Deciphering the Weather Map of Iowa: A Guide to Understanding the State’s Climate
Related Articles: Deciphering the Weather Map of Iowa: A Guide to Understanding the State’s Climate
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Deciphering the Weather Map of Iowa: A Guide to Understanding the State’s Climate. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Deciphering the Weather Map of Iowa: A Guide to Understanding the State’s Climate
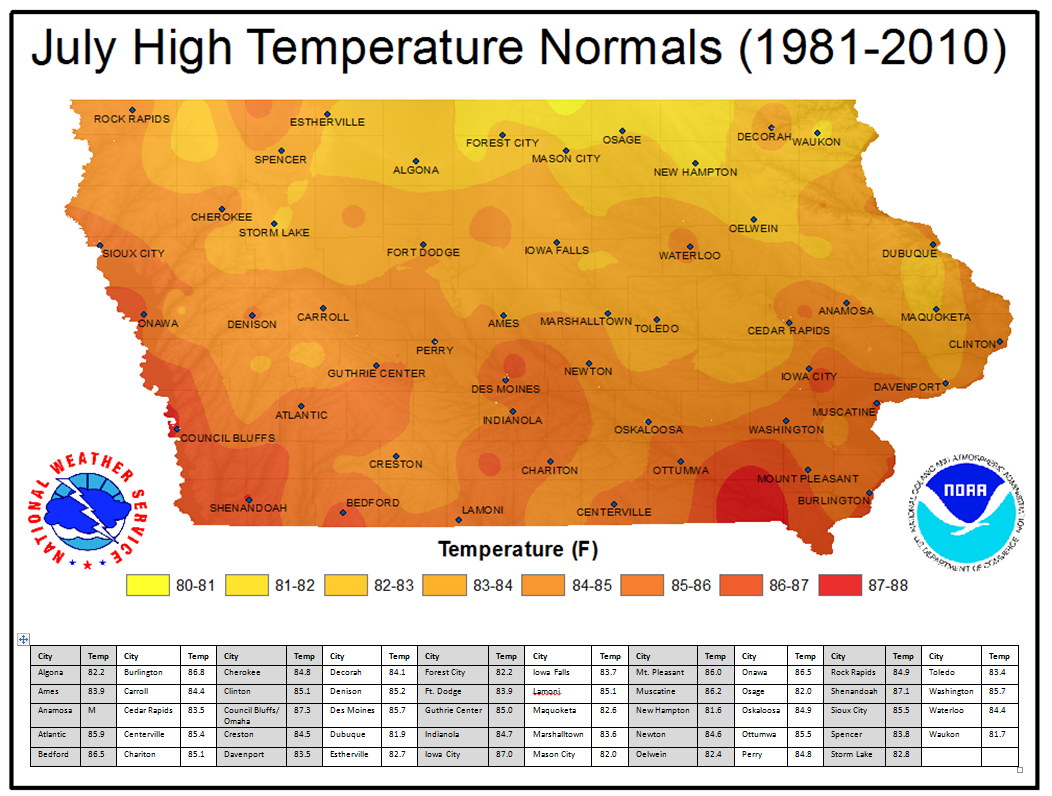
Iowa, known as the "Heartland" of America, boasts a diverse landscape and a climate that reflects its geographic position. Understanding the weather patterns of Iowa is crucial for residents, visitors, and industries alike. This article will delve into the intricacies of the Iowa weather map, providing a comprehensive guide to interpreting its various elements and their implications.
Decoding the Visuals:
The Iowa weather map, a visual representation of current and predicted weather conditions, typically includes the following elements:
- Temperature: Depicted using color gradients, with warmer temperatures often represented by reds and oranges, and cooler temperatures by blues and purples. Isoline lines, known as isotherms, connect areas with similar temperatures.
- Precipitation: Indicated by various symbols, such as rain drops, snowflakes, or a combination of both. The intensity of precipitation can be represented by the size or density of the symbols.
