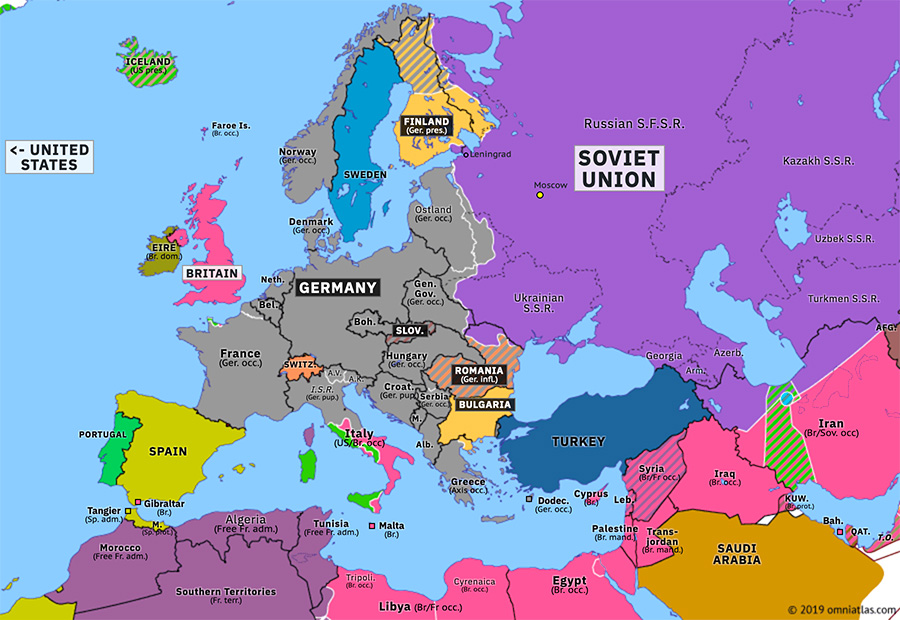
The year 1944 marked a pivotal turning point in the course of World War II. Across Europe, the tides of war were shifting, with the Allied forces pushing back against the Axis powers. A map of Europe in 1944, therefore, provides a snapshot of a continent in turmoil, its borders fluid and its future uncertain.
A Contested Landscape
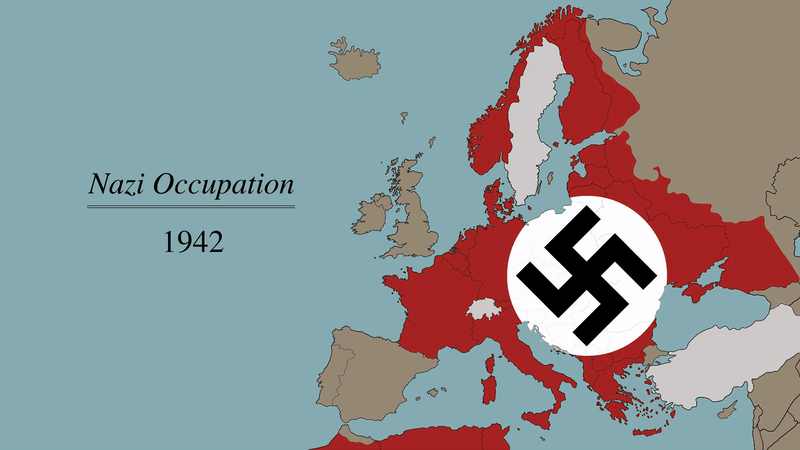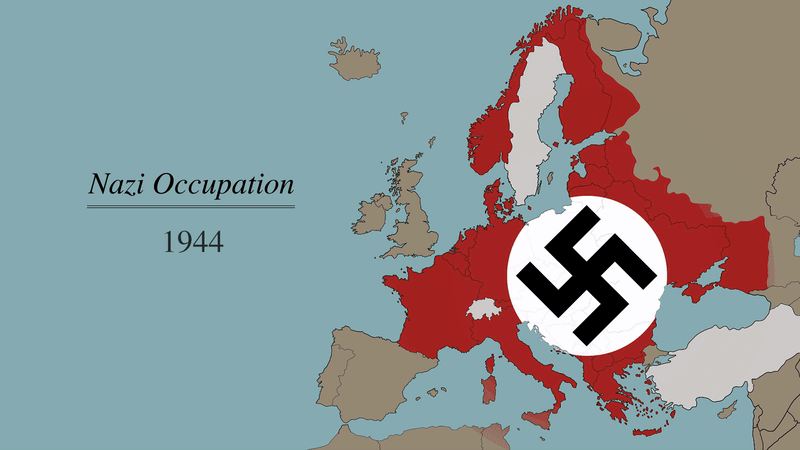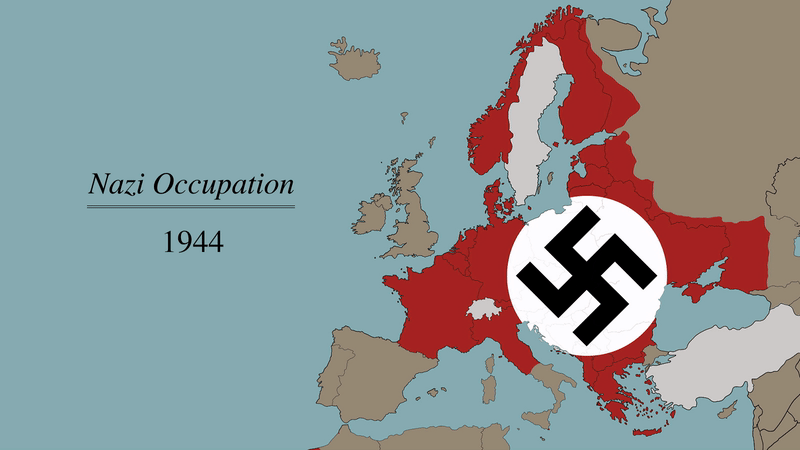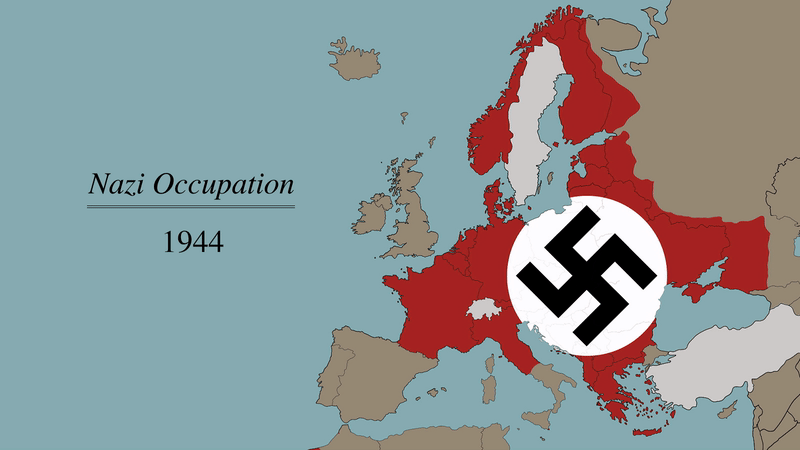
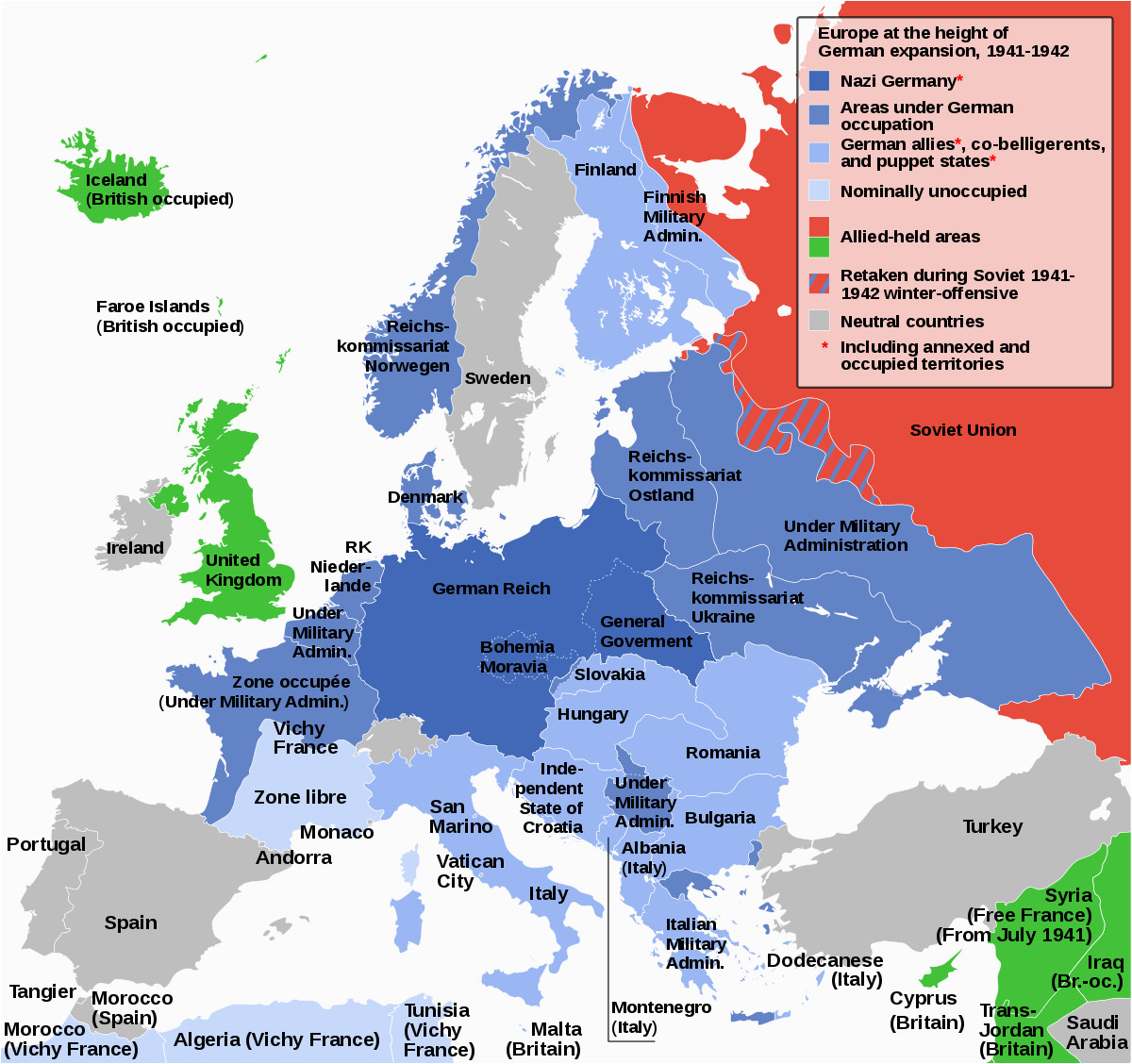
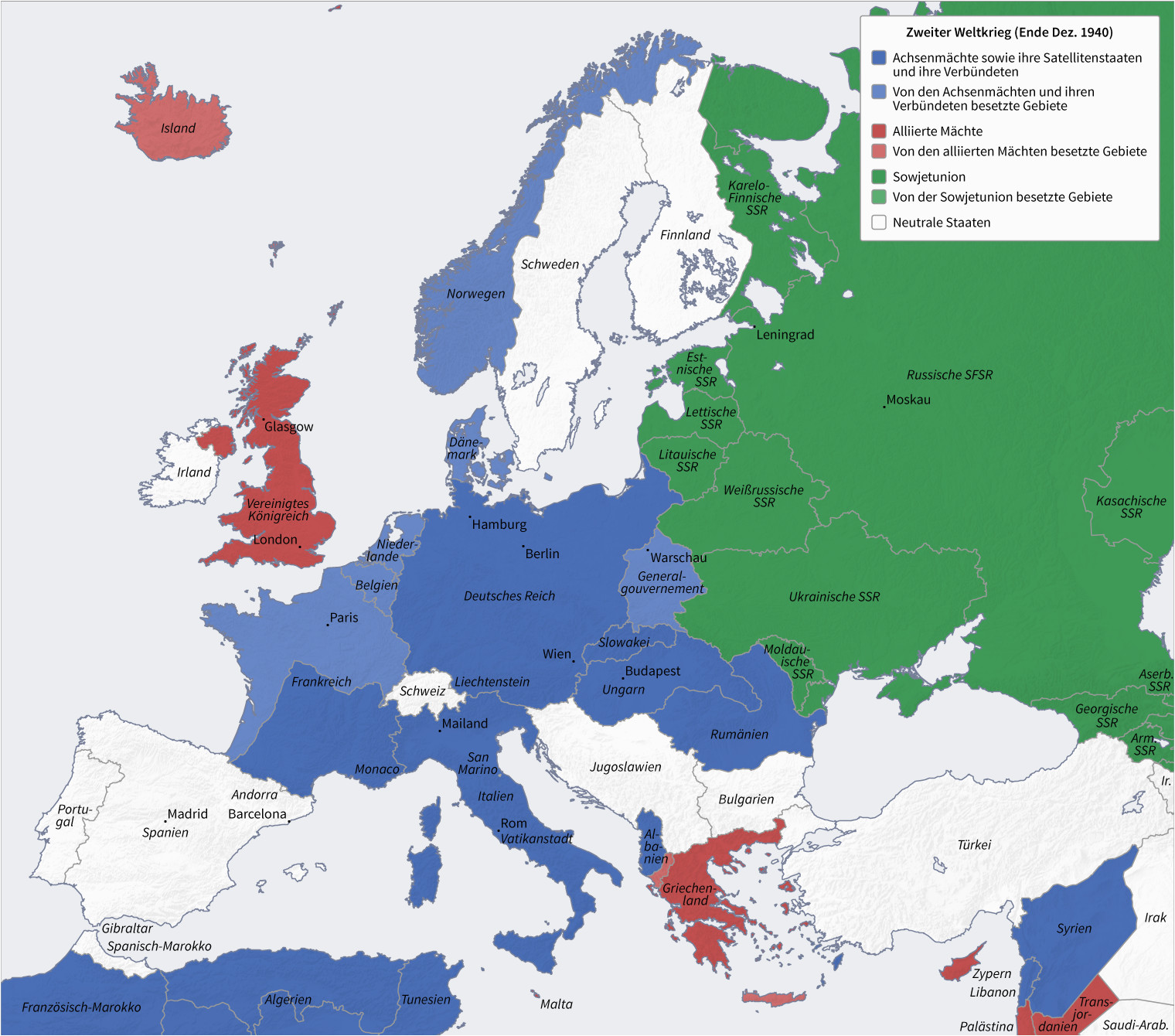
The map reveals a Europe divided. The Axis powers, led by Nazi Germany, held control over much of the continent. Germany occupied France, Belgium, the Netherlands, Denmark, Norway, and much of Eastern Europe, including Poland, Czechoslovakia, and parts of the Soviet Union. Italy, a member of the Axis, controlled much of the Balkan peninsula, while Hungary, Romania, and Bulgaria served as satellite states.
