A Journey Through the Majestic Backbone of North America: Understanding the Mountain Ranges
Related Articles: A Journey Through the Majestic Backbone of North America: Understanding the Mountain Ranges
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Journey Through the Majestic Backbone of North America: Understanding the Mountain Ranges. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Journey Through the Majestic Backbone of North America: Understanding the Mountain Ranges
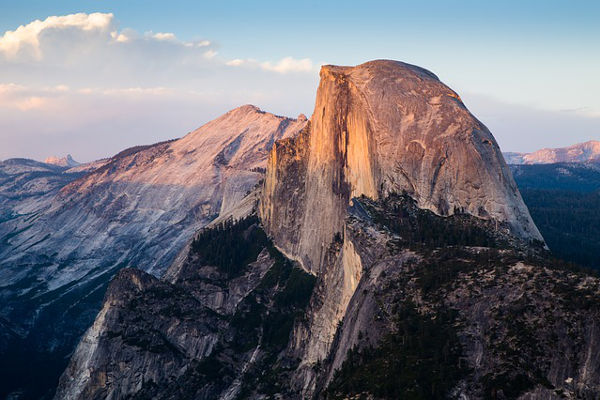

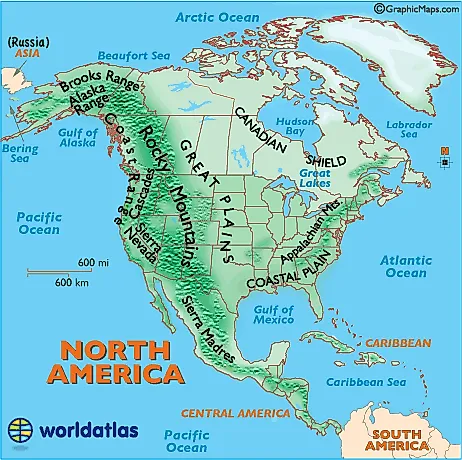
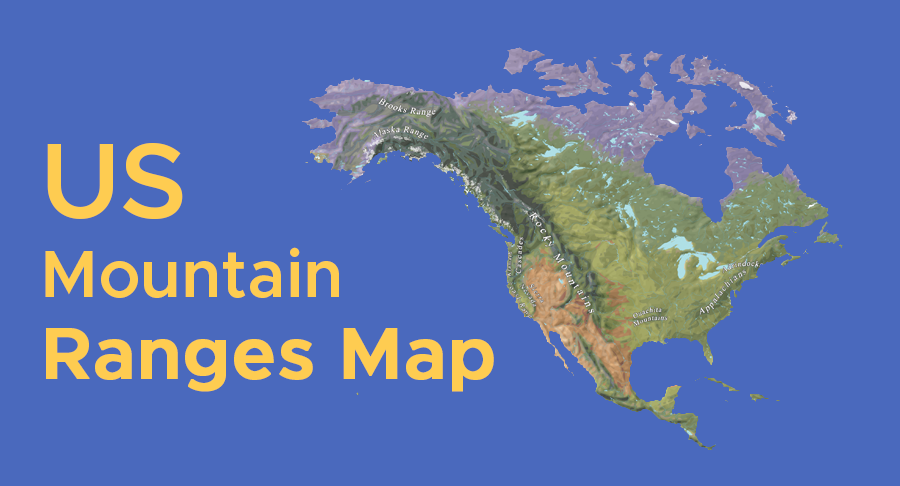
North America, a continent of vast landscapes and diverse ecosystems, is characterized by its majestic mountain ranges that stretch from the Arctic Circle to the southern tip of Mexico. These mountain chains, formed over millions of years through tectonic plate collisions and volcanic activity, are not mere geographical features; they are integral to the continent’s climate, biodiversity, and human history.
Understanding the North American mountain ranges is akin to deciphering the continent’s very essence. A map of these ranges serves as a visual guide, revealing the intricate interplay of geology, climate, and life that shapes the landscape. This article aims to explore the major mountain ranges of North America, highlighting their unique characteristics, geological origins, and ecological significance.
The Rocky Mountains: A Spine of Rugged Beauty
Stretching over 3,000 miles from northern Canada to New Mexico, the Rocky Mountains are the dominant mountain range in North America. They are a product of the Laramide Orogeny, a period of intense mountain building that began around 70 million years ago. This process involved the westward movement of the North American Plate over the Pacific Plate, resulting in the uplift of the Rocky Mountains and the formation of the Great Plains to their east.
The Rocky Mountains are characterized by their rugged peaks, deep canyons, and expansive forests. They are home to diverse wildlife, including grizzly bears, elk, mountain goats, and bighorn sheep. The range’s high altitude creates distinct microclimates, supporting a variety of plant life, from alpine meadows to dense coniferous forests.
The Appalachian Mountains: A Legacy of Ancient Times
The Appalachian Mountains, a much older range than the Rockies, stretch for over 1,500 miles from Newfoundland in Canada to Alabama in the United States. They are remnants of the ancient supercontinent Pangea, formed during the Paleozoic Era. The Appalachians have experienced erosion and weathering over millions of years, resulting in rounded peaks and gentle slopes, contrasting with the sharp peaks of the Rockies.