- Wind: Depicted by arrows, with the length of the arrow indicating wind speed and the arrowhead pointing in the direction of the wind.
- Fronts: Lines separating distinct air masses, with different colors representing different types of fronts (cold, warm, stationary, occluded).
- Cloud Cover: Represented by shading, with darker shading indicating denser cloud cover.
The Influence of Geographic Factors:
Iowa’s location in the midwestern United States places it at the confluence of several major weather systems, contributing to its variable climate.
- The Great Plains: The vast, flat expanse of the Great Plains to the west allows for unimpeded flow of air masses, influencing Iowa’s weather patterns.
- The Gulf of Mexico: Warm, moist air from the Gulf often brings precipitation and humidity, particularly during the summer months.
- The Rocky Mountains: The Rocky Mountains act as a barrier, blocking the flow of Pacific air masses and influencing the distribution of precipitation.
Seasonal Variations:
Iowa experiences four distinct seasons, each with its unique weather characteristics:
- Spring: Marked by a gradual warming trend, with temperatures ranging from cool to mild. Precipitation is common, with occasional thunderstorms and snow flurries.
- Summer: Typically hot and humid, with temperatures often reaching into the 80s and 90s Fahrenheit. Thunderstorms are frequent, and tornadoes are a possibility.
- Autumn: Characterized by cooler temperatures, with crisp air and vibrant fall foliage. Rainfall decreases, and the first frost typically occurs in late October or early November.
- Winter: Cold and snowy, with temperatures often dropping below freezing. Snowfall is frequent, and ice storms can pose significant hazards.
Understanding the Importance of the Iowa Weather Map:
The weather map serves as a vital tool for understanding the current and predicted weather conditions in Iowa, providing valuable information for a wide range of stakeholders:
- Farmers: The weather map helps farmers make critical decisions regarding planting, harvesting, and managing their crops.
- Transportation: Transportation agencies utilize the map to anticipate potential hazards, such as snowstorms or heavy rain, and make adjustments to schedules and routes.
- Emergency Management: The map assists emergency responders in preparing for and responding to weather-related events, such as floods, tornadoes, and blizzards.
- Public Health: The weather map helps public health officials monitor air quality, heat waves, and other weather-related health risks.
- Outdoor Recreation: The map provides valuable information for outdoor enthusiasts, allowing them to plan activities based on current and predicted weather conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about the Iowa Weather Map:
Q: Where can I find the most up-to-date weather map for Iowa?
A: Numerous online resources provide real-time weather information for Iowa, including the National Weather Service (NWS), local news websites, and weather apps.
Q: What are the most common weather hazards in Iowa?
A: Iowa is susceptible to a range of weather hazards, including tornadoes, severe thunderstorms, floods, blizzards, and heat waves.
Q: How can I interpret the symbols used on the weather map?
A: Most weather maps use standardized symbols to represent different weather conditions. Consult the map legend or an online guide for a detailed explanation of the symbols.
Q: What is the difference between a cold front and a warm front?
A: A cold front is a boundary where a cold air mass is replacing a warmer air mass, often resulting in rapid temperature drops, strong winds, and thunderstorms. A warm front is a boundary where a warm air mass is replacing a colder air mass, typically leading to a gradual increase in temperature and precipitation.
Tips for Using the Iowa Weather Map Effectively:
- Pay attention to the forecast: The weather map provides insights into both current and predicted conditions, enabling you to plan accordingly.
- Understand the symbols and legends: Familiarize yourself with the symbols and legends used on the map to interpret the information accurately.
- Check multiple sources: Refer to multiple sources, such as the NWS website and local news websites, for a comprehensive view of the weather forecast.
- Stay informed about severe weather warnings: Be aware of warnings issued by the NWS and take appropriate precautions during severe weather events.
Conclusion:
The Iowa weather map is an essential tool for understanding the state’s dynamic climate. By interpreting its various elements and understanding the influences of geographic factors, residents, visitors, and industries can make informed decisions and prepare for potential weather hazards. Utilizing the map effectively can enhance safety, optimize activities, and contribute to a greater understanding of the diverse weather patterns that shape the "Heartland."
