A Guide to New York’s Majestic Mountains: Exploring the State’s Diverse Topography
Related Articles: A Guide to New York’s Majestic Mountains: Exploring the State’s Diverse Topography
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Guide to New York’s Majestic Mountains: Exploring the State’s Diverse Topography. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Guide to New York’s Majestic Mountains: Exploring the State’s Diverse Topography
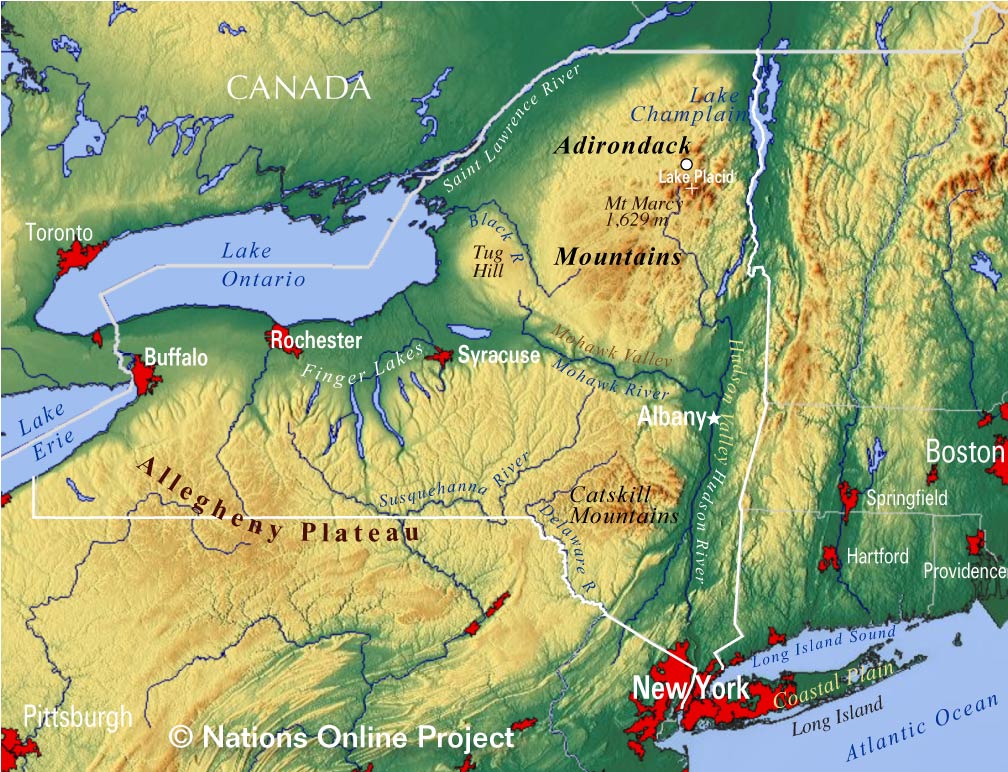
New York State, often associated with its bustling metropolis, harbors a remarkable landscape of mountains, offering a stark contrast to the urban sprawl. From the towering peaks of the Adirondacks to the rolling hills of the Catskills, the state’s mountainous terrain presents a diverse and captivating tapestry for exploration and appreciation.
Understanding New York’s Mountain Ranges
New York is home to two prominent mountain ranges: the Adirondacks and the Catskills, each with unique characteristics and geological histories.
The Adirondack Mountains:
- Location: Located in the northeastern part of the state, the Adirondacks cover a vast area of over 6 million acres.
- Formation: These mountains were formed over millions of years through the uplift and erosion of ancient bedrock.
