A Tapestry of Terrain: Exploring the Landforms of the United States
Related Articles: A Tapestry of Terrain: Exploring the Landforms of the United States
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Tapestry of Terrain: Exploring the Landforms of the United States. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Tapestry of Terrain: Exploring the Landforms of the United States

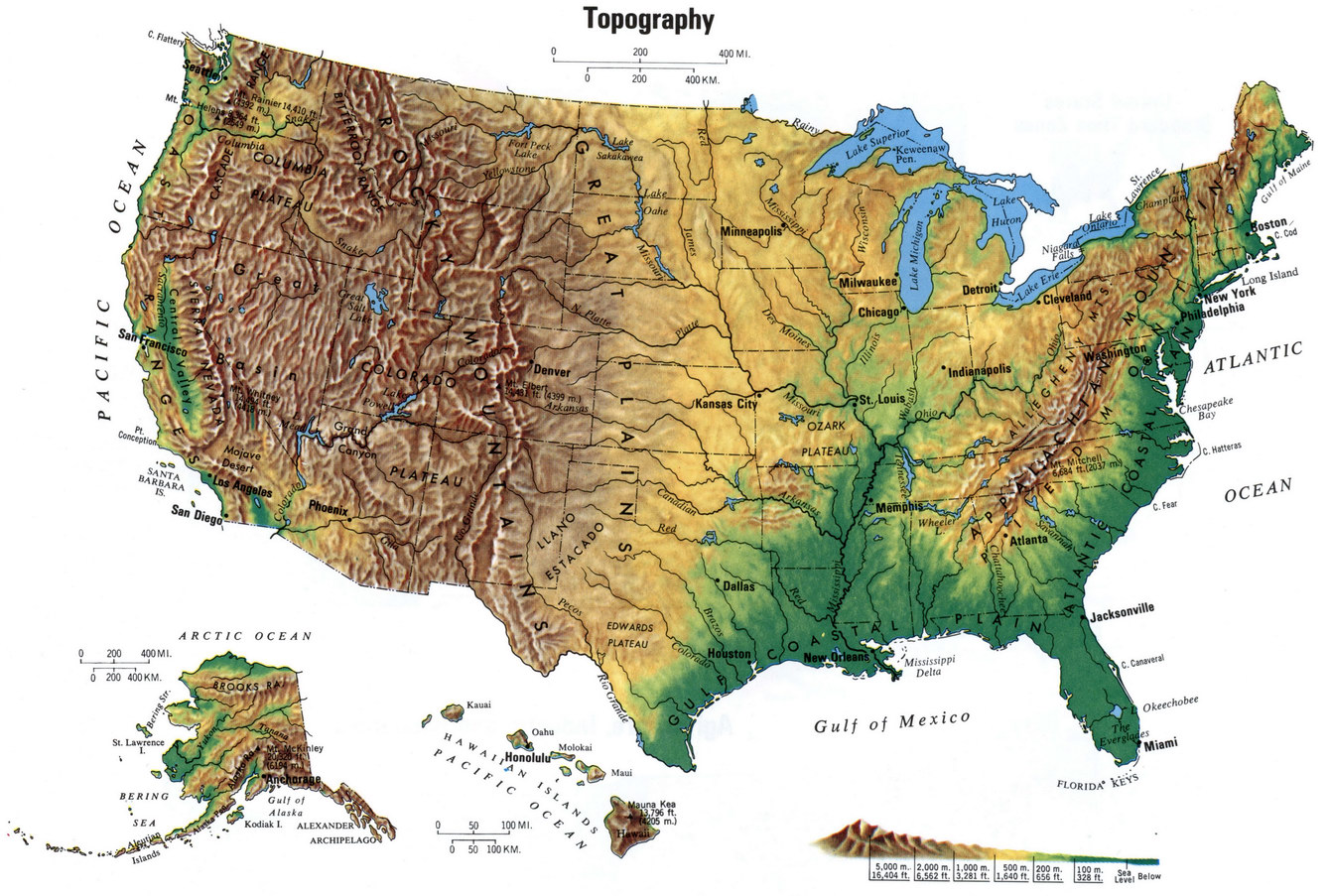
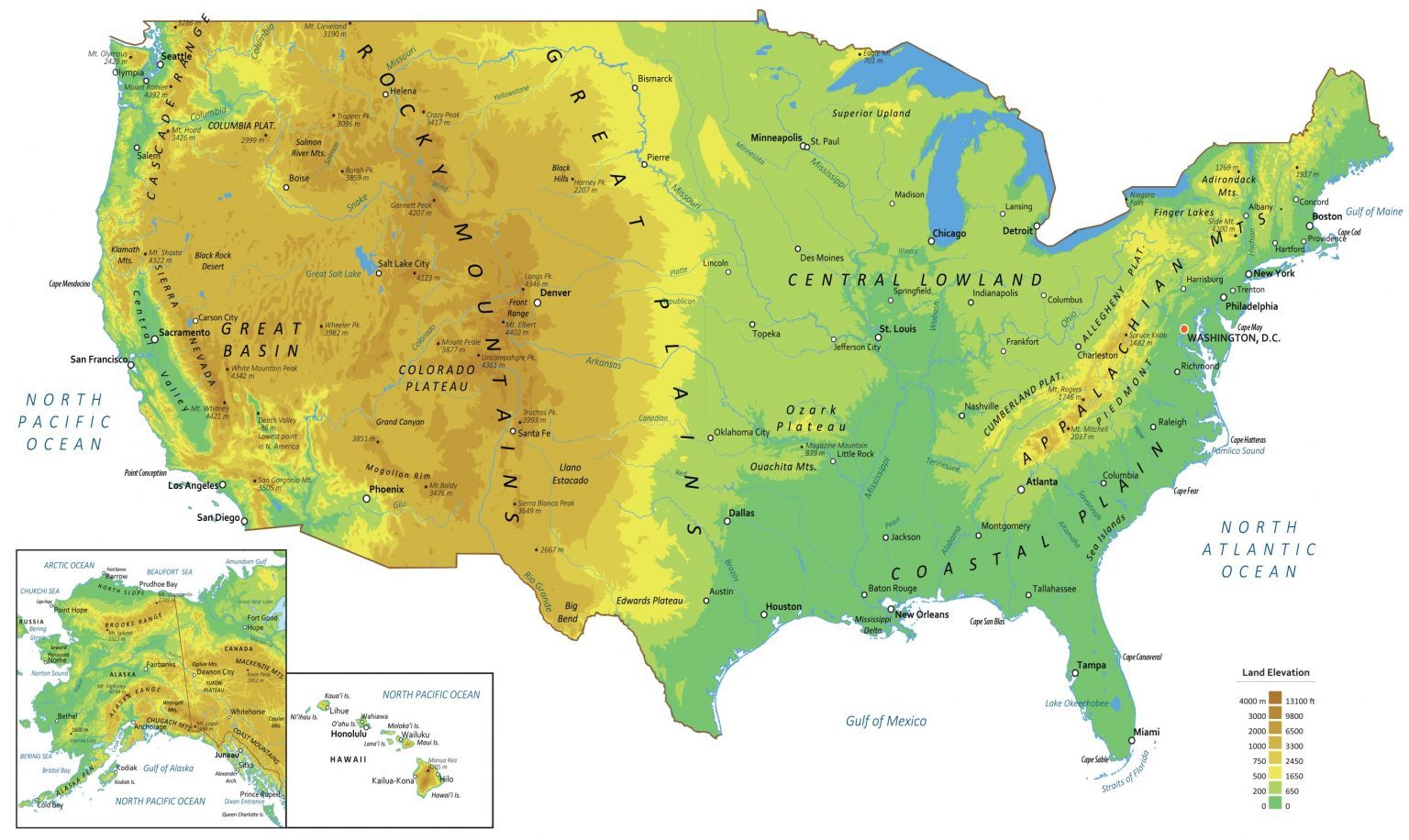
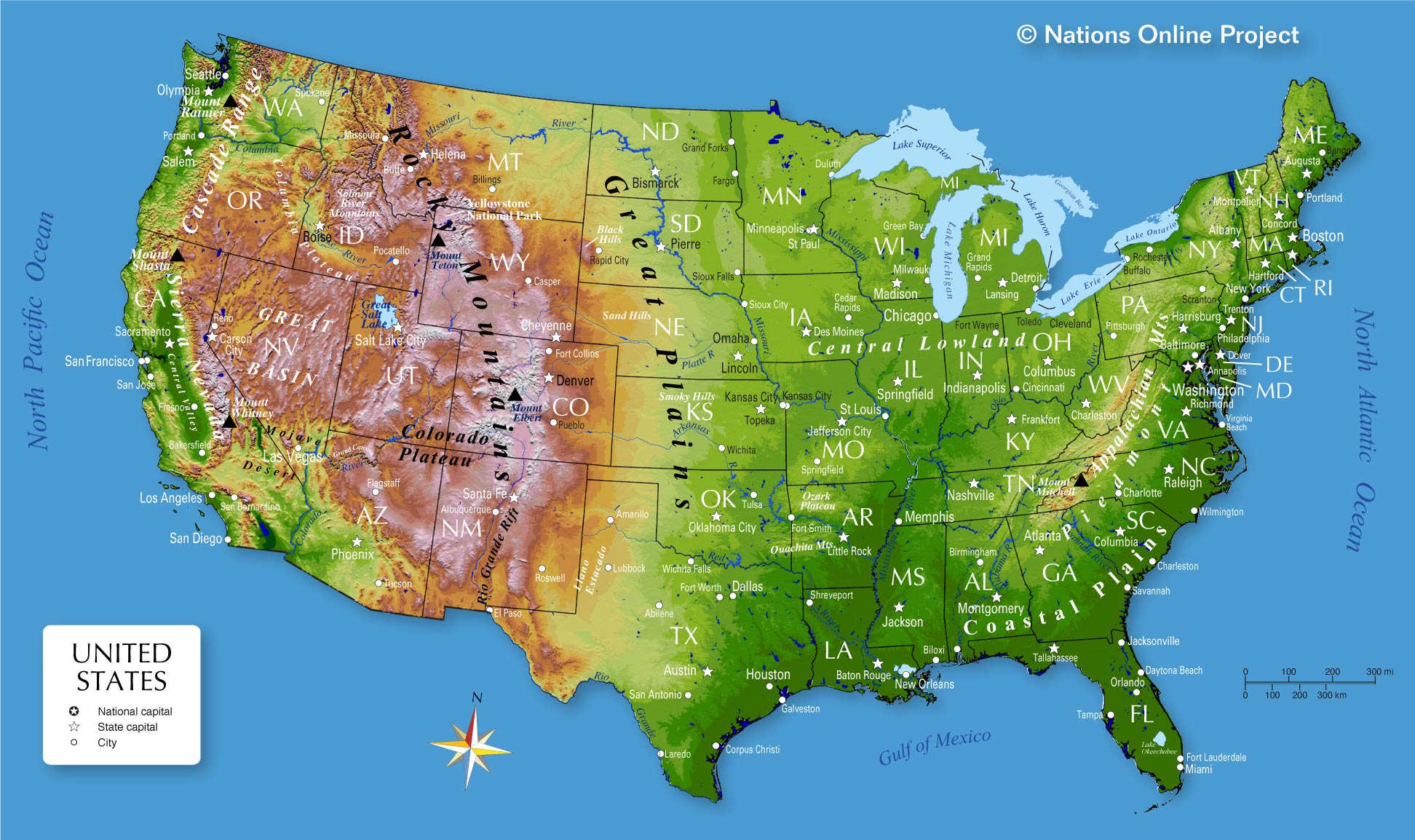
The United States, spanning a vast expanse of North America, boasts a remarkably diverse landscape. From towering mountain ranges to expansive plains, from fertile valleys to arid deserts, the country’s geographical tapestry reveals a captivating story of geological processes and ecological adaptation. Understanding the landforms of the United States provides insight into its history, its resources, and its unique challenges.