The Appalachian Mountains are known for their rich history and cultural heritage. They were home to indigenous cultures for centuries before European colonization, and their forests provided vital resources for early settlers. The range is also a significant source of coal, contributing to the industrial development of the eastern United States.
The Sierra Nevada: A Land of Giants
The Sierra Nevada, a mountain range in California, is renowned for its towering granite peaks, including Mount Whitney, the highest point in the contiguous United States. The range was formed by the uplift of the North American Plate over the Pacific Plate, similar to the Rocky Mountains, but with a distinct geological history.
The Sierra Nevada is a vital source of water for California, with its snowpack providing a significant portion of the state’s water supply. The range is also home to a diverse array of plant and animal life, including giant sequoia trees, the largest living organisms on Earth.
The Coast Mountains: A Rugged Coastal Frontier
The Coast Mountains, located in western Canada, run parallel to the Pacific Coast. They are part of the Pacific Cordillera, a vast mountain system that stretches along the western edge of North America. The Coast Mountains are known for their rugged peaks, steep slopes, and deep fjords carved by glaciers.
The Coast Mountains are a haven for outdoor enthusiasts, offering opportunities for hiking, skiing, and kayaking. The range is also home to a variety of wildlife, including black bears, mountain lions, and gray wolves.
The Cascade Range: A Chain of Volcanoes
The Cascade Range, extending from southern British Columbia to northern California, is a volcanic mountain range known for its active volcanoes, including Mount Rainier, Mount Shasta, and Mount Hood. The range was formed by the subduction of the Juan de Fuca Plate beneath the North American Plate.
The Cascade Range is a breathtaking landscape, characterized by volcanic peaks, deep valleys, and lush forests. The range is also a vital source of water for the Pacific Northwest, with its snowpack providing a significant portion of the region’s water supply.
The Importance of North American Mountain Ranges
The mountain ranges of North America play a critical role in shaping the continent’s environment and human history. They influence climate patterns, create diverse ecosystems, and provide valuable resources for human societies.
-
Climate Regulation: Mountains act as barriers to air masses, influencing precipitation patterns and creating distinct microclimates. The Rocky Mountains, for example, create a rain shadow effect, resulting in drier conditions to their east.
-
Biodiversity Hotspots: Mountain ranges provide a refuge for a wide variety of plant and animal life, creating unique ecosystems that support a diverse range of species. The Appalachian Mountains, for instance, are home to a significant number of endemic species found nowhere else on Earth.
-
Water Resources: Mountains are vital sources of water for surrounding regions, with snowpack providing a significant portion of the water supply for many communities. The Sierra Nevada, for example, provides water for millions of people in California.
-
Natural Resources: Mountains are rich in natural resources, including timber, minerals, and energy sources. The Appalachian Mountains, for example, have been a major source of coal for centuries.
-
Cultural Heritage: Mountain ranges have played a significant role in the cultural development of North America. Indigenous cultures have lived in these regions for millennia, developing unique traditions and ways of life. The Rocky Mountains, for example, hold cultural significance for many First Nations peoples.
FAQs about North American Mountain Ranges
Q: What is the tallest mountain in North America?
A: The tallest mountain in North America is Denali (formerly Mount McKinley), located in the Alaska Range, with a summit elevation of 20,310 feet (6,190 meters).
Q: Which mountain range is the oldest in North America?
A: The Appalachian Mountains are the oldest mountain range in North America, formed during the Paleozoic Era over 480 million years ago.
Q: What is the difference between the Rocky Mountains and the Appalachian Mountains?
A: The Rocky Mountains are much younger than the Appalachians and are characterized by their sharp peaks and rugged terrain. The Appalachians, on the other hand, are older and have experienced significant erosion, resulting in rounded peaks and gentle slopes.
Q: What is the significance of the Sierra Nevada?
A: The Sierra Nevada is a vital source of water for California, with its snowpack providing a significant portion of the state’s water supply. The range is also home to giant sequoia trees, the largest living organisms on Earth.
Q: How do mountains influence climate patterns?
A: Mountains act as barriers to air masses, influencing precipitation patterns and creating distinct microclimates. The Rocky Mountains, for example, create a rain shadow effect, resulting in drier conditions to their east.
Tips for Exploring North American Mountain Ranges
-
Plan your trip carefully: Research the specific range you are interested in, consider the best time of year to visit, and obtain necessary permits or reservations.
-
Pack appropriately: Dress in layers, bring appropriate footwear, and pack enough food and water for your trip.
-
Be aware of weather conditions: Mountain weather can change rapidly, so be prepared for all conditions.
-
Stay on marked trails: Stick to designated trails to avoid getting lost and minimize your impact on the environment.
-
Leave no trace: Pack out all trash and dispose of it properly.
-
Respect wildlife: Keep a safe distance from animals and avoid disturbing their habitat.
Conclusion
The mountain ranges of North America are a testament to the power of geological processes and the resilience of life. These majestic landscapes offer a glimpse into the continent’s history, its diverse ecosystems, and its enduring beauty. Whether you are an avid hiker, a nature enthusiast, or simply someone who appreciates the wonders of the natural world, exploring the North American mountain ranges is an experience that will leave a lasting impression.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Journey Through the Majestic Backbone of North America: Understanding the Mountain Ranges. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!