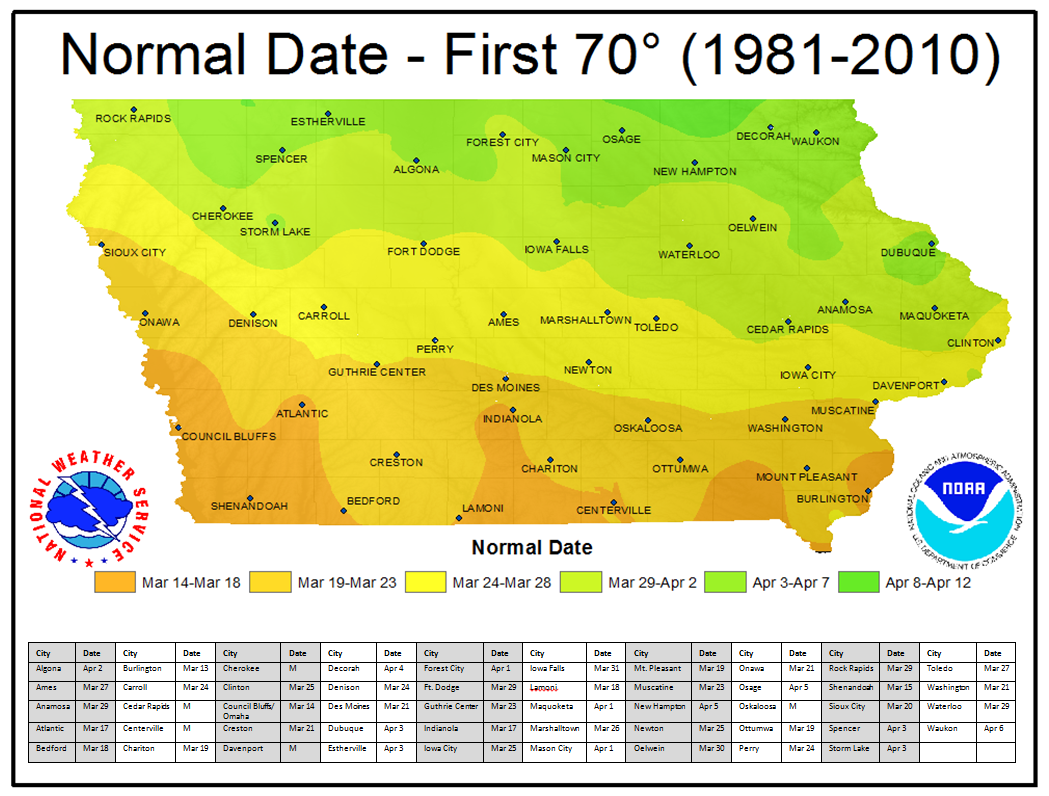
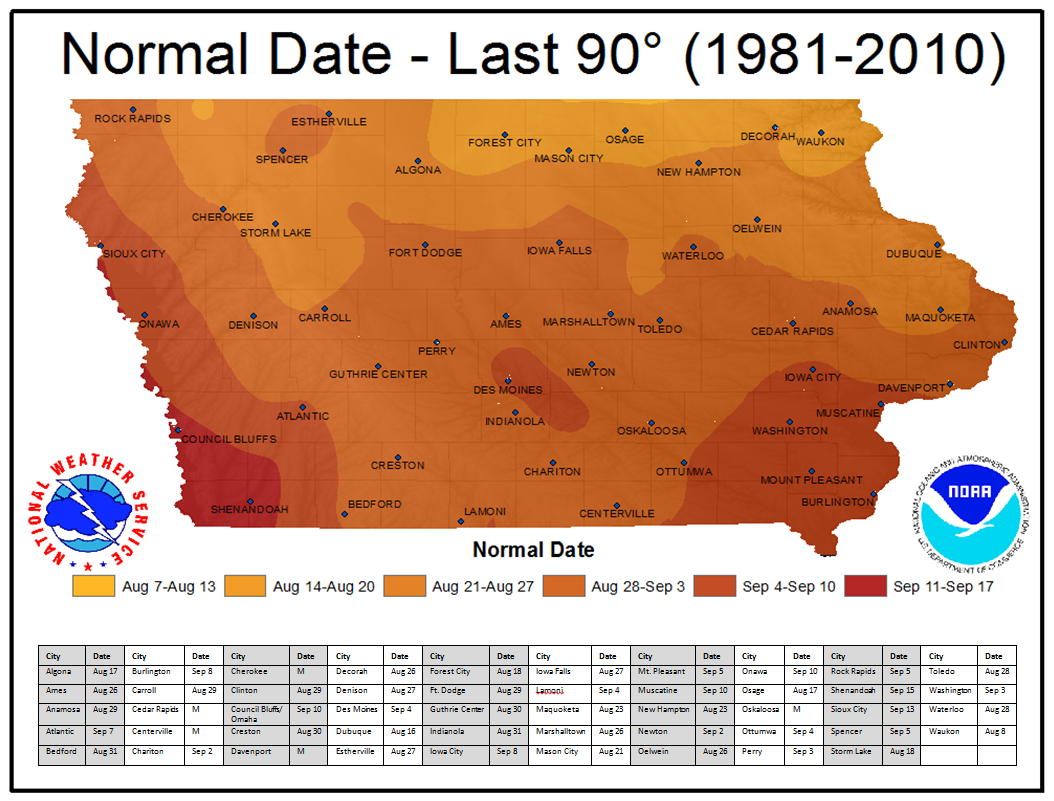