Mountain Ranges: The Backbone of the Nation
The United States is home to several prominent mountain ranges, each with its own distinct characteristics. The Rocky Mountains, stretching from Canada to New Mexico, form the western backbone of the country. These young, rugged peaks, sculpted by tectonic forces, are renowned for their towering heights, deep canyons, and abundant natural resources.
Further east, the Appalachian Mountains, older and more eroded than the Rockies, extend from Alabama to Maine. Their rounded peaks and gentle slopes are a testament to their long history of weathering. The Appalachians are a significant source of coal and timber, and their forests harbor a diverse array of plant and animal life.
Plains and Plateaus: Expansive Horizons
The vast expanse of the Great Plains, stretching from the Rocky Mountains to the Mississippi River, is characterized by its flat, rolling terrain and fertile soils. This region, once dominated by grasslands, is now largely dedicated to agriculture, supporting a significant portion of the nation’s food production.
The Colorado Plateau, located in the southwestern United States, features a unique landscape of mesas, canyons, and buttes. The iconic Grand Canyon, carved by the Colorado River over millions of years, is a testament to the region’s geological history.
Coastal Plains and Coastal Features: Where Land Meets Water
The Atlantic Coastal Plain, stretching from Maine to Florida, is a low-lying region characterized by sandy beaches, barrier islands, and coastal marshes. Its fertile soils support a variety of agriculture, while its coastal ecosystems provide important habitat for marine life.
