Charting the Colossus: A Journey Through Ancient Alexandria’s Map
Related Articles: Charting the Colossus: A Journey Through Ancient Alexandria’s Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Charting the Colossus: A Journey Through Ancient Alexandria’s Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Charting the Colossus: A Journey Through Ancient Alexandria’s Map
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Charting the Colossus: A Journey Through Ancient Alexandria’s Map
- 3.1 Reconstructing the City of Knowledge: The Challenges and Rewards
- 3.2 Key Features of the Ancient Alexandria Map: A Glimpse into the City’s Heart
- 3.3 Beyond the Map: Understanding the City’s Dynamics
- 3.4 FAQs: Unraveling the Mysteries of Ancient Alexandria
- 3.5 Tips for Exploring Ancient Alexandria
- 3.6 Conclusion: A Legacy of Learning and Innovation
- 4 Closure
Charting the Colossus: A Journey Through Ancient Alexandria’s Map

Ancient Alexandria, a city that once rivaled Rome in its grandeur and influence, stands as a testament to human ingenuity and ambition. While the city’s physical remains are scattered and fragmented, its legacy persists in the form of written accounts, archaeological discoveries, and, perhaps most importantly, its ancient maps. These maps, though incomplete and often based on interpretations of surviving texts, offer a unique window into the urban planning, social structure, and cultural landscape of this once-thriving metropolis.
Reconstructing the City of Knowledge: The Challenges and Rewards
The task of reconstructing a map of ancient Alexandria is a complex and intricate endeavor. Unlike modern cities, which leave behind a wealth of detailed blueprints and aerial photographs, ancient Alexandria’s map must be pieced together from a mosaic of fragmented evidence. This evidence includes:
- Literary Sources: Greek and Roman writers, such as Strabo, Diodorus Siculus, and Pliny the Elder, provide valuable textual descriptions of Alexandria’s layout, its prominent landmarks, and its geographical features.
- Archaeological Discoveries: Excavations have unearthed remnants of buildings, streets, and infrastructure, offering tangible proof of the city’s physical form. These discoveries, however, often provide only partial insights, requiring careful analysis and interpretation.
- Papyri and Inscriptions: Ancient documents, particularly papyri found in the sands of Egypt, contain references to specific locations, streets, and neighborhoods, offering crucial details for mapping purposes.
- Numismatics: Coins minted in Alexandria often depict symbolic representations of the city’s landmarks, providing further clues about its layout.
Despite the challenges, the rewards of reconstructing Alexandria’s map are significant. By piecing together these fragmented clues, historians and archaeologists can:
- Visualize the city’s spatial organization: Understand the relationship between its major districts, its harbor, its public spaces, and its residential areas.
- Trace the evolution of urban planning: Identify the different stages of the city’s growth, from its founding by Alexander the Great to its decline under Roman rule.
- Gain insights into social dynamics: Analyze the distribution of wealth and power within the city, by studying the location of palaces, temples, and residential areas.
- Reveal the city’s cultural and economic landscape: Identify the areas dedicated to trade, commerce, education, and religious activities.