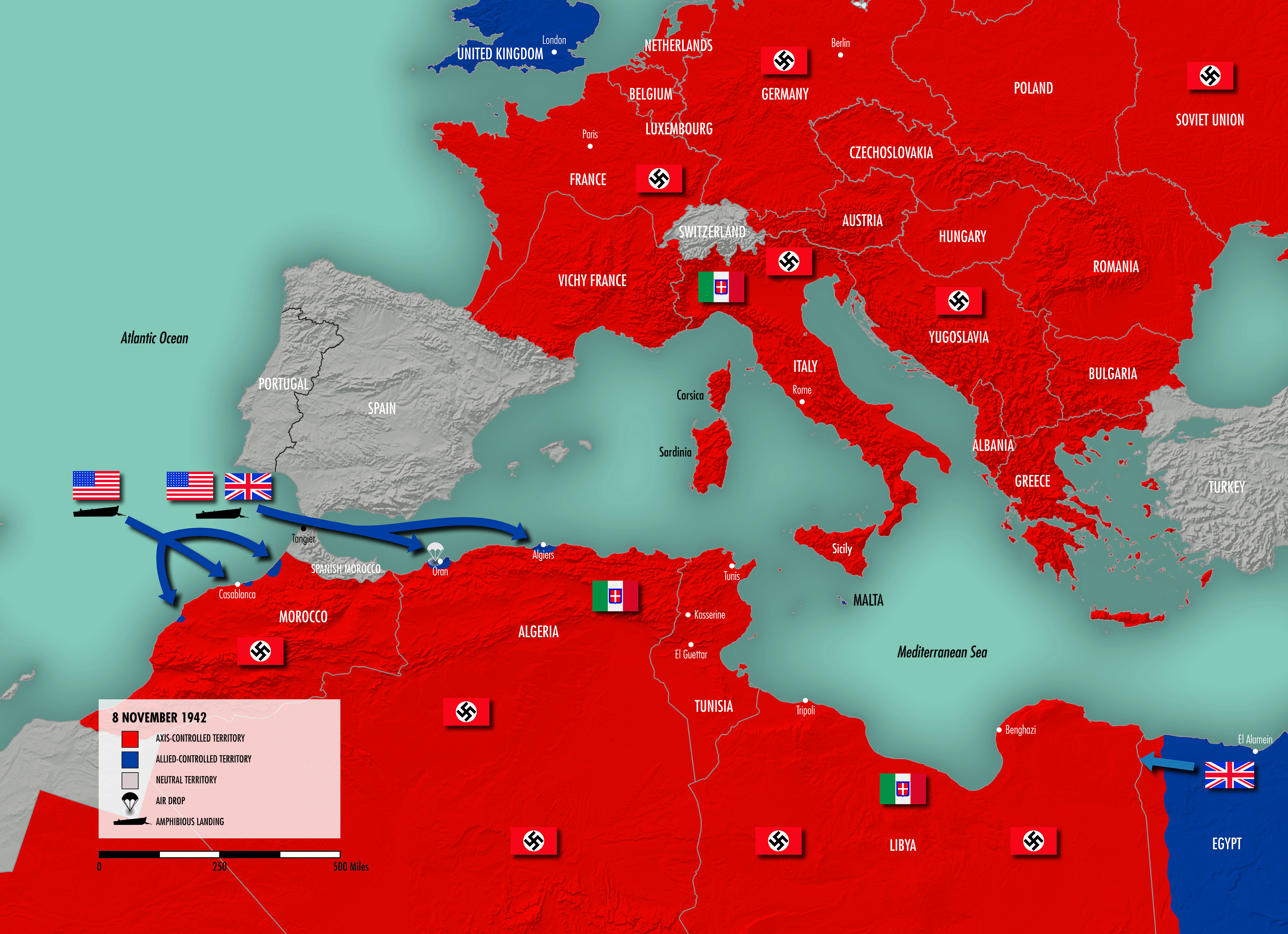
However, the Allied forces, comprising primarily Britain, the United States, and the Soviet Union, were making significant gains. The Soviet Union had launched a massive counteroffensive, pushing back the German forces from the eastern front. In the west, the Allied invasion of Normandy in June 1944, known as D-Day, had opened a second front in Europe, forcing Germany to fight on two fronts.
A Changing Landscape
The map illustrates the dynamic nature of the conflict. The front lines were constantly shifting, with territories changing hands as battles raged across the continent. The liberation of France, Belgium, and the Netherlands from Nazi occupation was a major turning point, while the Soviet advance in the east continued to cripple the German war machine.
The Importance of the Map
A map of Europe in 1944 offers a valuable historical tool for understanding the complexity of the war. It provides a visual representation of the geographic scope of the conflict, the changing power dynamics, and the strategic importance of key locations.