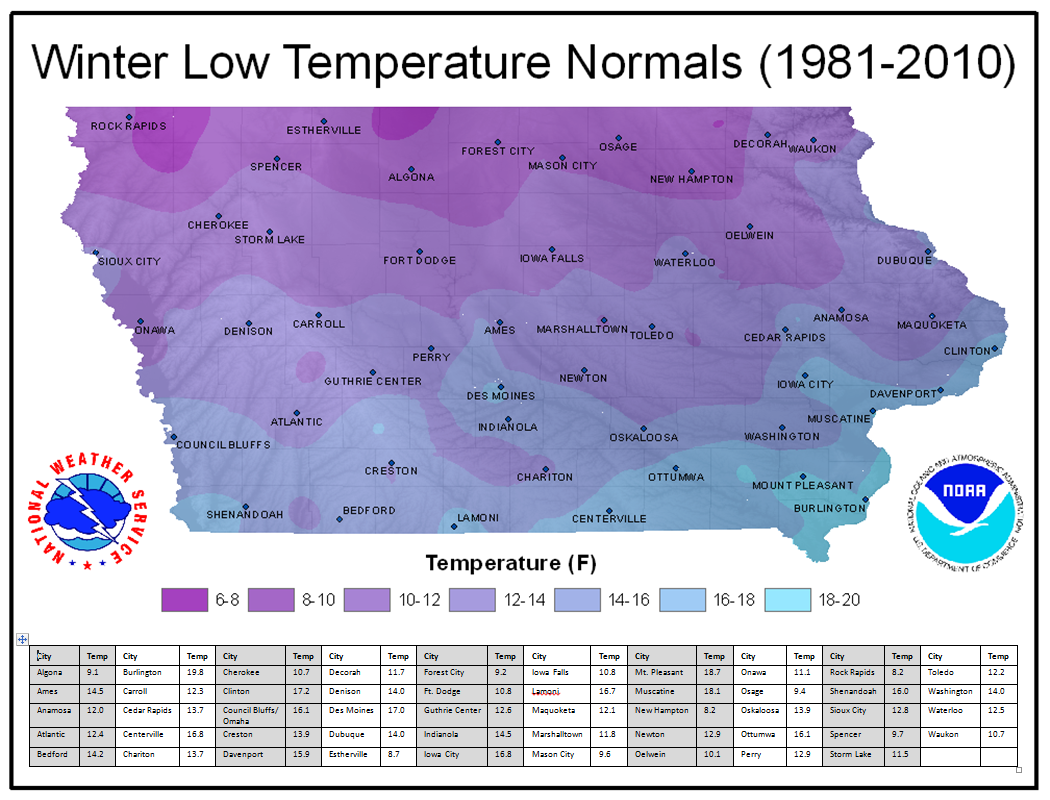
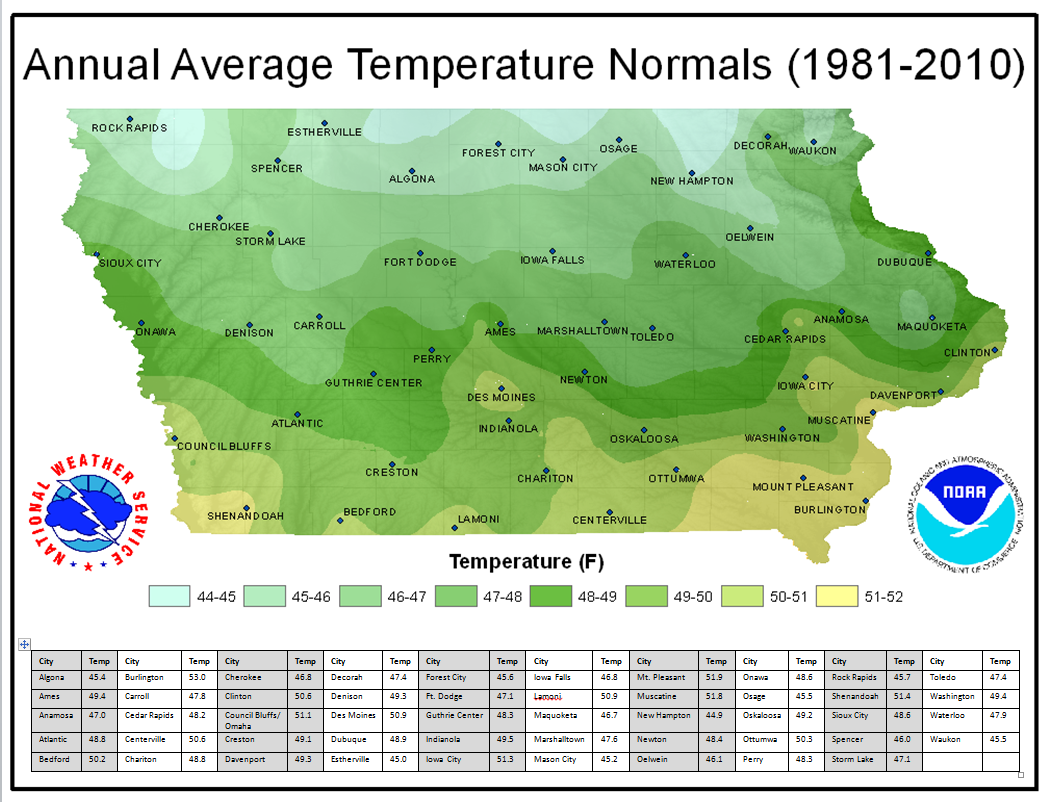
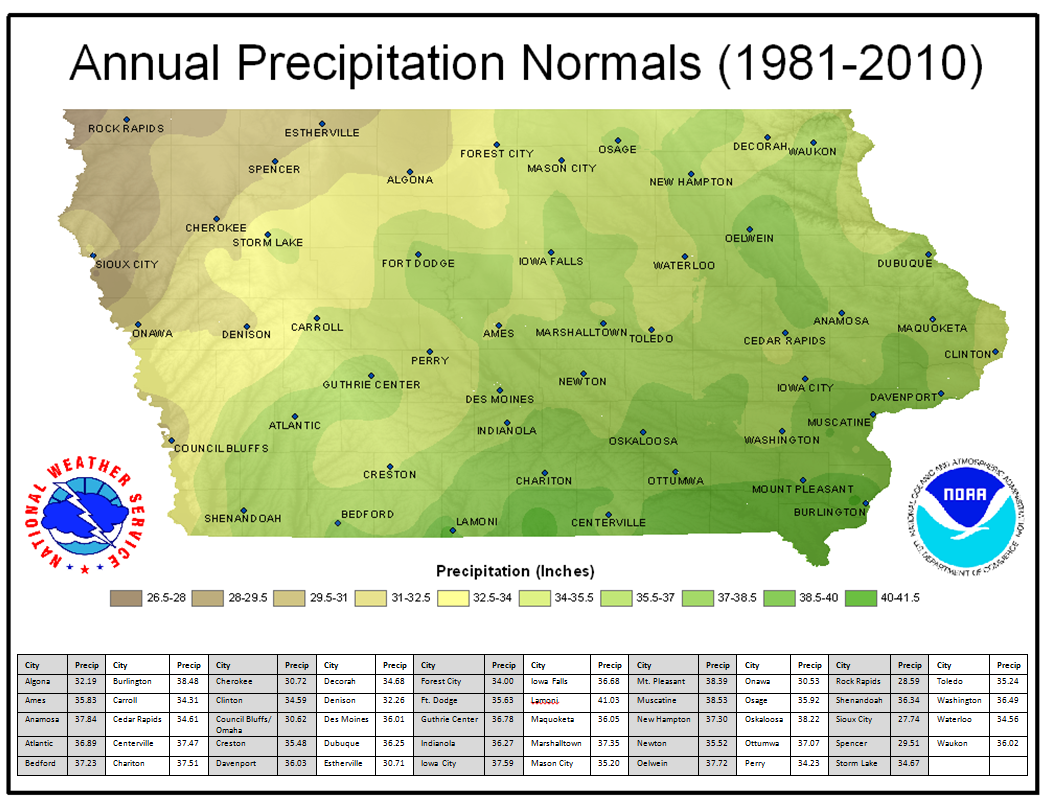