Key Features of the Ancient Alexandria Map: A Glimpse into the City’s Heart
The ancient map of Alexandria reveals a city meticulously planned and designed to reflect its ambition and its role as a center of learning and commerce. Some of its key features include:
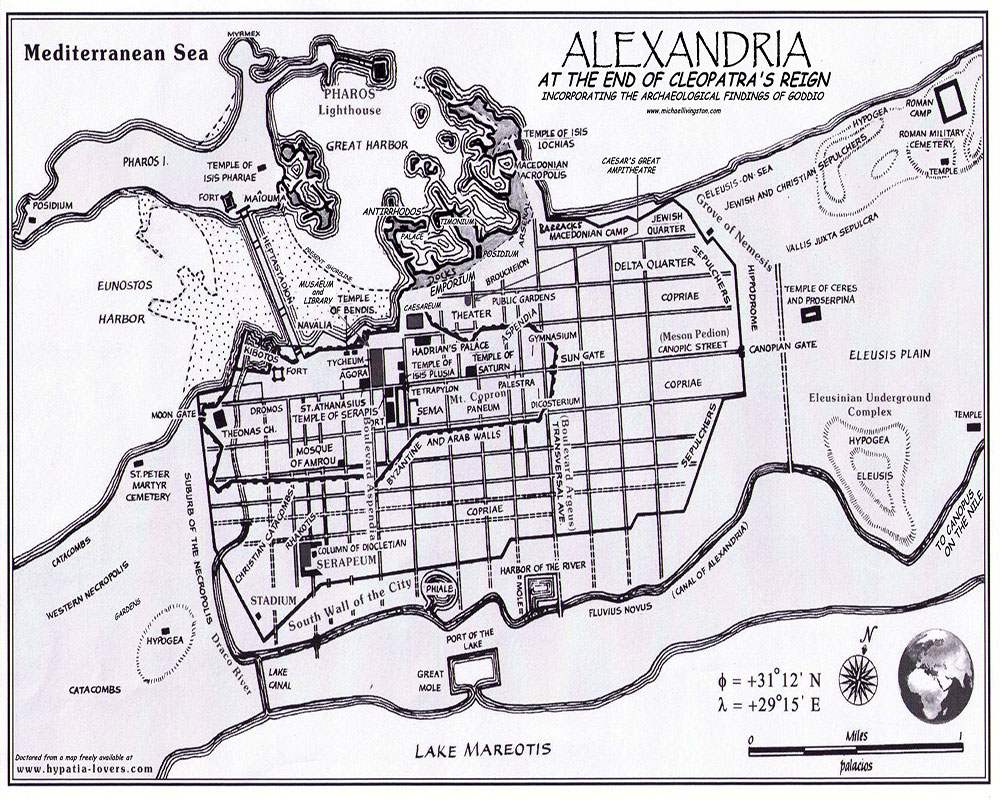
- The Royal Quarter: Located on the western edge of the city, this area housed the royal palace, the royal library, and other significant government buildings. The presence of these structures highlights the city’s political importance and its role as a center of power.
- The Harbor: Alexandria’s harbor, known as the Great Harbor, was a vital artery for trade and commerce, connecting the city to the Mediterranean world. Its strategic location facilitated the flow of goods and ideas, contributing to the city’s economic prosperity and cultural exchange.
- The Canopic Way: This grand avenue, named after the city of Canopus, served as the main thoroughfare through the city, connecting the harbor to the Royal Quarter and the Necropolis. Its presence reflects the city’s emphasis on order and organization, as well as its desire to showcase its grandeur.
- The Necropolis: Located on the outskirts of the city, the Necropolis was a vast cemetery complex, home to elaborate tombs and mausoleums. Its presence highlights the city’s commitment to honoring its dead and its belief in the afterlife.
- The Serapeum: This grand temple complex, dedicated to the god Serapis, was a major religious center in the city. Its location in the heart of the city underscores the importance of religion in the lives of Alexandrians.
- The Lighthouse: The Pharos of Alexandria, one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World, stood at the entrance of the harbor, serving as a beacon for ships navigating the treacherous waters. Its presence reflects the city’s technological prowess and its commitment to trade and navigation.
Beyond the Map: Understanding the City’s Dynamics
While the map offers a static representation of Alexandria’s physical layout, it is crucial to remember that it represents only a snapshot in time. The city was a dynamic and evolving entity, constantly adapting to changing political, economic, and social landscapes. The map, therefore, should be seen as a starting point for understanding the city’s complexity, not as a definitive portrayal.
To truly appreciate Alexandria’s dynamism, it is essential to consider factors beyond the map itself. These factors include:
- The Role of the Ptolemies: The Ptolemaic dynasty, which ruled Egypt for over 300 years, played a significant role in shaping Alexandria’s development. Their patronage of arts and sciences, their investment in infrastructure, and their efforts to promote trade all contributed to the city’s growth and influence.