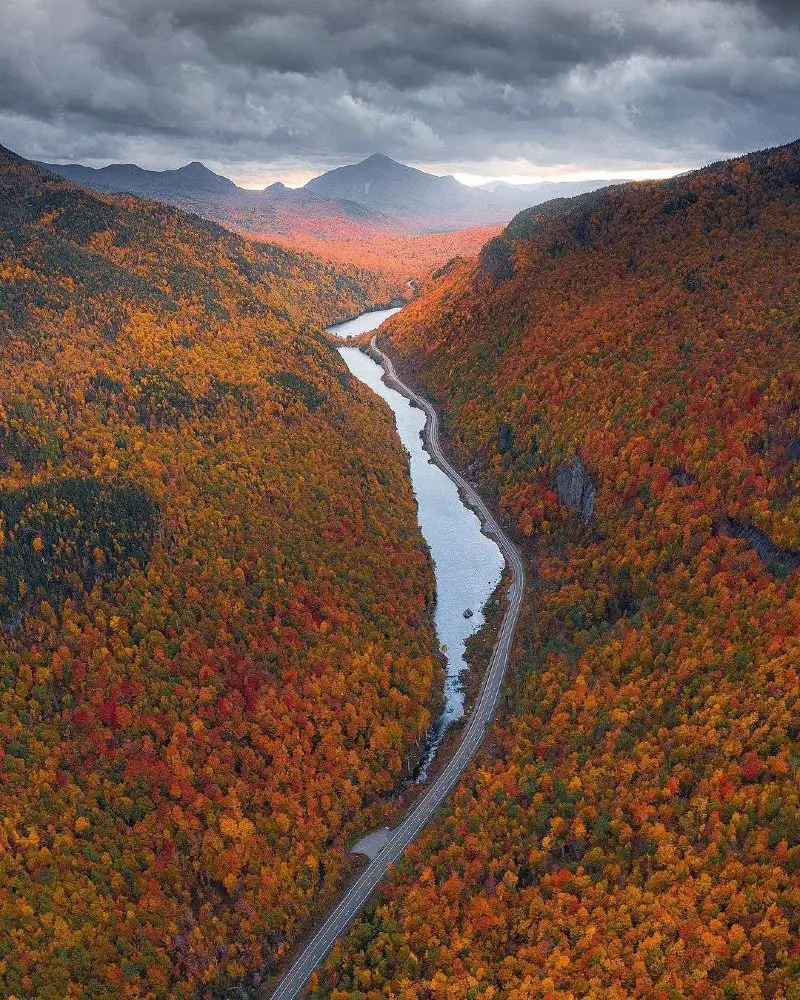
- Characteristics: The Adirondacks are known for their rugged peaks, deep forests, and numerous lakes and rivers. The region’s highest peak, Mount Marcy, reaches an elevation of 5,344 feet.
- Activities: The Adirondacks are a popular destination for outdoor recreation, including hiking, camping, fishing, skiing, and snowshoeing.
The Catskill Mountains:
- Location: Located south of the Adirondacks, the Catskills are situated in the southeastern part of the state.
- Formation: The Catskills were formed by the erosion of ancient plateau, resulting in a landscape of rounded peaks and valleys.
- Characteristics: The Catskills are known for their rolling hills, lush forests, and scenic waterfalls. The region’s highest peak, Slide Mountain, reaches an elevation of 4,204 feet.
- Activities: The Catskills are a popular destination for hiking, camping, fishing, and enjoying scenic views.
Beyond the Adirondacks and Catskills:
While the Adirondacks and Catskills dominate New York’s mountain landscape, other smaller mountain ranges and hills contribute to the state’s diverse topography. These include:
- The Shawangunk Mountains: Located in the southeastern part of the state, the Shawangunks are known for their steep cliffs and rock formations, making them a popular destination for rock climbing.
- The Taconic Mountains: Located along the eastern border of the state, the Taconic Mountains are known for their rolling hills and scenic views.
- The Allegheny Plateau: Located in the southwestern part of the state, the Allegheny Plateau is characterized by its rolling hills and deep valleys.
Navigating the Map of New York’s Mountains
Understanding the geography of New York’s mountains requires a comprehensive map that highlights the key features and locations. A detailed map should include:
- Elevation: This information allows for understanding the height of each mountain peak and range.
- Trails: Hiking trails, both established and less-traveled, are crucial for planning outdoor adventures.
- Roads: The map should indicate major roads and access points to different areas within the mountains.
- Water Features: Lakes, rivers, and streams are integral to the landscape and offer opportunities for water-based activities.
- Towns and Cities: Identifying nearby towns and cities provides context for planning accommodation and supplies.
The Significance of New York’s Mountains
Beyond their aesthetic beauty, New York’s mountains play a crucial role in the state’s ecology, economy, and culture.
- Ecological Importance: The mountains act as natural reservoirs, regulating water flow and providing habitat for diverse flora and fauna.
- Economic Impact: The mountains attract tourists, contributing significantly to the state’s economy through tourism and outdoor recreation industries.
- Cultural Significance: The mountains have inspired artists, writers, and musicians, contributing to the state’s cultural heritage.
FAQs about New York’s Mountains
-
Q: What is the highest mountain in New York State?
- A: Mount Marcy, located in the Adirondack Mountains, is the highest peak in New York State, reaching an elevation of 5,344 feet.
-
Q: What are the best times to visit New York’s mountains?
- A: The best time to visit depends on your interests. Summer offers hiking, camping, and water activities, while fall showcases vibrant foliage. Winter brings skiing, snowshoeing, and scenic winter landscapes.
-
Q: What are the best places to go hiking in New York’s mountains?