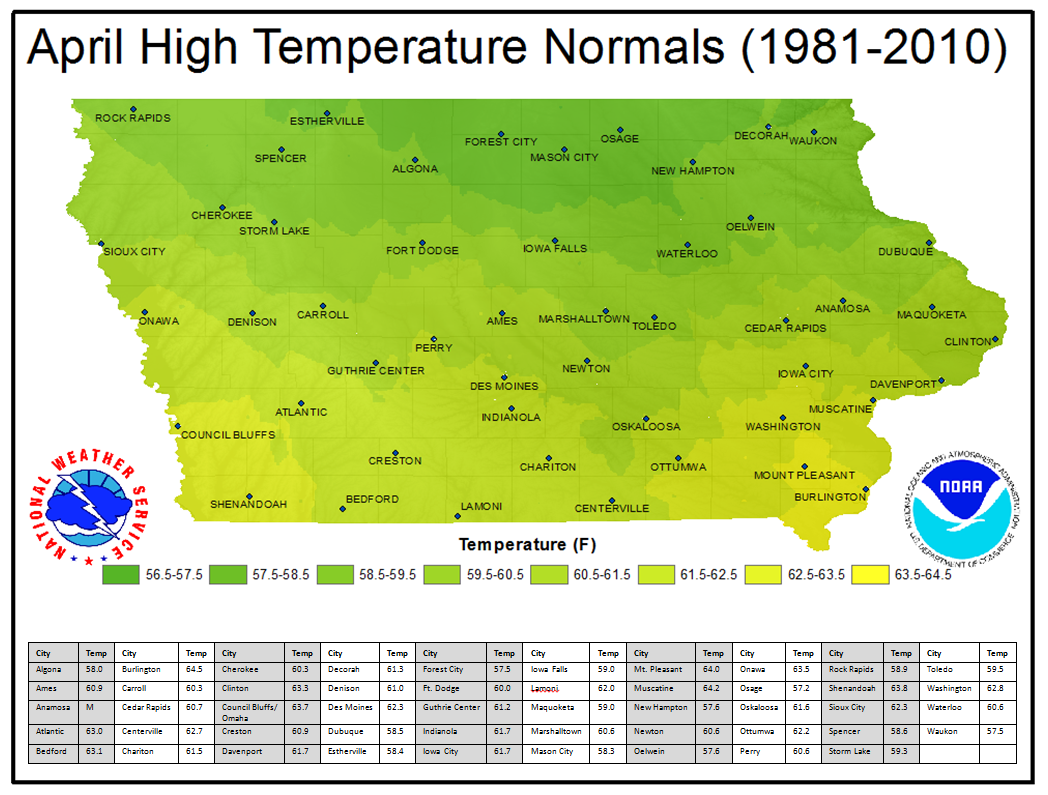
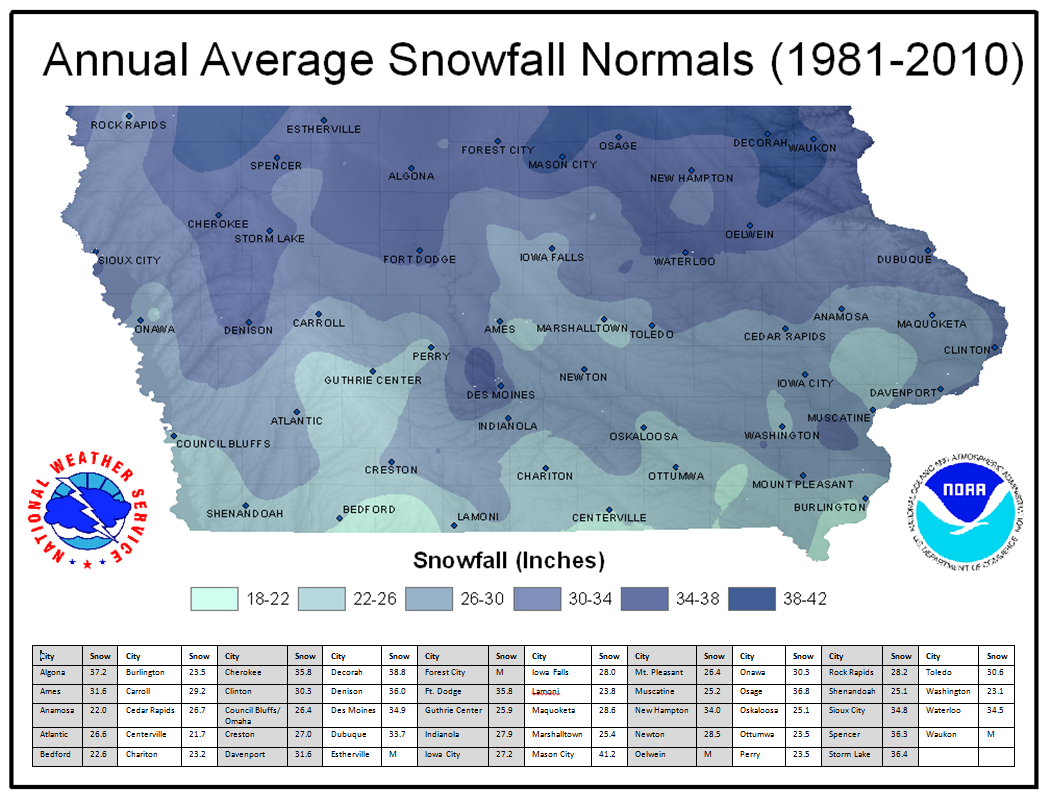
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Deciphering the Weather Map of Iowa: A Guide to Understanding the State’s Climate. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!