- The Rise of Roman Power: The Roman conquest of Egypt in 30 BC marked a significant turning point in Alexandria’s history. While the Romans initially maintained the city’s status as a center of learning and commerce, their rule also brought about changes in the city’s administration, its social structure, and its cultural landscape.
- The Impact of Religion: The presence of various religious communities, including Jews, Christians, and pagans, shaped the city’s social and cultural fabric. The rise of Christianity in Alexandria, for instance, led to the construction of numerous churches and the establishment of theological schools, contributing to the city’s intellectual and spiritual life.
- The City’s Decline: Despite its initial success, Alexandria began to decline in the late Roman period, facing challenges such as political instability, economic hardship, and the rise of other major cities in the Mediterranean world. The city’s decline, however, did not erase its legacy, as it continued to play a significant role in the history of the region.
FAQs: Unraveling the Mysteries of Ancient Alexandria
Q: What was the approximate population of ancient Alexandria?
A: Estimates vary, but ancient Alexandria is believed to have had a population ranging from 300,000 to 500,000 people at its peak, making it one of the largest cities in the ancient world.
Q: What was the purpose of the Royal Library of Alexandria?
A: The Royal Library was a vast repository of knowledge, containing scrolls and texts from across the Mediterranean world. It served as a center of learning, scholarship, and research, attracting scholars and intellectuals from across the ancient world.
Q: How did the city’s layout contribute to its economic success?
A: Alexandria’s strategic location, its well-designed harbor, and its extensive network of roads and canals facilitated trade and commerce, making it a major economic hub in the ancient world.
Q: What were the main sources of revenue for the city?
A: Alexandria’s primary sources of revenue included trade, taxation, and the exploitation of natural resources, such as grain and papyrus.
Q: What happened to the Pharos of Alexandria?
A: The Pharos of Alexandria was destroyed by a series of earthquakes in the 14th century CE. Today, only fragments of the lighthouse remain, providing a glimpse into its former grandeur.
Q: How did the city’s cultural diversity contribute to its intellectual life?
A: Alexandria’s diverse population, including Greeks, Egyptians, Jews, and Romans, fostered a vibrant intellectual environment. The city became a center of philosophical debate, scientific inquiry, and literary production.
Q: What are some of the most significant discoveries made at the site of ancient Alexandria?
A: Archaeological discoveries at Alexandria include the remnants of the Royal Quarter, the harbor, the Serapeum, and the Necropolis, providing valuable insights into the city’s layout, its social structure, and its cultural life.
Tips for Exploring Ancient Alexandria
- Visit the Alexandria National Museum: This museum houses a collection of artifacts from ancient Alexandria, offering a glimpse into the city’s history and culture.
- Explore the Catacombs of Kom el-Shuqqafa: This ancient necropolis, dating back to the Roman period, offers a fascinating glimpse into the city’s funerary practices.
- Visit the Bibliotheca Alexandrina: This modern library, built on the site of the ancient Royal Library, serves as a testament to the city’s enduring legacy as a center of learning.
- Read historical accounts: Works by Strabo, Diodorus Siculus, and Pliny the Elder provide valuable insights into the city’s history, its layout, and its cultural life.
- Explore online resources: Numerous websites and digital maps offer interactive visualizations of ancient Alexandria, allowing you to explore the city’s layout and its key landmarks.
Conclusion: A Legacy of Learning and Innovation
The ancient map of Alexandria, though incomplete and fragmented, offers a powerful reminder of the city’s enduring legacy. It serves as a testament to the ingenuity and ambition of its builders, its role as a center of learning and commerce, and its contribution to the development of human civilization. By piecing together the fragments of evidence, we can continue to explore the mysteries of this once-thriving metropolis and appreciate the enduring impact it has had on the world. Ancient Alexandria, through its map and its legacy, continues to inspire and captivate, reminding us of the power of human creativity and the potential for cities to become centers of knowledge and progress.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Charting the Colossus: A Journey Through Ancient Alexandria’s Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!