- A: The Adirondacks and Catskills offer a vast array of hiking trails, ranging from easy to challenging. Popular options include the High Peaks region in the Adirondacks, the Catskill Escarpment Trail, and the Shawangunk Ridge Trail.
-
Q: What are some tips for planning a trip to New York’s mountains?
- A: Research your destination, check weather conditions, pack appropriate clothing and gear, be aware of potential hazards, and follow Leave No Trace principles.
Conclusion
New York’s mountains offer a unique and captivating landscape, providing opportunities for outdoor recreation, cultural exploration, and appreciating the state’s natural beauty. Whether you’re an avid hiker, a casual nature enthusiast, or simply seeking a change of scenery, the mountains of New York State provide a rewarding and memorable experience.
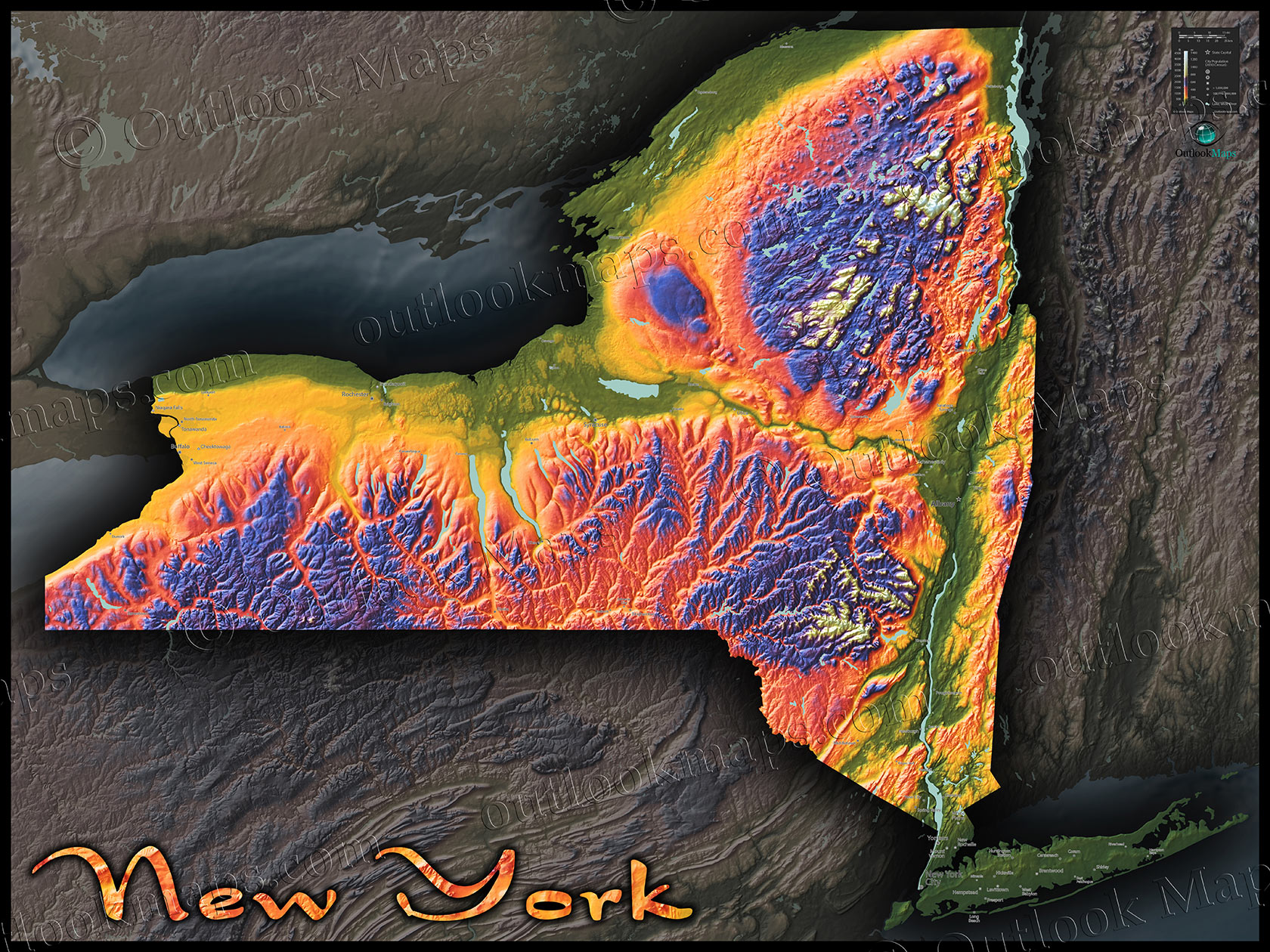







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Guide to New York’s Majestic Mountains: Exploring the State’s Diverse Topography. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!