The Gulf Coastal Plain, bordering the Gulf of Mexico, shares similar characteristics with the Atlantic Coastal Plain, but features a more tropical climate and abundant wetlands. The Mississippi River Delta, a vast network of waterways and islands, is a vital ecosystem for migratory birds and other wildlife.
Deserts and Basins: Arid Landscapes
The Mojave Desert, located in the southwestern United States, is one of the hottest and driest deserts in North America. Its unique flora and fauna have adapted to survive in extreme conditions.
The Great Basin, located in the western United States, is a vast, arid region characterized by its numerous mountain ranges and valleys. The region’s unique geology and climate support a variety of ecosystems, including sagebrush steppe and alpine meadows.
Volcanic Landscapes: Evidence of Earth’s Power
The United States is home to several active and extinct volcanoes, remnants of past volcanic activity. The Cascade Range, extending from northern California to British Columbia, is known for its majestic volcanic peaks, including Mount Rainier and Mount Shasta.
The Hawaiian Islands, formed by volcanic eruptions over millions of years, offer a unique glimpse into the power of volcanic processes. Their fertile volcanic soils support a diverse range of plant and animal life, including endemic species found nowhere else on Earth.
River Systems: Veins of the Nation
The United States boasts a network of major river systems that have shaped its landscape and its history. The Mississippi River, the longest river in North America, flows through the heartland of the country, connecting the Great Lakes to the Gulf of Mexico.
The Colorado River, carving through the Colorado Plateau, is renowned for its scenic beauty and its role in providing water to millions of people. Other major river systems, such as the Missouri River, the Ohio River, and the Rio Grande, play vital roles in transportation, agriculture, and recreation.
Glacial Landscapes: Remnants of an Ice Age
The United States bears the mark of past glaciation, with numerous glacial features shaping its landscape. The Great Lakes, formed by the melting of massive ice sheets, are a testament to the power of glacial erosion.
Glacial valleys, carved by glaciers, are common throughout the northern United States, while moraines, piles of debris left behind by glaciers, create distinctive landforms.
The Importance of Understanding Landforms
The landforms of the United States are not merely geographical features; they are the foundation upon which the nation’s history, economy, and culture have been built.
- Resource Management: Understanding landforms is crucial for managing natural resources, including water, minerals, and timber.
- Environmental Protection: Landforms play a vital role in shaping ecosystems and supporting biodiversity. Understanding their vulnerabilities is essential for protecting the environment.
- Infrastructure Development: Landforms influence the design and construction of roads, bridges, and other infrastructure projects.
- Recreation and Tourism: The diverse landscapes of the United States attract millions of visitors each year, contributing to the economy and providing opportunities for recreation.
FAQs: Exploring the Landforms of the United States
Q: What are the major landforms of the United States?
A: The major landforms of the United States include mountain ranges, plains, plateaus, coastal plains, deserts, basins, volcanic landscapes, river systems, and glacial landscapes.
Q: How did the landforms of the United States form?
A: The landforms of the United States are a result of a complex interplay of geological processes, including tectonic activity, erosion, deposition, and glaciation.
Q: What are some of the benefits of understanding the landforms of the United States?
A: Understanding landforms helps us manage natural resources, protect the environment, develop infrastructure, and promote recreation and tourism.
Q: What are some of the challenges associated with the landforms of the United States?
A: The landforms of the United States present challenges such as natural disasters, resource scarcity, and environmental degradation.
Q: How do landforms influence the climate of the United States?
A: Landforms play a significant role in shaping the climate of the United States. Mountain ranges can create rain shadows, while coastal plains experience milder climates.
Tips for Exploring Landforms of the United States
- Visit national parks and monuments: These protected areas offer opportunities to experience the diversity of landforms firsthand.
- Explore maps and atlases: These resources provide detailed information about the landforms of the United States.
- Read books and articles: There are numerous resources available that delve into the history, formation, and significance of landforms.
- Engage with local communities: Learn from those who live and work in areas with distinct landforms.
Conclusion: A Legacy of Landforms
The landforms of the United States are a testament to the dynamic forces that have shaped the Earth over millions of years. They are not merely geographical features, but rather a vital part of the nation’s identity, its natural resources, and its cultural heritage. Understanding and appreciating these landforms is essential for ensuring their continued preservation and for fostering a deeper connection to the natural world.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Tapestry of Terrain: Exploring the Landforms of the United States. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!