Examining Key Regions:
- Western Front: The map highlights the Allied beachheads in Normandy and the gradual push eastward, liberating France, Belgium, and the Netherlands. The Western Front was characterized by fierce battles, including the Battle of the Bulge, a last desperate German offensive in December 1944.
- Eastern Front: The map demonstrates the brutal nature of the Eastern Front, where the Soviet Union bore the brunt of the German invasion. The map shows the Soviet advance from the east, liberating Eastern Europe and pushing back the German forces.
- Italy: The map reveals the Italian campaign, a complex and lengthy struggle marked by Allied landings in Sicily and the eventual liberation of Rome.
- Balkans: The map shows the volatile situation in the Balkans, where Axis forces clashed with resistance movements and Allied forces. The region witnessed fierce battles and shifting allegiances.
Frequently Asked Questions:
- Why was the year 1944 so significant? 1944 marked a turning point in the war, with the Allied forces gaining momentum on both the Western and Eastern Fronts. The liberation of France and the Soviet advances significantly weakened the Axis powers.
- What were the key battles of 1944? Key battles included the Normandy landings, the Battle of the Bulge, the Soviet offensive in Eastern Europe, and the Italian campaign.
- How did the map of Europe change throughout the war? The map changed dramatically as the war progressed. The Allied advance steadily pushed back the Axis forces, liberating territories and shifting the borders.
- What were the key factors contributing to the Allied victory? The Allied victory was a result of several factors, including superior industrial capacity, strategic coordination, and the resilience of the Allied forces. The Soviet Union’s contribution on the Eastern Front was crucial in depleting German resources and manpower.
Tips for Understanding the Map:
- Focus on key locations: Identify major cities, battlefields, and geographical features that played a significant role in the war.
- Analyze the front lines: Track the movement of the front lines throughout the year, noting the ebb and flow of battles.
- Consider the political context: Understand the political landscape of Europe at the time, including the alliances and rivalries that shaped the conflict.
- Research key events: Explore the details of significant battles, political events, and resistance movements that occurred in 1944.
Conclusion:
A map of Europe in 1944 serves as a potent reminder of the devastation and upheaval of World War II. It highlights the strategic importance of geography, the dynamic nature of warfare, and the human cost of conflict. By studying this map, we can gain a deeper understanding of this pivotal year and the enduring consequences of the war.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Europe in 1944: A Continent at War. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!